Abstract
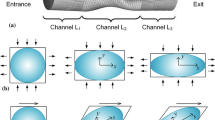
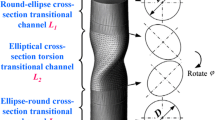
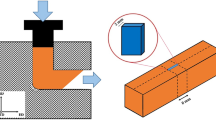
The aim of this work is to study the effect of six-pass elliptical cross-sectional spiral equal-channel extrusion (ECSEE) on the microstructure and performance of ultrafine-grained (UFG) copper. Equiaxed grains of average grain size of less than 1 μm are formed into shear bands in the low strain region of ECSEE deformed specimen. More homogeneous and equiaxed microstructure with high misorientation angles is obtained in the high strain. Moreover, the microstructure evolution of ECSEE-induced copper is a dynamic equilibrium process of shear deformation accompanying the interactions of high dislocation density, cellular structure and high-angle grain boundaries. The grain ECSEE refinement mechanism is described as the formation process of dislocations, cells, local grain sub-boundaries rotation and large angle grain restructure. The significantly non-uniform hardness distribution is consistent with the deformation behavior and microstructure refinement in the ECSEE-induced specimen. The homogeneity of microstructure and hardness improves as the ECSEE pass increases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zhang, X. Wu, H. Haryono, and K. Xia, Natural Polymer Biocomposites Produced from Processing Raw Wood Flour by Severe Shear Deformation, Carbohydr. Polym., 2014, 113(113), p 46–52
R.Z. Valiev and A.K. Mukherjee, Nanostructures and Unique Properties in Intermetallics, Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation, Scr. Mater., 2001, 44(8–9), p 1747–1750
R.Z. Valiev, Y.V. Ivanisenko, E.F. Rauch, and B. Baudelet, Structure and Deformaton Behaviour of Armco Iron Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation, Acta Mater., 1996, 44(12), p 4705–4712
S.E. Mousavi, M. Meratian, and A. Rezaeian, Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Fracture Surfaces of Dual-Phase 60–40 Brass Alloy Processed by Warm Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(13), p 8041–8051
J.M. Rosalie, J. Guo, R. Pippan, and Z. Zhang, On Nanostructured Molybdenum–Copper Composites Produced by High-Pressure Torsion, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(16), p 9872–9883
R. Łyszkowski, T. Czujko, and R.A. Varin, Multi-Axial Forging of Fe3Al-Base Intermetallic Alloy and Its Mechanical Properties, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(5), p 2902–2914
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, W. Lei, and H.J. Qiao, Review on Modified and Novel Techniques of Severe Plastic Deformation, Sci. China Technol. Sci., 2012, 55(9), p 2377–2390
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, B. Chen, Z.W. Yuan, and H.Y. Lu, Severe Plastic Deformation Techniques for Bulk Ultrafine-Grained Materials, Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 2012, 41(6), p 941–946
V. Yamakov, D. Wolf, S.R. Phillpot, A.K. Mukherjee, and H. Gleiter, Dislocation Processes in the Deformation of Nanocrystalline Aluminium by Molecular-Dynamics Simulation, Nat. Mater., 2002, 1(1), p 45–49
V. Yamakov, D. Wolf, S.R. Phillpot, and H. Gleiter, Dislocation–Dislocation and Dislocation–Twin Reactions in Nanocrystalline Al by Molecular Dynamics Simulation, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(14), p 4135–4147
Y.T. Zhu, X.L. Wu, X.Z. Liao, J. Narayan, L.J. Kecskes, and S.N. Mathaudhu, Dislocation–Twin interactions in Nanocrystalline fcc Metals, Acta Mater., 2011, 59(2), p 812–821
M.Y. Gutkin, I.A. Ovidkol, and N.V. Skiba, Crossover from Grain Boundary Sliding to Rotational Deformation in Nanocrystalline Materials, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(14), p 4059–4071
A.A. Fedorov, M.Y. Gutkin, and I.A. Ovidko, Transformations of Grain Boundary Dislocation Pile-Ups in Nano- and Polycrystalline Materials, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(4), p 887–898
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, Q.H. Li, J. Li, L. Wang, and J.Z. Dong, A Novel Severe Plastic Deformation Method for Fabricating Ultrafine Grained Pure Copper, Mater Des., 2013, 43, p 492–498
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, Q.H. Li, and L. Wang, Numerical and Experimental Studies of Pure Copper Processed by a New Severe Plastic Deformation Method, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 548(3), p 19–26
J.H. Li, F.G. Li, X.K. Ma, H. Chen, Z.C. Ma, and J. Li, Microhardness Distribution and Microstructural Evolution in Pure Aluminum Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation: Elliptical Cross-Sectioned Spiral Equal-Channel Extrusion (ECSEE), J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(11), p 4543–4550
M.I. Latypov and K.H. Seop, Comparative Analysis of Two Twist-Based SPD Processes: Elliptical Cross-Section Spiral Equal-Channel Extrusion vs Twist Extrusion, Mater. Trans., 2013, 54(9), p 1587–1591
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, H.Y. Lu, Z.W. Yuan, B. Chen, and H.J. Qiao, Deformation Analysis of Elliptical Cross-Section Spiral Equal Channel Extrusion Technique, Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 2013, 42(4), p 679–683
