Abstract
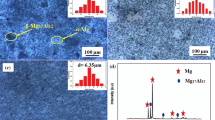
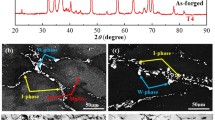
The effect of grain boundary and crystallographic orientation on the stress corrosion behavior of an Al-4.5Zn-1.4Mg alloy was investigated by comparing the performance of constant load stress corrosion test (CLSCT) and tensile test of specimens parallel to the longitudinal and transverse directions of the extruded plate. The results revealed that the strength of the longitudinal and transverse specimens decreased by 9.68 and 18.13%, respectively, after 10-day CLSCT. The transverse specimens show poor resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC). The grain boundaries (GB) of the longitudinal section are less dense, and more of them are distributed along the extrusion direction compared with the cross section with selected areas of the same size. The SCC of all specimens starts from the side faces of the specimen, and it is dominated by intergranular cracking. But the corrosion of the transverse specimens was more serious. The cracks of all specimens tend to propagate along the GBs with misorientation of about 50°-60°, and the difference of Schmidt factor (SF) values of grains on both sides of the crack is significantly large. The crack of longitudinal specimens propagates relatively parallel to the tensile direction, while propagation of the crack in transverse specimens is more zigzag.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Heinz, A. Haszler, C. Keidel, S. Moldenhauer, R. Benedictus, and W.S. Miller, Recent Development in Aluminium Alloys for Aerospace Applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 280, p 102–107
W.S. Miller, L. Zhuang, J. Bottema, A.J. Wittebrood, P. De Smet, A. Haszler, and A. Vieregge, Recent Development in Aluminium Alloys for the Automotive Industry, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 280, p 37–49
J. Hirsch and T. Al-Samman, Superior Light Metals by Texture Engineering: Optimized Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys for Automotive Applications, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, p 818–843
X.Y. Sun, B. Zhang, H.Q. Lin, Y. Zhou, L. Sun, J.Q. Wang, E.H. Han, and W. Ke, Correlations Between Stress Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility and Grain Boundary Microstructures for an Al-Zn-Mg Alloy, Corros. Sci., 2013, 77, p 103–112
Y.P. Xiao, Q.L. Pan, W.B. Li, X.Y. Liu, and Y.B. He, Influence of Retrogression and Re-aging Treatment on Corrosion Behaviour of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 2149–2156
T.C. Tsai and T.H. Chuang, Role of Grain Size on the Stress Aluminum Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 225, p 135–144
J. Chen, X. Zhang, L. Zou, Y. Yu, and Q. Li, Effect of Precipitate State on the Stress Corrosion Behavior of 7050 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2016, 114, p 1–8
C. Cao, D. Zhang, X. Wang, Q. Ma, L. Zhuang, and J. Zhang, Effects of Cu Addition on the Precipitation Hardening Response and Intergranular Corrosion of Al-5.2Mg-2.0Zn (wt%) Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2016, 122, p 177–182
S.P. Knight, N. Birbilis, B.C. Muddle, A.R. Trueman, and S.P. Lynch, Correlations Between Intergranular Stress Corrosion Cracking, Grain-Boundary Microchemistry, and Grain-Boundary Electrochemistry for Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 4073–4080
G. Peng, K. Chen, S. Chen, and H. Fang, Influence of Repetitious-RRA Treatment on the Strength and SCC Resistance of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 4014–4018
T. Ramgopal, P.I. Gouma, and G.S. Frankel, Role of Grain-Boundary Precipitates and Solute-Depleted Zone on the Intergranular Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy 7150, Corrosion, 2012, 58, p 687–697
S.D. Liu, B. Chen, C.B. Li, Y. Dai, Y.L. Deng, and X.M. Zhang, Mechanism of Low Exfoliation Corrosion Resistance Due to Slow Quenching in High Strength Aluminium Alloy, Corros. Sci., 2015, 91, p 203–212
R.G. Song, W. Dietzel, B.J. Zhang, W.J. Liu, M.K. Tseng, and A. Atrens, Stress Corrosion Cracking and Hydrogen Embrittlement of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 4727–4743
R.K. Viswanadham, T.S. Sun, and J.A.S. Green, Grain Boundary Segregation in Al-Zn-Mg Alloys—Implications to Stress Corrosion Cracking, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1980, 11, p 85–89
K. Kyzioł, K. Koper, M. Środa, M. Klich, and Ł. Kaczmarek, Influence of Gas Mixture During N + Ion Modification Under Plasma Conditions on Surface Structure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn Alloys, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 278, p 30–37
C.M. Abreu, M.J. Cristóbal, R. Figueroa, and G. Pena, Wear and Corrosion Performance of Two Different Tempers (T6 and T73) of AA7075 Aluminium Alloy After Nitrogen Implantation, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 327, p 51–61
