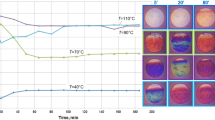
Abstract
Two different lubricants containing zinc dialkyldithiophosphate (ZDDP) additive were tested in a rolling–sliding contact test rig (micropitting rig) at different relative humidities. The effect of relative humidity on the bulk properties (e.g., viscosity, water concentration, water saturation level) of the lubricants and their tribological performance (e.g., friction, wear, micropitting level) as well as the related tribochemistry was extensively explored. Relative humidity had a limited effect on the viscosity of the tested lubricants. However, the friction and micropitting level decreased, while the wear increased at higher relative humidity. This increased wear was attributed to a thinner tribofilm and shorter chain length of the polyphosphates derived from the ZDDP additive. Hydrolysis of the ZDDP additive occurred, and the polar water molecules limited the access of the ZDDP additive to the substrate. The different polarities of the two base oils (Ester, polyalphaolefin) also led to different tribological and tribochemical performance.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.K. Lancaster, A Review of the Influence of Environmental Humidity and Water on Friction, Lubrication and Wear, Tribol. Int., 1990, 23(6), p 371–389.
W.M. Needelman, M.A. Barris and G.L. Lavallee, Contamination Control for Wind Turbine Gearboxes, Power Eng., 2009, 113(11), p 112–120.
A.C. Gonçalves and L.R. Padovese, “Vibration and Oil Analysis for Monitoring Problems Related to Water Contamination in Rolling,” Proceedings-International Brazilian Conference on Tribology, 2010, p 80–90.
E. Harika, J. Bouyer, M. Fillon and M. Hélène, Effects of Water Contamination of Lubricants on Hydrodynamic Lubrication: Rheological and Thermal Modeling, J. Tribol., 2013, 135(4), p 1–10.
E. Harika, J. Bouyer, M. Fillon and M. Hélène, Measurements of Lubrication Characteristics of a Tilting Pad Thrust Bearing Disturbed by a Water-Contaminated Lubricant, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Eng. Tribol., 2013, 227(1), p 16–25.
A. Ruellan, X. Kleber, F. Ville, J. Cavoret and B. Liatard, Understanding White Etching Cracks in Rolling Element Bearings: Formation Mechanisms and Influent Tribochemical Drivers, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. J. Eng. Tribol., 2015, 229(8), p 886–901.
H. Dhieb, J.G. Buijnsters, K. Elleuch and J.P. Celis, Effect of Relative Humidity and Full Immersion in Water on Friction, Wear and Debonding of Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy under Reciprocating Sliding, Compos. Part B Eng., 2016, 88, p 240–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.11.011
A. Oila and S.J. Bull, Assessment of the Factors Influencing Micropitting in Rolling/Sliding Contacts, Wear, 2005, 258(10), p 1510–1524.
A. V. Olver, D. Dini, E. Lainé, T.A. Beveridge, and D.Y. Hua, “Roughness and Lubricant Chemistry Effects in Micropitting,” American Gear Manufacturers Association - Fall Technical Meeting of the American Gear Manufacturers Association 2007, AGMA, 2007, p 151–160, http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-49549104854&partnerID=tZOtx3y1.
H.A. Spikes, A.V. Olver and P.B. Macpherson, Wear in Rolling Contacts, Wear, 1986, 112(2), p 121–144.
M. Meheux, C. Minfray, F. Ville, T. Le Mogne, A.A. Lubrecht, J.M. Martin and H.P. Lieurade, Influence of Slide-to-Roll Ratio on Tribofilm Generation, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. J. J. Eng. Tribol., 2008, 222(3), p 325–334.
H. Cen, A. Morina and A. Neville, Effect of Slide to Roll Ratio on the Micropitting Behaviour in Rolling-Sliding Contacts Lubricated with ZDDP-Containing Lubricants, Tribol. Int., 2018, 122, p 210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.02.038
P.H. Winter and D.P. Oster, Influence of Lubrication on Pitting and Micropitting Resistance of Gears, Gear Technol., 1990, 7(2), p 16–23.
