Abstract
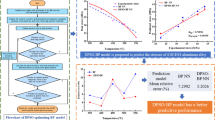
The mechanical properties of titanium alloy castings are very important for their wide applications in high-end equipment and engineering; however, testing and characterization of the mechanical parameters of titanium alloy castings are complicated and costly. Therefore, the present work proposed a novel method based on a back-propagation (BP) neural network to predict the mechanical properties of a TC4 titanium alloy casting, specifically, the presence of shrinkage cavities at a given location. It was found that the statistical error between predicted values of the BP neural network and experimental results was less than 10%, indicating that the proposed model is suitable for predicting the presence of shrinkage cavities in TC4 titanium alloy castings. Moreover, the BP neural network model was also used to predict the grain size and hardness of the titanium alloy casting. The correlation between predicted and experimental results was r = 0.99485, thus indicating that the proposed model could effectively predict the grain size and hardness of TC4 titanium alloy castings.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Pan, S.Y. Liang, H. Garmestani and D.S. Shih, Prediction of Machining-Induced Phase Transformation and Grain Growth of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech., 2016, 87, p 859.
A. Palmquist, F. Lindberg, L. Emanuelsson, R. Brånemark, H. Engqvist and P. Thomsen, Morphological Studies on Machined Implants of Commercially Pure Titanium and Titanium Alloy (Ti6Al4V) in The Rabbit, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater., 2010, 91B, p 309.
Y. Niu, H. Hou, M. Li and Z. Li, High Temperature Deformation Behavior of a Near Alpha Ti600 Titanium Alloy, Mat. Sci. Eng. R, 2018, 492, p 24.
M. Calamaz, D. Coupard and F. Girot, A New Material Model for 2D Numerical Simulation of Serrated Chip Formation when Machining Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V, Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf., 2008, 48, p 275.
R. Ghosh, H.K. Thota and R.U. Rani, Silicate Spray-Coated Nickel-Plated Titanium Alloy for Space Applications: Corrosion Resistance and Thermo-Optical Properties, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 1378.
M. Hassaan, M. Junaid, T. Shahbaz, M. Ilyas and J. Haider, Nanomechanical Response of Pulsed Tungsten Inert Gas Welded Titanium Alloy by Nanoindentation and Atomic Force Microscopy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 1490.
M. Paghandeh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H.R. Abedi, Y. Vahidshad and T. Lampke, Compressive/Tensile Deformation Behavior and the Correlated Microstructure Evolution of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy at Warm Temperatures, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 10, p 1291.
R. Sun, S. Keller, Y. Zhu, W. Guo and B. Klusemann, Experimental-Numerical Study of Laser-Shock-Peening-Induced Retardation of Fatigue Crack Propagation in Ti-17 Titanium Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2020, 145, p 106081.
J.S. Jesus, L.P. Borrego, J.A.M. Ferreira, J.D. Costa and C. Capela, Fatigue Crack Growth Behaviour in Ti6Al4V Alloy Specimens Produced by Selective Laser Melting, Int. J. Fract., 2020, 223, p 123.
N. Hrabe, T. Gnaeupel-Herold and T. Quinn, Fatigue Properties of a Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) Fabricated via Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Effectsof Internal Defects and Residual Stress, Int. J. Fatigue, 2017, 94, p 202.
T. Furuhara, Role of Defects on Microstructure Development of Beta Titanium Alloys, Met. Mater. Int., 2000, 6, p 221.
B. Hu, Y. Liu and R. Yu, Magnetic Anomaly Characteristics of Surface Crack Defects in a Titanium Alloy Plate, Nondestruct. Test. Eva., 2021, 36, p 209.
D.L. Sun, S.B. Kang and H.S. Koo, Characteristics of Morphology and Crystal Structure of α-Phase in Two Al-Mn-Mg Alloys, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2000, 63, p 37.
K. Mroczka, Characteristics of Alsi9mg/2017A Aluminum Alloys Friction Stir Welded with Offset Welding Line and Root-Side Heating, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2014, 59, p 1293.
L. Liu, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty and S. Valtierra, Characteristics of α-Dendritic and Eutectic Structures in Sr-Treated Al-Si Casting Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, 39, p 215.
