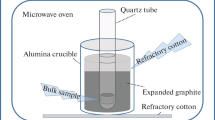
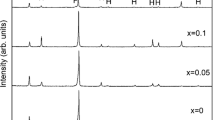
Abstract
Thermoelectric TiNiSn-based half Heusler compound reveals high Seebeck coefficient and electrical conductivity, leading to high power factor. As a consequence of the solidification path, TiNiSn single phase cannot be obtained directly from the liquid phase. Thus, a long annealing step is needed to homogenize the alloy. In this work, we present a new processing route for half Heusler compound formation, combining arc melting of pure elements, rapid solidification of the molten alloy and sintering. Rapid solidification of the molten alloy allows to obtain almost single TiNiSn phase, limiting the formation of the primary TiNi2Sn phase as a consequence of the deep undercooling of the liquid. The rapidly solidified alloy was ground to powder and sintered by open die pressing. As-sintered samples show a density around 95% of the theoretical value. Thermal cycling of the sintered samples shows evolution of the phases, suggesting that after sintering the sample is not in equilibrium yet. After the second thermal cycle thermoelectric properties become reproducible, indicating the attainment of the equilibrium. In conclusion, the proposed processing route allows to obtain dense TiNiSn in bulk form avoiding the time-consuming annealing step, typically used to homogenize this alloy after solidification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.J. DiSalvo, Thermoelectric Cooling and Power Generation, Science, 1999, 285, p 703–706
M. Zebarjadi, K. Esfarjani, M.S. Dresselhaus, Z.F. Ren, and G. Chen, Perspectives on Thermoelectrics: From Fundamentals to Device Applications, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(1), p 5147–5162
B. Dado, Y. Gelbstein, D. Mogilansky, V. Ezersky, and M.P. Dariel, Structural Evolution Following Spinodal Decomposition of the Pseudo-Ternary Compound (Pb0.3Sn0.1Ge0.6)Te, J. Electron. Mater., 2010, 39(9), p 2165–2171
Y. Gelbstein, Z. Dashevsky, and M.P. Dariel, Highly Efficient Bismuth Telluride Doped p-Type Pb0.13Ge0.87Te for Thermoelectric Applications, Phys. Status Solidi (RRL), 2007, 1(6), p 232–234
G. Rogl and P. Rogl, Skutterudites, a Most Promising Group of Thermoelectric Materials, Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem., 2017, 4, p 50–57
D.M. Rowe, V.S. Shukla, and N. Savvides, Phonon Scattering at Grain Boundaries in Heavily Doped Fine-Grained Silicon-Germanium Alloys, Nature, 1981, 290(5809), p 765–766
C.B. Vining, W. Laskow, J.O. Hanson, R.R. Van Der Beck, and P.D. Gorsuch, Thermoelectric Properties of Pressure-Sintered Si0.8Ge0.2 Thermoelectric Alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 1991, 69(8), p 4333–4340
O. Appel, T. Zilber, S. Kalabukhov, O. Beeri, and Y. Gelbstein, Morphological Effects on the Thermoelectric Properties of Ti0.3Zr0.35Hf0.35Ni1+δSn Alloys Following Phase Separation, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3(44), p 11653–11659
O. Appel, M. Schwall, M. Kohne, B. Balke, and Y. Gelbstein, Microstructural Evolution Effects of Spark Plasma Sintered Ti0.3Zr0.35Hf0.35NiSn Half-Heusler Compound on the Thermoelectric Properties, J. Electron. Mater., 2013, 42(7), p 1340–1345
J. Krez and B. Balke, Thermoeletric Heusler Compounds, Heusler Alloys: Properties, Growth, Applications, C. Felser and A. Hirohata, Ed., Springer, Cham, 2016, p 249–267
K. Gofryk, D. Kaczorowski, T. Plackowski, A. Leithe-Jasper, and Y. Grin, Magnetic and Transport Properties of Rare-Earth-Based Half-Heusler Phases RPdBi: Prospective Systems for Topological Quantum Phenomena, Phys. Rev. B, 2011, 84(3), p 035208
