Abstract
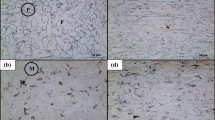
Different layers of a low-carbon Fe-Cr-C-Mo-Mn electrode were deposited on a plain low-carbon steel using shielded metal arc welding (SMAW). The microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of the clads were investigated by optical microscope, scanning electron microscope (SEM), hardness test, and sand-rubber wheel wear test. Microstructure of the single-layered clad consisted of lath martensite and a small amount of retained austenite. Three different microstructural regions including plate martensite surrounded by delta ferrite, tempered martensite surrounded by delta ferrite, and tempered martensite were observed at the top, middle and bottom regions of the multilayered clads, respectively. The hardness of single-, double- and triple-layered clads was, respectively, 3.2, 4.1 and 4.3 times more than that of the substrate. The hardness of multilayered clads increased gradually from bottom to the top of the clads. A direct relation was observed between wear resistance and hardness of the clads. In comparison with the single-layered clad, the wear rates of the double- and triple-layered clads were reduced by 33 and 67%, respectively. Wear mechanism changed from severe delamination and abrasion to insignificant abrasion by increasing the number of layers.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Kumar, P. Kumari and K.L.A. Khan, A Review Paper on Research Work Done in Hardfacing, Int. J. Appl. Innov. Eng. Manag., 2016, 5(9), p 129–134.
X.H. Wang, F. Han, X.M. Liu, S.Y. Qu and Z.D. Zou, Effect of Molybdenum on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Fe-Based Hardfacing Coatings, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 489(1–2), p 193–200.
V.E. Buchanan, Solidification and Microstructural Characterisation of Iron-Chromium Based Hardfaced Coatings Deposited by SMAW and Electric Arc Spraying, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2009, 203(23), p 3638–3646.
V.E. Buchanan, P.H. Shipway and D.G. McCartney, Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Behaviour of Shielded Metal Arc Welding Hardfacings Used in the Sugarcane Industry, Wear, 2007, 263(1–6), p 99–110.
J. Hornung, A. Zikin, K. Pichelbauer, M. Kalin and M. Kirchgaßner, Influence of Cooling Speed on the Microstructure and Wear Behaviour of Hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C Hardfacings, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 576, p 243–251.
Y.K. Singla, R. Chhibber, N. Arora, K. Singh and K. Khanna, On the Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Fe–xCr–4Mn–3C Hardfacing Alloys, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2017, 70, p 1555–1561.
M. Eroglu, Boride Coatings on Steel Using Shielded Metal Arc Welding Electrode: Microstructure and Hardness, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2009, 203, p 2229–2235.
C.M. Lin, C.M. Chang, J.H. Chen, C.C. Hsieh and W. Wu, Microstructure and Wear Characteristics of High-Carbon Cr-Based Alloy Claddings Formed by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Surf. Coatings Technol., 2010, 205(7), p 2590–2596.
M. Kirchgaßner, E. Badisch and F. Franek, Behaviour of Iron-Based Hardfacing Alloys under Abrasion and Impact, Wear, 2008, 265(5–6), p 772–779.
D. Liu, R. Liu, Y. Wei, Y. Ma and K. Zhu, Microstructure and Wear Properties of Fe-15Cr-2.5Ti-2C-xB wt% Hardfacing Alloys, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 271, p 253–259.
C.M. Chang, Y.C. Chen and W. Wu, Microstructural and Abrasive Characteristics of High Carbon Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Alloy, Tribol. Int., 2010, 43(5–6), p 929–934.
J.J. Coronado, H.F. Caicedo and A.L. Gómez, The Effects of Welding Processes on Abrasive Wear Resistance for Hardfacing Deposits, Tribol., 2009, 42(5), p 745–749.
N.U. Rahman, L. Capuano, A. Van der Meer, M.B. De Rooij, D.T.A. Matthews, G. Walmag, M. Sinnaeve, A. Garcia-Junceda, M. Castillo and G.R.B.E. Römer, Development and Characterization of Multilayer Laser Cladded High Speed Steels, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 24, p 76–85.
M. Shamanian, S.M.R.M. Abarghouie and S.R.M. Pour, Effects of Surface Alloying on Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Ductile Iron, Mater. Des., 2010, 31(6), p 2760–2766.
N.G. Chaidemenopoulos, P.P. Psyllaki, E. Pavlidou and G. Vourlias, Aspects on Carbides Transformations of Fe-Based Hardfacing Deposits, Surf. CoatingsTechnol, 2018, 2019(57), p 651–661.
F. Sadeghi, H. Najafi and A. Abbasi, The Effect of Ta Substitution for Nb on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance of an Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Alloy, Surf Coatings Technol., 2017, 324, p 85–91.
J. Wang, T. Liu, Y. Zho, Y. Xing, X. Liu et al., Effect of Nitrogen Alloying on the Microstructure and Abrasive Impact Wear Resistance of Fe-Cr-C-Ti-Nb Hardfacing Alloy, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2017, 309, p 1072–1080.
S.D. Sun, D. Fabijanic, M. Annasamy et al., Microstructure, Abrasive Wear and Corrosion Characterization of Laser Metal Deposited Fe-30Cr-6Mo-10Ni-2.2C Alloy, Wear, 2019, 438–439(May), p 203070.
