Abstract
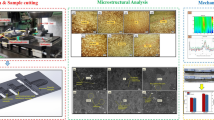
The effect of trace amounts of rare earth element Ce on the wettability, mechanical properties and microstructure of Ag17CuZnSn filler metal was investigated systematically by means of microstructure and spectroscopic characterizations. H62 brass and 304 stainless steel were brazed with Ag17CuZnSn-xCe filler metals. The results indicate that wettability and oxidation resistance of filler metal are remarkably improved with adding trace amount of Ce. The shear strength of brazed joint increases 29% compared to that of brazed joint without adding Ce. Moreover, it is observed that the trace amount of Ce in Ag17CuZnSn filler metal refines the brazed joint matrix microstructure. The elements diffusion is examined during the brazing process. More Ce can diffuse into the stainless steel than that of either Cu or Zn. Compared to the Cu solid solution, Fe prefers to diffuse into the Ag solid solution. When the Ce content is 0.3 wt.%, some bright and brittle Ce-bearing particles appear in the bottom of dimples which deteriorate the shear strength of brazed joint. The results of this study can stimulate the use of low-silver brazing filler metals for various applications.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Schwartz, Brazing, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2003, p 102–105
A. Khorram and M. Ghoreishi, Comparative Study on Laser Brazing and Furnace Brazing of Inconel 718 Alloys with Silver Based Filler Metal, Opt. Laser. Tchnol., 2014, 56, p p443–p450
A. Winiowski, Mechanical and Structural Properties of Joints of Stainless Steel and Titanium Brazed with Silver Filler Metals Containing Tin, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2010, 55(4), p 991–1000
F. Sui, W. Long, S. Liu, G. Zhang, L. Bao, H. Li, and Y. Chen, Effect of Calcium on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Brazed Joint Using Ag-Cu-Zn Brazing Filler Metal, Mater. Des., 2013, 46, p 605–608
B. Daly, Basics of Brazing with Induction Heating, Weld. J, 2013, 92, p 52–54
Z. Lai, S. Xue, X. Han, L. Gu, and W. Gu, Study on Microstructure and Property of Brazed Joint of AgCuZn- X (Ga, Sn, In, Ni) Brazing Alloy, Rare Metal. Mater. Eng., 2010, 39(3), p 397–400
L. Zhang, J. Feng, B. Zhang, and X. Jing, Ag-Cu-Zn Alloy for Brazing TiC Cermet/Steel, Mater. Lett., 2005, 59(1), p 110–113
B.D. Thorne and P.J. Hewitt, Chemical Composition and Particle Morphology of Brazing Fume from Cadmium Brazing Alloy and Fluoroborate Flux, Ann. Occup. Hyg., 1988, 32(4), p 489–497
T. Nishida, K. Kimura, and M. Inagaki, Behavior of Cadmium on Brazing, Quart. J. Japan Welding., 1994, 12, p 485–494
V.F. Khorunov, S.V. Maksymova, and B.V. Stefaniv, Effect of Palladium on Structure and Technological Properties of Ag-Cu-Zn-Ni-Mn System Brazing Filler Alloys, The Paton Welding J, 2012, 9, p 20–25
X. Ma, L.F. Li, Z.H. Zhang, H. Wang, E.Z. Wang, and T. Qiu, Microstructure and Melting Properties of Ag-Cu-In Intermediate-Temperature Brazing Alloys, Rare Met., 2015, 34(5), p 324–328
L.I. Zhuoran, N. Jiao, J. Feng, and Y. Chen, Effect of P and Rare-Earth La on Microstructure and Property of AgCuZnSn Brazing Alloy, Trans. China Weld. Inst., 2007, 28(12), p 1–4
C.M.L. Wu, D.Q. Yu, C.M.T. Law, and L. Wang, Properties of Lead-Free Solder Alloys with Rare Earth Element Additions, Mater. Sci. Eng., R, 2004, 44(1), p p41–p44
C.Y. Yang, J.H. Xu, W.F. Ding, Z.Z. Chen, and Y.C. Fu, Effect of Cerium on Microstructure, Wetting and Mechanical Properties of Ag-Cu-Ti Filler Alloy, J. Rare. Earth, 2009, 27(6), p 1051–1055
J. Cao, L.X. Zhang, H.Q. Wang, L.Z. Wu, and J.C. Feng, Effect of Silver Content on Microstructure and Properties of Brass/steel Induction Brazing Joint Using Ag-Cu-Zn-Sn Filler Metal, Corros. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, 27(4), p 377–381
GB/T 11364-2008, Test Method of Wettability for Brazing Filler Metals (China Standard Press)
GB/T 11363-2008, Test Method of the Strength for Brazed and Soldered Joint (China Standard Press)
GB/T 27552-2001, Destructive Tests on Welds in Metallic Materials-Microhardness Testing of Welded Joints (China Standard Press)
D.K. Chattoraj, K.S. Birdi, Adsorption and the Gibbs Surface Excess (1984)
Y.H. Hu, S.B. Xue, H. Ye, and Z.X. Xiao, Reliability Studies of Sn-9Zn/Cu and Sn-9Zn-0.06Nd/Cu Joints with Aging Treatment, Mater. Des., 2012, 34, p p768–p775
A.Z. Al-Yaseri, H. Roshan, M. Lebedev, A. Barifcani, and S. Iglauer, Dependence of Quartz Wettability on Fluid Density, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2016, 43(8), p 3771–3776
Z. Han, S. Xue, L. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Wu, and X. Huang, Effects of Micro-Amount of Cerium on Microstructures of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder and Soldered Joint, J. Rare Earths, 2006, 24(2), p 232–236
W.X. Chen, S. Xue, H. Wang, Y.H. Hu, and J. Wang, Effects of Rare Earth Ce on Properties of Sn-9Zn Lead-Free Solder, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2010, 21(7), p 719–725
L. Zhang, J.G. Han, Y.H. Guo, and L. Sun, Reliability of SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe Solder Joints with Different Heights for Electronic Packaging, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2014, 25(10), p 4489–4494
P. Boulet, D. Mazzone, H. Noël, P. Riani, P. Rogl, and R.Ferro, The System Ce-Ag-Sn: Phase Equilibria and Magnetic Properties, Intermetallics, 1999, 7(8), p 931–935
H. Wang, K. Wang, R. Zheng, K.S. Prasad, and S.P. Ringer, Microscopic Bonding Mechanism of Welding Interface with Molten Cu-4Zn Deposited on Solid-State Steel, Mater. Charact., 2008, 59(5), p 542–546
I. Magnabosco, P. Ferro, F. Bonollo, and L. Arnberg, An Investigation of Fusion Zone Microstructures in Electron Beam Welding of Copper–Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci., 2006, 424(1), p 163–173
J. Feng, S. Xue, and D. Wei, Reliability Studies of Cu/Al Joints Brazed with Zn-Al-Ce Filler Metals, Mater. Des., 2012, 42, p 156–163
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51375233 and Grant No. 51575016), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (General Financial Grant 2014M550289, Special Financial Grant 2015T80548) and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), P.R. China. The authors specially thank to Zhejiang Metallurgical Research Institute Co., Ltd for the assistance in providing experimental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Xue, S., Wang, B. et al. Effect of Ce Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of Ag17CuZnSn Filler Metal. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 3180–3190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2761-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2761-0