O. Pavlosiuk, X. Fabreges, A. Gukasov, M. Meven, D. Kaczorowski, and P. Wiśniewski, Magnetic Structures of REPdBi Half-Heusler Bismuthides (RE = Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er), Physica B, 2018, 536, p 56–59
J.-W.G. Bos and R.A. Downie, Half-Heusler Thermoelectric: A Complex Class of Materials, J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 2014, 26(43), p 433201
R. Gautier, X. Zhang, L. Hu, L. Yu, Y. Lin, T.O.L. Sunde, D. Chon, K.R. Poeppelmeier, and A. Zunger, Prediction and Accelerated Laboratory Discovery of Previously Unknown 18-Electron ABX Compounds, Nat. Chem., 2015, 7(4), p 308–316
T. Zhu, C. Fu, H. Xie, Y. Liu, and X. Zhao, High Efficiency Half-Heusler Thermoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting, Adv. Energy Mater., 2015, 5(19), p 1500588
L. Huang, Q. Zhang, B. Yuan, X. Lai, X. Yan, and Z. Ren, Recent Progress in Half-Heusler Thermoelectric Materials, Mater. Res. Bull., 2016, 76, p 107–112
F.G. Aliev, A.I. Belogorokhov, N.B. Brandt, V.V. Kozyr’kov, R.V. Skolozdra, and Y.V. Stadnyk, Optical Properties of the Vacancy MNiSn Lattices (M = Ti, Zr, Hf), JETP Lett., 1988, 47(3), p 184–187
C. Uher, J. Yang, S. Hu, D.T. Morelli, and G.P. Meisner, Transport Properties of Pure and Doped MNiSn (M = Zr, Hf), Phys. Rev. B, 1999, 59(13), p 8615–8621
C.S. Birkel, J.E. Douglas, B.R. Lettiere, G. Seward, N. Verma, Y. Zhang, T.M. Pollock, R. Seshadri, and G.D. Stucky, Influence of Ni Nanoparticle Addition and Spark Plasma Sintering on the TiNiSn-Ni System: Structure, Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties, Solid State Sci., 2013, 26, p 16–22
C.S. Birkel, J.E. Douglas, B.R. Lettiere, G. Seward, N. Verma, Y. Zhang, T.M. Pollock, R. Seshadri, and G.D. Stucky, Improving the Thermoelectric Properties of Half-Heusler TiNiSn Through Inclusion of a Second Full-Heusler Phase: Microwave Preparation and Spark Plasma Sintering of TiNi1+xSn, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(18), p 6990–6997
J.E. Douglas, C.S. Birkel, N. Verma, V.M. Miller, M.-S. Miao, G.D. Stucky, T.M. Pollock, and R. Seshadri, Phase Stability and Property Evolution of Biphasic Ti-Ni-Sn Alloys for Use in Thermoelectric Applications, J. Appl. Phys., 2014, 115(4), p 043720
R.A. Downie, R.I. Smith, D.A. MacLaren, and J.-W.G. Bos, Metal Distributions, Efficient n-Type Doping, and Evidence for in-Gap States in TiNiMySn (M = Co, Ni, Cu) half-Heusler nanocomposites, Chem. Mater., 2015, 27(7), p 2449–2459
Y. Tang, X. Li, L.H.J. Martin, E. Cuervo Reyes, T. Ivas, C. Leinenbach, S. Anand, M. Peters, G.J. Snyder, and C. Battaglia, Impact of Ni Content on the Thermoelectric Properties of Half-Heusler TiNiSn, Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11(2), p 311–320
S.A. Barczak, J. Buckman, R.I. Smith, A.R. Baker, E. Don, I. Forbes, and J.-W.G. Bos, Impact of Interstitial Ni on the Thermoelectric Properties of the Half-Heusler TiNiSn, Materials, 2018, 11(4), p 536
M. Schrade, K. Berland, S.N.H. Eliassen, M.N. Guzik, C. Echevarria-Bonet, M.H. Sørby, P. Jenuš, B.C. Hauback, R. Tofan, A.E. Gunnæs, C. Persson, O.M. Løvvik, and T.G. Finstad, The Role of Grain Boundary Scattering in Reducing the Thermal Conductivity of Polycrystalline XNiSn (X = Hf, Zr, Ti) Half-Heusler Alloys, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), p 13760
S. Bhattacharya, M.J. Skove, M. Russell, T.M. Tritt, Y. Xia, V. Ponnambalam, S.J. Poon, and N. Thadhani, Effect of Boundary Scattering on the Thermal Conductivity of TiNiSn-Based Half-Heusler Alloys, Phys. Rev. B, 2008, 77(18), p 184203