M.N. Webster and C.J.J. Norbart, An Experimental Investigation of Micropitting Using a Roller Disk Machine, Tribol. Trans., 1995, 38(4), p 883–893. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402009508983485
E. Lainé, A.V. Olver and T.A. Beveridge, Effect of Lubricants on Micropitting and Wear, Tribol. Int., 2008, 41(11), p 1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.03.016
E. Lainé, A.V. Olver, M.F. Lekstrom, B.A. Shollock, T.A. Beveridge and D.Y. Hua, The Effect of a Friction Modifier Additive on Micropitting, Tribol. Trans., 2009, 52(4), p 526–533. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402000902745507
S. Soltanahmadi, A. Morina, M.C.P. van Eijk, I. Nedelcu and A. Neville, Investigation of the Effect of a Diamine-Based Friction Modifier on Micropitting and the Properties of Tribofilms in Rolling-Sliding Contacts, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys., 2016, 49(50), p 505302. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/50/505302
S. Soltanahmadi, A. Morina, M.C.P. van Eijk, I. Nedelcu and A. Neville, Experimental Observation of Zinc Dialkyl Dithiophosphate (ZDDP)-Induced Iron Sulphide Formation, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 414, p 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.023
S. Maya-Johnson, J. Felipe Santa and A. Toro, Dry and Lubricated Wear of Rail Steel under Rolling Contact Fatigue - Wear Mechanisms and Crack Growth, Wear, 2017, 380–381, p 240–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2017.03.025
G.E. Morales-Espejel, P. Rycerz and A. Kadiric, Prediction of Micropitting Damage in Gear Teeth Contacts Considering the Concurrent Effects of Surface Fatigue and Mild Wear, Wear, 2018, 398–399, p 99–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2017.11.016
V. Brizmer, H.R. Pasaribu and G.E. Morales-Espejel, Micropitting Performance of Oil Additives in Lubricated Rolling Contacts, Tribol. Trans., 2013, 56(5), p 739–748.
A. Naveira Suarez, M. Grahn, R. Pasaribu and R. Larsson, The Influence of Base Oil Polarity on the Tribological Performance of Zinc Dialkyl Dithiophospate Additives, Tribol. Int., 2010, 43(12), p 2268–2278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.07.016
A. Naveira Suarez, A. Tomala, M. Grahn, M. Zaccheddu, R. Pasaribu and R. Larsson, The Influence of Base Oil Polarity and Slide-Roll Ratio on Additive-Derived Reaction Layer Formation, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. J. J. Eng. Tribol., 2011, 225(7), p 565–576.
H. Cen, A. Morina and A. Neville, Effect of Base Oil Polarity on the Micropitting Behaviour in Rolling-sliding Contacts, Lubr. Sci., 2019 https://doi.org/10.1002/ls.1453
H. Cen, A. Morina, A. Neville, R. Pasaribu and I. Nedelcu, Effect of Water on ZDDP Anti-Wear Performance and Related Tribochemistry in Lubricated Steel/Steel Pure Sliding Contacts, Tribol. Int., 2012, 56, p 47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.06.011
H. Cen, A. Morina and A. Neville, Effect of Lubricant Ageing on Lubricant Physical and Chemical Properties and Tribological Performance. Part I: Effect of Lubricant Chemistry, Ind. Lubr. Tribol., 2018 https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-03-2017-0059
H. Cen, A. Morina and A. Neville, Effect of Ageing on Lubricants’ Physical and Chemical Properties and Tribological Performance: Part II: Effect of Water Contamination on Lubricant, Ind. Lubr. Tribol., 2019, 71(1), p 48–53.