Ł. Kaczmarek, M. Steglinski, J. Sawicki, J. Swiniarski, D. Batory, K. Kyzioł, Ł. Kołodziejczyk, W. Szymanski, P. Zawadzki, and D. Kottfer, Optimization of the Heat Treatment and Tribological Properties of 2024 and 7075 Aluminium Alloys, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2013, 58, p 535–540
K.D. Ralston, D. Fabijanic, and N. Birbilis, Effect of Grain Size on Corrosion of High Purity Aluminium, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, p 1729–1736
K.D. Ralston, N. Birbilis, and C.H.J. Davies, Revealing the Relationship Between Grain Size and Corrosion Rate of Metals, Scr. Mater., 2010, 63, p 1201–1204
M. Chen, Y. Deng, J. Tang, S. Fan, and X. Zhang, A Study of the Crystallographic Pitting Behavior of Al-0.54Mg-0.66Si Aluminum Alloy in Acidic Chloride Solutions, Mater. Charact., 2019, 148, p 259–265
C. Meng, D. Zhang, L. Zhuang, and J. Zhang, Correlations Between Stress Corrosion Cracking, Grain Boundary Precipitates and Zn Content of Al-Mg-Zn Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 655, p 178–187
V.S. Sinyavskii, V.V. Ulanova, and V.D. Kalinin, On the Mechanism of Intergranular Corrosion of Aluminum Alloys, Prot. Metals, 2004, 40, p 481–490
H.C. Fang, H. Chao, and K.H. Chen, Effect of Recrystallization on Intergranular Fracture and Corrosion of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 622, p 166–173
X. Lu, X. Han, Z. Du, G. Wang, L. Lu, J. Lei, and T. Zhou, Effect of Microstructure on Exfoliation Corrosion Resistance in an Al-Zn-Mg Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2018, 135, p 167–174
G. Peng, K. Chen, H. Fang, and S. Chen, Effect of Cr and Yb Additions on Microstructure and Properties of Low Copper Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr Alloy, Mater. Des., 2012, 36, p 279–283
S. Chen, K. Chen, P. Dong, S. Ye, and L. Huang, Effect of Recrystallization and Heat Treatment on Strength and SCC of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 581, p 705–709
Y. Shi, Q. Pan, M. Li, X. Huang, and B. Li, Effect of Sc and Zr Additions on Corrosion Behaviour of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 612, p 42–50
H.C. Fang, H. Chao, and K.H. Chen, Effect of Zr, Er and Cr Additions on Microstructures and Properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 610, p 10–16
J.F. Li, N. Birbilis, C.X. Li, Z.Q. Jia, B. Cai, and Z.Q. Zheng, Influence of Retrogression Temperature and Time on the Mechanical Properties and Exfoliation Corrosion Behavior of Aluminium Alloy AA7150, Mater. Charact., 2009, 60, p 1334–1341
S.P. Knight, K. Pohl, N.J.H. Holroyd, N. Birbilis, P.A. Rometsch, B.C. Muddle, R. Goswami, and S.P. Lynch, Some Effects of Alloy Composition on Stress Corrosion Cracking in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2015, 98, p 50–62
A.C.U. Rao, V. Vasu, M. Govindaraju, and K.V.S. Srinadh, Stress Corrosion Cracking Behaviour of 7xxx Aluminum Alloys: A Literature Review, Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc., 2016, 26, p 1447–1471
G.M. Scamans, Discontinuous Propagation of Stress Corrosion Cracks in Al-Zn-Mg Alloys, Scr. Metall., 1979, 13, p 245–250
L. Christodoulou and H.M. Flower, Hydrogen Embrittlement and Trapping in Al-6%Zn-3%Mg, Acta Metall., 1980, 28, p 481–487
D. Hardie, N.J.H. Holroyd, and R.N. Parkins, Reduced Ductility of High-Strength Aluminium Alloy During or After Exposure to Water, Metal Sci., 1979, 13, p 603–610
E. Dix, Acceleration of the Rate of Corrosion by High Constant Stresses, AIME Trans, 1940, 137, p 11–40
Y. Shi, Q. Pan, M. Li, X. Huang, and B. Li, Influence of Alloyed Sc and Zr, and Heat Treatment on Microstructures and Stress Corrosion Cracking of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 621, p 173–181
D. Tanguy, B. Bayle, R. Dif, and T. Magnin, Hydrogen Effects During IGSCC of pure Al-5Mg Alloy in NaCl Media, Corros. Sci., 2002, 44, p 1163–1175
D. Najjar, T. Magnin, and T.J. Warner, Influence of Critical Surface Defects and Localized Competition Between Anodic Dissolution and Hydrogen Effects During Stress Corrosion Cracking of a 7050 Aluminium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, 238, p 293–302
Acknowledgments
This present work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (Project No. 51474240) and Provincial Science and Technology Major Project of Hunan province (Project No. 2016KG1004), which are greatly acknowledged by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Zhang, Y., Ye, L. et al. Effect of Grain Boundary and Crystallographic Orientation on the Stress Corrosion Behavior of an Al-Zn-Mg Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 2954–2966 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04050-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04050-x