B.A. Cook, J.L. Harringa, Z.S. Tan, W.A. Jesser, TiNiSn: A Gateway to the (1,1,1) Intermetallic Compounds, in 15th International Conference on Thermoelectrics, 26–29 March 1996 (IEEE, Pasadena, CA, 1996), pp. 122–127
M. Zou, J.-F. Li, B. Du, D. Liu, and T. Kita, Fabrication and Thermoelectric Properties of Fine-Grained TiNiSn Compounds, J. Solid State Chem., 2009, 182(11), p 3138–3142
M. Gürth, A. Grytsiv, J. Vrestal, V.V. Romaka, G. Giester, E. Bauer, and P. Rogl, On the Constitution and Thermodynamic Modelling of the System Ti-Ni-Sn, RSC Adv., 2015, 5(112), p 92270–92291
M. Baricco, E. Bosco, E. Olivetti, M. Palumbo, P. Rizzi, A. Stantero, and L. Battezzati, Rapid Solidification of Alloys, Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol., 2004, 20(5–6), p 358–376
D. Lussana, A. Castellero, M. Vedani, D. Ripamonti, G. Angella, and M. Baricco, Microstructure Refinement and Hardening of Ag–20 wt% Cu Alloy by Rapid Solidification, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 615(S1), p S633–S637
D. Lussana, A. Castellero, D. Ripamonti, G. Angella, M. Vedani, A. Zambon, and M. Baricco, Effect of Rapid Quenching and Severe Plastic Deformation on Silver, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2012, 103(9), p 1117–1121
C. Artini, A. Castellero, M. Baricco, M.T. Buscaglia, and R. Carlini, Structure, Microstructure and Microhardness of Rapidly Solidified Smy(FexNi1−x)4Sb12 (x = 0.45, 0.50, 0.70, 1) Thermoelectric Compounds, Solid State Sci., 2018, 79, p 71–78
A. Castellero, G. Fiore, E. Evenstein, M. Baricco, and Y. Amouyal, Effects of Rapid Solidification on Phase Formation and Microstructure Evolution of AgSbTe2-Based Thermoelectric Compounds, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2017, 17(3), p 1650–1656
Yu Cui, T.-J. Zhu, K. Xiao, J.-J. Shen, S.-H. Yang, and X.-B. Zhao, Reduced Grain Size and Improved Thermoelectric Properties of Melt Spun (Hf, Zr)NiSn Half-Heusler Alloys, J. Electron. Mater., 2010, 39(9), p 2008–2012
S. Ceresara, C. Fanciulli, F. Passaretti, and D. Vasilevskiy, Texturing of (Bi0.2Sb0.8)2 Te3 Nanopowders by Open Die Pressing, J. Electron. Mater., 2013, 42(7), p 1529–1534
S. Boldrini, A. Famengo, F. Montagner, S. Battiston, S. Fiameni, M. Fabrizio, and S. Barison, Test rig for High-Temperature Thermopower and Electrical Conductivity Measurements, J. Electron. Mater., 2013, 42(7), p 1319–1323
R.F. Speyer, Thermal Analysis of Materials, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1994, p 79–80
D.A. Porter and K.E. Easterling, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed., Chapman & Hall, New York, 1992, p 208–214
International Center for Diffraction Data, Powder Diffraction File 03-065-0991
International Center for Diffraction Data, Powder Diffraction File 00-052-0905
Acknowledgments
Alberto Castellero thanks University of Turin and Compagnia di Sanpaolo for financial support (Project No. CSTO162398). The authors also thank Dr. G. Fiore (University of Turin) and Mr E. Bassani (CNR-ICMATE, Unità di Lecco) for the support in the arc melting and ODP processing of the samples, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aversano, F., Ferrario, A., Boldrini, S. et al. Thermoelectric Properties of TiNiSn Half Heusler Alloy Obtained by Rapid Solidification and Sintering. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6306–6313 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3735-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3735-6