E.O. Correa, N.G. Alcântara, L.C. Valeriano, N.D. Barbedo and R.R. Chaves, The Effect of Microstructure on Abrasive Wear of a Fe-Cr-C-Nb Hardfacing Alloy Deposited by the Open Arc Welding Process, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2015, 276, p 479–484.
J.H. Bulloch, Alloy Classification of Hardfacing Materials, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Piping, 1991, 47, p 127–158.
M. Hajihashemi, M. Shamanian and G. Azimi, Physical, Mechanical, and Dry Sliding Wear Properties of Fe-Cr-WC Hardfacing Alloys under Different Tungsten Addition, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, 46(2), p 919–927.
G. Azimi and M. Shamanian, Effect of Silicon Content on the Microstructure and Properties of Fe–Cr–C Hardfacing Alloys, J. Mater. Sci, 2010, 45(3), p 842–849.
G. Azimi and M. Shamanian, Effects of Silicon Content on the Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Fe–Cr–C Hardfacing Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 505(2), p 598–603.
B. Srikarun, H.Z. Oo, S. Petchsang and P. Muangjunburee, The Effects of Dilution and Choice of Added Powder on Hardfacing Deposited by Submerged Arc Welding, Wear, 2019, 424–425(February), p 246–254.
M. Morsy and E. El-Kashif, The Effect of Microstructure on High-stress Abrasion Resistance of Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Deposits, Weld Word, 2014, 58, p 491–497.
B. Gülenç and N. Kahraman, Wear Behaviour of Bulldozer Rollers Welded using a Submerged Arc Welding Process, Mater. Des., 2003, 24(7), p 537–542.
P.F. Mendez, N. Barnes, K. Bell et al., Welding Processes for Wear Resistant Overlays, J. Manuf. Process., 2014, 16(1), p 4–25.
N. Ur Rahman, M.B. de Rooij, D.T.A. Matthews, G. Walmag, M. Sinnaeve and G.R.B.E. Römer, Wear Characterization of Multilayer Laser Cladded High Speed Steels, Tribol. Int., 2019, 130, p 52–62.
K.Y. Luo, X. Xu, Z. Zhao, S.S. Zhao, Z.G. Cheng and J.Z. Lu, Microstructural Evolution and Characteristics of Bonding Zone in Multilayer Laser Cladding of Fe-Based Coating, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, 2019(263), p 50–58.
S.S. Sandhu and A.S. Shahi, Metallurgical, Wear and Fatigue Performance of Inconel 625 Weld Claddings, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016, 233, p 1–8.
C.M. Chang, Y.C. Chen and W. Wu, Microstructural and Abrasive Characteristics of High Carbon Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Alloy, Tribol Int., 2010, 43(5–6), p 929–934.
L. Lu, H. Soda and A. McLean, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe_/Cr_/C Eutectic Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 347, p 214–222.
J.N. Lemke, L. Rovatti, M. Colombo and M. Vedani, Interrelation Between Macroscopic, Microscopic and Chemical Dilution in Hardfacing Alloys, Mater. Des., 2016, 91, p 368–377.
American Society of Metals, Volume 3, Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2004.
M. Atkins, Atlas of continious cooling transformation diagrams for engineering steels, ASM International, Metals Park, Ohio, 1980.
J. Trzaska, A. Jagiełło and L.A. Dobrzañski, The Calculation of CCT Diagrams for Engineering Steels, Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, 39(1), p 13–20.
P. Ma, Y. Wu, P. Zhang and J. Chen, Solidification Prediction of Laser Cladding 316L by the Finite Element Simulation, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 103(1–4), p 957–969.
V. Javaheri, A. Pohjonen, J.I. Asperheim, D. Ivanov and D. Porter, Physically Based Modeling, Characterization and Design of an Induction Hardening Process for a New Slurry Pipeline Steel, Mater. Des., 2019, 182, p 108047.
J. Trzaska, Calculation of the Steel Hardness after Continuous Cooling, Arch Mater Sci Eng., 2013, 61(2), p 87–92.
Q. Wu and M.A. Zikry, Microstructural Modeling of Crack Nucleation and Propagation in High Strength Martensitic Steels, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2014, 51(25–26), p 4345–4356.
S. Zidelmel, O. Allaoui, O. Laidi and A. Benchatti, Influence of the Heat Treatments on Martensite Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Behavior of X52 Dual-Phase Steel, Adv. Model. Anal. A., 2017, 86(3), p 582–592.
O.P. Modi, P. Pandit, D.P. Mondal, B.K. Prasad, A.H. Yegneswaran and A. Chrysanthou, High-Stress Abrasive Wear Response of 0.2% Carbon Dual Phase Steel: Effects of Microstructural Features and Experimental Conditions, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 458, p 303–311.
S. Bhowmick and B.K. Show, Effect of Prior Heat Treatment on Wear Behaviour of 0.23% Carbon Dual Phase Steel, Can. Metall. Q., 2014, 53(1), p 93–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pournajaf, E., Abbasi, A. & Najafi, H. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Single- and Multi-Layered Low-Carbon Fe-Cr-C-Mo-Mn Clads Deposited by Shielded Metal Arc Welding. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 7704–7715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05901-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05901-2