Y. Ling, J. Zhou, H. Nan, L. Zhu and Y. Yin, A Shrinkage Cavity Model Based on Pressure Distribution for Ti-6Al-4V Vertical Centrifugal Castings, J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2018, 251, p 295.
L. Jia, D. Xu, M. Li, J. Guo and H. Fu, Casting Defects of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy in Vertical Centrifugal Casting Processes with Graphite Molds, Met. Mater. Int., 2012, 18, p 55.
S.P. Wu, D.R. Liu, J.J. Guo, Y.Q. Su and H.Z. Fu, Influence of Process Parameters on Cet in Ti-Al Alloy Ingot with Consideration of Shrinkage Cavity Formation: A Computer Simulation, J. Alloy Compd., 2007, 441, p 267.
M. Wu, J. Schädlich-Stubenrauch, M. Augthun, P.R. Sahm and H. Spiekermann, Computer Aided Prediction and Control of Shrinkage Porosity in Titanium Dental Castings, Dent. Mater., 1998, 14, p 321.
R. Hwang, Y. Chen and H. Huang, Artificial Intelligent Analyzer for Mechanical Properties of Rolled Steel Bar by Using Neural Networks, Expert. Syst. Appl., 2010, 37, p 3136.
S.K. Singh, K. Mahesh and A.K. Gupta, Prediction of Mechanical Properties of Extra Deep Drawn Steel in Blue Brittle Region Using Artificial Neural Network, Mater. Design, 2010, 31, p 2288.
G. Dini, A. Najafizadeh, S.M. Monir-Vaghefi and A. Ebnonnasir, Predicting of Mechanical Properties of Fe-Mn-(Al, Si) TRIP/TWIP Steels Using Neural Network Modeling, Comp. Mater. Sci., 2009, 45, p 959.
A. Bahrami, S.H. Mousavi Anijdan and A. Ekrami, Prediction of Mechanical Properties of DP Steels Using Neural Network Model, J. Alloy Compd., 2005, 392, p 177.
Y. Zhang, Z. Wen, H. Pei, J. Wang, Z. Li and Z. Yue, Equivalent Method of Evaluating Mechanical Properties of Perforated Ni-Based Single Crystal Plates Using Artificial Neural Networks, Comput. Method Appl. M., 2020, 360, p 112725.
X. Yang, J. Zhu, Z. Nong, D. He, Z. Lai, Y. Liu and F. Liu, Prediction of Mechanical Properties of A357 Alloy Using Artificial Neural Network, Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2013, 23, p 788.
H. Fazilat, M. Ghatarband, S. Mazinani, Z.A. Asadi, M.E. Shiri and M.R. Kalaee, Predicting the Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers via Artificial Neural Network and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, 58, p 31.
Z. Jiang, L. Gyurova, Z. Zhang, K. Friedrich and A.K. Schlarb, Neural Network based Prediction on Mechanical and Wear Properties of Short Fibers Reinforced Polyamide Composites, Mater. Des., 2008, 29, p 628.
Y. Sun, W. Zeng, Y. Han, X. Ma, Y. Zhao, P. Guo, G. Wang and M.S. Dargusch, Determination of the Influence of Processing Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Using an Artificial Neural Network, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, 60, p 239.
Z. Guo, S. Malinov and W. Sha, Modelling Beta Transus Temperature of Titanium Alloys Using Artificial Neural Network, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2005, 32, p 1.
N.S. Reddy, H.J. Choi and H.B. Young, Practical Model for Predicting Beta Transus Temperature of Titanium Alloys, Korean J. Mater. Res., 2014, 24, p 381.
S.A. Niknam, R. Khettabi and V. Songmene, Machinability and Machining of Titanium Alloys: A Review, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2014.
R. Hecht-Nielsen, Counterpropagation Networks, Appl. Opt., 1987, 26, p 4979.
A. Zell, T. Korb, T. Sommer, R. Bayer, Neural Network Simulation Environment, Appl. Artif. Neural Netw., 1990.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2015-188-48-2). We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest during the preparation of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Sha, A., Li, X. et al. Prediction of the Mechanical Properties of Titanium Alloy Castings Based on a Back-Propagation Neural Network. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 8040–8047 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06035-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06035-1