I. Nedelcu, E. Piras, A. Rossi and H.R. Pasaribu, XPS Analysis on the Influence of Water on the Evolution of Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphate-Derived Reaction Layer in Lubricated Rolling Contacts, Surf. Interface Anal., 2012, 44(8), p 1219–1224. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.4853
P. Parsaeian, A. Ghanbarzadeh, M. Wilson, M.C.P. Van Eijk, I. Nedelcu, D. Dowson, A. Neville and A. Morina, An Experimental and Analytical Study of the Effect of Water and Its Tribochemistry on the Tribocorrosive Wear of Boundary Lubricated Systems with ZDDP-Containing Oil, Wear, 2016, 358–359, p 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.03.017
P. Parsaeian, A. Ghanbarzadeh, M.C.P. Van Eijk, I. Nedelcu, A. Morina and A. Neville, Study of the Interfacial Mechanism of ZDDP Tribofilm in Humid Environment and Its Effect on Tribochemical Wear; Part II: Numerical, Tribol. Int., 2017, 107, p 33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.11.015
S. Soltanahmadi, A. Morina, M.C.P. van Eijk, I. Nedelcu and A. Neville, Tribochemical Study of Micropitting in Tribocorrosive Lubricated Contacts: The Influence of Water and Relative Humidity, Tribol. Int., 2016, 2017(107), p 184–198.
ASTM, Standard D7042: Test Method for Dynamic Viscosity and Density of Liquids by Stabinger Viscometer (and the Calculation of Kinematic Viscosity), Am. Natl. Stand. Inst., 2013, 12a, p 1–11, https://doi.org/10.1520/D7042-12A.2.
H. Cen, D. Bai, Y. Chao and Y. Li, Effect of Relative Humidity on the Tribological Performance of Pure Sliding Contacts Lubricated with Phosphorus Additive Containing Lubricants, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(7), p 4786–4793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04977-6
Z. Pawlak and B.E. Klamecki, Hard-Core Reverse Micelles in Tribofilm Formation and Solubilization Processes in Engine Oil, XIX-th ARS Separatoria, 2004, p 128–133.
J. Fang, Y. Sun, Y. Xia and W. Liu, Base Medium Effect on the Tribological Behavior of Oil-Water Double Soluble Bismuth Dithiophosphate, Ind. Lubr. Tribol., 2010, 62(4), p 197–206.
L.J. Taylor and H.A. Spikes, Friction-Enhancing Properties of Zddp Antiwear Additive: Part I—Friction and Morphology of Zddp Reaction Films, Tribol. Trans., 2003, 46(3), p 303–309.
L.J. Taylor and H.A. Spikes, Friction-Enhancing Properties of ZDDP Antiwear Additive: Part II—Influence of ZDDP Reaction Films on EHD Lubrication, Tribol. Trans., 2003, 46(3), p 310–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402000308982631
N.L. Wolfe, Organophosphate and Organophosphorothionate Esters: Application of Linear Free Energy Relationships to Estimate Hydrolysis Rate Constants for Use in Environmental Fate Assessment, Chemosphere, 1980, 9(9), p 571–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(80)90075-2
Z. Chen, X. He, C. Xiao and S.H. Kim, Effect of Humidity on Friction and Wear—A Critical Review, Lubricants, 2018, 6(3), p 1–26.
H. Spikes, The History and Mechanisms of ZDDP, Tribol. Lett., 2004, 17(3), p 469–489. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRIL.0000044495.26882.b5
P. Parsaeian, M.C.P. Van Eijk, I. Nedelcu, A. Neville and A. Morina, Study of the Interfacial Mechanism of ZDDP Tribofilm in Humid Environment and Its Effect on Tribochemical Wear; Part I: Experimental, Tribol. Int., 2017, 107, p 135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.11.012