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, and J.C. Liu, Deformational Features and Microstructure Evolution of Copper Fabricated by a Single Pass of the Elliptical Cross-Section Spiral Equal-Channel Extrusion (ECSEE) Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(6), p 2967–2977
J.H. Li, F.G. Li, C. Zhao, H. Chen, X.K. Ma, and J. Li, Experimental Study on Pure Copper Subjected to Different Severe Plastic Deformation Modes, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 656, p 142–150
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, H.Y. Lu, Z.W. Yuan, and B. Chen, Optimization of Structural Parameters for Elliptical Cross-Section Spiral Equal-Channel Extrusion Dies Based on Grey Theory, Chin. J. Aeronaut., 2013, 26(1), p 209–216
T. Hu, K. Ma, T.D. Topping, J.M. Schoenung, and E.J. Lavernia, Precipitation Phenomena in an Ultrafine-Grained Al Alloy, Acta Mater., 2013, 61(6), p 2163–2178
Y. Miyajima, S. Okubo, H. Abe, H. Okumura, T. Fujii, S. Onaka, and K. Masaharu, Dislocation Density of Pure Copper Processed by Accumulative Roll Bonding and Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Charact., 2015, 104, p 101–106
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov, Bulk Nanostructured Materials from Severe Plastic Deformation, Prog. Mater Sci., 2000, 45(2), p 103–189
A.S. Malin and M. Hatherly, Microstructure of Cold-Rolled Copper, Mater. Sci., 1979, 13(8), p 463–472
E. Bonnot, A.L. Helbert, F. Brisset, and T. Baudin, Microstructure and Texture Evolution During the Ultra Grain Refinement of the Armco Iron Deformed by Accumulative Roll Bonding (ARB), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 561(3), p 60–66
F. Salimyanfard, M.R. Toroghinejad, F. Ashrafizadeh, and M. Jafari, EBSD Analysis of Nano-Structured Copper Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(16–17), p 5348–5355
X. Molodova, G. Gottstein, M. Winning, and R.J. Hellmig, Thermal Stability of ECAP Processed Pure Copper, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, s460-461(1), p 204–213
A. Mishra, B.K. Kad, F. Gregori, and M.A. Meyers, Microstructural Evolution in Copper Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation: Experiments and Analysis, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(1), p 13–28
S. Ferrasse, K.T. Hartwig, R.E. Goforth, and V.M. Segal, Microstructure and Properties of Copper and Aluminum Alloy 3003 Heavily Worked by Equal Channel Angular Extrusion, Metall. Mater. Trans., 1997, 28(4), p 1047–1057
J.Y. Huang, Y.T. Zhu, H. Jiang, and T.C. Lowe, Microstructures and Dislocation Configurations in Nanostructured Cu Processed by Repetitive Corrugation and Straightening, Acta Mater., 2001, 49(9), p 1497–1505
N. Hansen and R.F. Mehl, New Discoveries in Deformed Metals, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32(12), p 2917–2935
N. Hansen and D.J. Jensen, Development of Microstructure in FCC Metals During Cold Work, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 1999, 357(1756), p 1447–1469
Y. Wang, Y. Xin, H. Yu, L. Lv, and Q. Liu, Formation and Microstructure of Shear Bands During Hot Rolling of a Mg-6Zn-0.5Zr Alloy Plate with a Basal Texture, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 644, p 147–154
V.M. Segal, Severe Plastic Deformation: Simple Shear Versus Pure Shear, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 338(1–2), p 331–344
A. Mishra, B.K. Kad, F. Gregori, and M.A. Meyers, Microstructural Evolution in Copper Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation: Experiments and Analysis, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(1), p 13–28
N. Lugo, N. Llorca, J.M. Cabrera, and Z. Horita, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Pure Copper Deformed Severely by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing and High Pressure Torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 477(1), p 366–371
Q. Liu, X. Huang, D.J. Lloyd, and N. Hansen, Microstructure and Strength of Commercial Purity Aluminium (AA 1200) Cold-Rolled to Large Strains, Acta Mater., 2002, 50(15), p 3789–3802
E. Nes, T. Pettersen, and K. Marthinsen, On the Mechanisms of Work Hardening and Flow-Stress Saturation, Scr. Mater., 2000, 43(1), p 55–62
M.J. Starink, X.G. Qiao, J. Zhang, and N. Gao, Predicting Grain Refinement by Cold Severe Plastic Deformation in Alloys Using Volume Averaged Dislocation Generation, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(19), p 5796–5811
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51275414 and 51172161), the School Youth Foundation (No. 1205-04020202), Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (17JCQNJC04900) and the fund of the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing in NWPU (No. SKLSP201517).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Song, D., Fan, J. et al. Microstructure Evolution and Microhardness Distribution of Copper Processed Using Multiple Passes of Elliptical Cross-Sectional Spiral Equal-Channel Extrusion. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6665–6675 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3738-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3738-3