Abstract
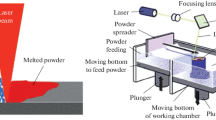
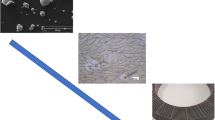
Nd-Fe-B-type permanent magnets are used in applications that require a high-energy product/volume ratio in order to reduce weight. Automotive industry, hard drives, or wind turbines are just examples of an application where their use can be found. Conventional casting techniques reveal the formation of a high quantity of α-Fe and large Nd-rich regions. On the other hand, new techniques, like strip casting, melt-spinning and centrifugal atomization, produce homogeneous and fine-scaled microstructures. This paper discusses the application of rapid solidification by means of the centrifugal atomization method for preparation of Nd-Fe-B flakes. The effect of alloy composition and various process parameters of centrifugal atomization on the microstructure of rapidly solidified Nd-Fe-B alloy were investigated. The microstructures and the phase composition were examined by metallographic techniques, namely optical and scanning electron microscopy. Additionally, the influence of the processing parameters on the microstructures of as-cast flakes and subsequent magnetic properties of the prepared magnets will be discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher, Fundaments of Solidification, Trans Tech Publications, Brookfield, 1989
H. Jones, Rapid Solidification of Metals and Alloys, Monograph No. 8, The institution of metallurgists, London, 1982
H.H. Liebermann, Rapidly Solidified Alloys, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1993
E.I. Anderson, W. Tang, and R.W. Mccallum, Particulate Processing and Properties of High-Performance Permanent Magnets, Int. J. Powder Metal., 2004, 40(6), p 37–60
J.M.D. Coey, Magnetism and magnetic materials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010, p 614
O. Gutfleisch, Rare Earth Magnets: Materials, V: Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2nd ed., Elsevier, Oxford, 2001, p 8022–8025
B.E. Davies, R.S. Mottram, and I.R. Harris, Recent Developments in the Sintering of NdFeB, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2001, 67(1–3), p 272–281
P. Tenaud, H. Lemaire, and F. Vial, Recent Improvements in NdFeB Sintered Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1991, 101, p 328–332
S. Guo, Q.Y. Zhou, R.J. Chen, D. Lee, and A.R. Yan, Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Sintered Nd-Fe-B Magnets with High Hydrogen Content, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 109, p 07A734
G. Bai, R.W. Gao, Y. Sun, G.B. Han, and B. Wang, Study of High-Coercivity Sintered NdFeB Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007, 308, p 20–23
W. Rodewald, B. Wall, M. Katter, and K. Ustuner, Top NdFeB Magnets with Greater than 56 MGOe Energy Density and 9.8 kOe Coercivity, IEEE Trans. Magn., 2002, 38, p 2955–2957
R.S. Sheridan, A.J. Williams, I. Harris, and A. Walton, Improved HDDR Processing Route for Production of Anisotropic Powder from Sintered NdFeB Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2014, 350, p 114–118
D. Brown, B.M. Ma, and Z. Chen, Developments in the Processing and Properties of Nd-Fe-N-Type Permanent Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2002, 248, p 432–440
S. Ozawa, T. Saito, and T. Motegi, Effects of Cooling Rate on Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2004, 363(1–2), p 268–275
J. Bernardi, J. Fidler, M. Sagawa, and Y. Hirose, Microstructural Analysis of Strip-Cast Nd-Fe-B Alloys for High (BH)max Magnets, J. Appl. Phys., 1998, 83, p 6396
L.Q. Yu, M. Yan, J.M. Wu, W. Luo, X.G. Cui, and H.G. Ying, On the Cooling Rate of Strip Cast Ingots for Sintered NdFeB Magnets, Phys. B, 2007, 393, p 1–5
Z. Tian, S. Li, K. Peng, B. Gu, and Y. Du, The Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of NdFeB Magnets Directly Solidified at a Low Cooling Rate, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 380, p 143–146
G. Binglin, L. Bo, W. Dongling, Y. Xiaojun, and H. Jifan, Influence of Cooling Rate on Microstructure of NdFeB Strip Casting Flakes, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, 475–479, p 2169–2172
X. Jing, Y. Shihong, Y. Dunbo, L. Zongan, L. Shipeng, and L. Hongwei, Influence of Solidification Rate on Microstructures of Cast Strips and Corresponding Sintered NdFeB Magnets, J. Rare Earths, 2006, 24(1), p 306–309
D. Goll, S. Schweizer, C. Wegierski, and G. Schneider, Towards a Better Understanding of Intergranular Phases in Fe-Nd-B Sintered Magnets, Phys. Status Solidi RRL, 2012, 6(9–10), p 388–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited submission to JMEP selected from presentations at the Symposium “Solidification, Casting, Foundry and Liquid Metal Processing,” belonging to the Topic “Joining” at the European Congress and Exhibition on Advanced Materials and Processes (EUROMAT 2017), held September 17-22, 2017, in Thessaloniki, Greece, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunčko, M., Erman, Ž., Kirbiš, P. et al. The Application of Centrifugal Atomization Method for Preparation of Rapidly Solidified Nd-Fe-B Flakes Used for Production of Permanent Magnets. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 5136–5140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3564-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3564-7