H. Spedding and C.R. Watkins, The Antiwear Mechanism of Zddp’s: Part I, Tribol. Int., 1982, 15(1), p 9–12.
H. Spedding and R.C. Watkins, The Antiwear Mechanism of Zddp’s Part II, Tribol. Int., 1982, 15(1), p 13–15.
G.E. Morales-Espejel and V. Brizmer, Micropitting Modelling in Rolling-Sliding Contacts: Application to Rolling Bearings, Tribol. Trans., 2011, 54(4), p 625–643. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2011.587633
S. Hutt, A. Clarke and H.P. Evans, Generation of Acoustic Emission from the Running-in and Subsequent Micropitting of a Mixed-Elastohydrodynamic Contact, Tribol. Int., 2018, 119, p 270–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.11.011
E. Lainé, Effect of Lubricant on Micropitting and Wear, Tribol. Int., 2009, 41, p 1–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.03.016
Y. Shimizu and H.A. Spikes, The Influence of Slide-Roll Ratio on ZDDP Tribofilm Formation, Tribol. Lett., 2016, 64(2), p 19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0738-z
M.A. Nicholls, T. Do, P.R. Norton, M. Kasrai and G.M. Bancroft, Review of the Lubrication of Metallic Surfaces by Zinc Dialkyl-Dithiophosphates, Tribol. Int., 2005, 38(1), p 15–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2004.05.009
A. Rossi, M. Eglin, F.M. Piras, K. Matsumoto and N.D. Spencer, Surface Analytical Studies of Surface-Additive Interactions, by Means of in Situ and Combinatorial Approaches, Wear, 2004, 256(6), p 578–584.
A. Morina, H. Zhao and J.F.W. Mosselmans, In-Situ Reflection-XANES Study of ZDDP and MoDTC Lubricant Films Formed on Steel and Diamond like Carbon (DLC) Surfaces, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 297, p 167–175.
P. Parsaeian, A. Ghanbarzadeh, M.C.P. Van Eijk, I. Nedelcu, A. Neville and A. Morina, A New Insight into the Interfacial Mechanisms of the Tribofilm Formed by Zinc Dialkyl Dithiophosphate, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 403, p 472–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.178
F.M. Piras, A. Rossi and N.D. Spencer, Combined in Situ (ATR FT-IR) and Ex Situ (XPS) Study of the ZnDTP-Iron Surface Interaction, Tribol. Lett., 2003, 15(3), p 181–192.
J.F. Moulder, J. Chastain and R.C. King, Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1992, 220(1), p 7–10.
B. Winter, E.F. Aziz, U. Hergenhahn, M. Faubel and I.V. Hertel, Hydrogen Bonds in Liquid Water Studied by Photoelectron Spectroscopy, J. Chem. Phys., 2007, 126(12), p 6.
J.M. Martin, Antiwear Mechanisms of Zinc Dithiophosphate: A Chemical Hardness Approach, Tribol. Lett., 1999, 6(1), p 1–8.
M.L.S. Fuller, M. Kasrai, G.M. Bancroft, K. Fyfe and K.H. Tan, Solution Decomposition of Zinc Dialkyl Dithiophosphate and Its Effect on Antiwear and Thermal Film Formation Studied by X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy, Tribol. Int., 1998, 31(10), p 627–644.
T. Hard and O. Chemistry, The Hard Soft Acid Bases (HSAB) Principle and Organic Chemistry, Chem. Rev., 1975, 75(1), p 1–20.
R.G. Pearson, Chemical Hardness-Applications from Molecules to Solids, VCH, Wiley, Weinheim, 1997.
J. Zhang and H. Spikes, On the Mechanism of ZDDP Antiwear Film Formation, Tribol. Lett., 2016, 63(2), p 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0706-7
A.J. Pidduck and G.C. Smith, Scanning Probe Microscopy of Automotive Anti-Wear Films, Wear, 1997, 212(2), p 254–264.
S. Bec, A. Tonck, J.-M. Georges, R.C. Coy, J.C. Bell, and G.W. Roper, “Relationship between Mechanical Properties and Structures of Zinc Dithiophosphate Anti–Wear Films,” Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, The Royal Society, 1999, p 4181–4203.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Number 51905463]; the Outstanding Young Core Teacher Program of Xuchang University; the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students in Henan Province [Grant Number S202010480028]; and the training plan of young core teachers in universities of Henan Province [Grant Number 2020GGJS207]. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Ileana Nedelcu from SKF ERC, the Netherlands, for carrying out the XPS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cen, H., Bai, D., Chao, Y. et al. Effect of Relative Humidity on Micropitting Behavior in Rolling–Sliding Contacts with Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphate-Containing Lubricants. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 2781–2797 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05561-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05561-2