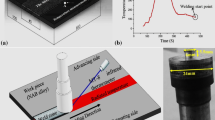
Abstract
In this study, the applicability of friction stir welding to cast NAB alloy (i.e., C95800) with a thickness of 9 mm has been investigated. The joint performance was determined by conducting optical microscopy, microhardness measurements, and mechanical testing (e.g., tensile and Charpy impact tests). The effect of stir intensity on joint performance was also determined. A grain refinement (equiaxed fine grain structure) as well as evolution of a Widmanstätten structure was achieved within the stir zone of all the joints produced. Thus, all of the joints produced exhibited higher proof stress (i.e., between 512 and 616 MPa) than that of the base material, i.e., 397 MPa. On the other hand, only half of the specimens exhibited higher tensile strength values than that of the base plate (i.e., 794 MPa), whereas the other specimens displayed lower tensile strength than the base plate due to the existence of weld defects, namely cold bonding and/or tunnel defect.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASM handbook, Welding, Brazing and Soldering, vol. 6, ed. by D.L. Olsonet al (ASM International, Materials Park, 1993)
G. Çam, Friction Stir Welded Structural Materials: Beyond Al-alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 2011, 56(1), p 1–48
K. Oh-Ishi, A.M. Cuevas, D.L. Swisher, and T.R. McNelley, The Influence of Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Properties of a Cast Nickel-Aluminum Bronze Material, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2003, 426–432, p 2885–2890
K. Oh-Ishi and T.R. McNelley, Microstructural Modification of As-Cast NiAl Bronze by Friction Stir Processing, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35A, p 2951–2961
K. Oh-Ishi and T.R. McNelley, The Influence of Friction Stir Processing Parameters on Microstructure of As-Cast NiAl Bronze, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36A, p 1575–1585
K. Oh-Ishi, A.P. Zhilyaev, and T.R. McNelley, A Microtexture Investigation of Recrystallization During Friction Stir Processing of As-Cast NiAl Bronze, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, 37A, p 2239–2251
T.R. McNelley, K. Oh-Ishi, and A.P. Zhilyaev, Microstructure Evolution and Microstructure-Property Relationships in Friction Stir Processing of NiAl Bronze, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, 539–543, p 3745–3750
M.W. Mahoney, W.H. Bingel, S.R. Sharma, and R.S. Mishra, Microstructural Modification and Resultant Properties of Friction Stir Processed Cast NiAl Bronze, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2003, 426-432, p 2843–2848
M.D. Fuller, S. Swaminathan, A.P. Zhilyaev, and T.R. McNelley, Microstructural Transformations and Mechanical Properties of Cast NiAl Bronze: Effects of Fusion Welding and Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, A463, p 128–137
D.R. Ni, P. Xue, D. Wang, B.L. Xiao, and Z.Y. Ma, Inhomogeneous Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Processed NiAl Bronze, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, A524, p 119–128
G. Çam, S. Mistikoglu, and M. Pakdil, Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Friction Stir Butt Joint Welded 63% Cu-37% Zn Brass Plate, Weld. J., 2009, 88(11), p 225s–232s
G. Çam, H.T. Serindag, A. Çakan, S. Mistikoglu, and H. Yavuz, The Effect of Weld Parameters on Friction Stir Welding of Brass Plates, Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech., 2008, 39(6), p 394–399
R.S. Mishra and Z.Y. Ma, Friction Stir Welding and Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2005, R50(1–2), p 1–78
R. Nandan, T. DebRoy, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Recent Advances in Friction-Stir Welding—Process, Weldment Structure and Properties, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2008, 53(6), p 980–1023
P.L. Threadgill, A.J. Leonard, H.R. Shercliff, and P.J. Withers, Friction Stir Welding of Aluminium Alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 2009, 54(2), p 49–93
G. Çam and S. Mıstıkoğlu, Recent Developments in Friction Stir Welding of Al-Alloys, JMEPEG, 2014, 23(6), p 1936–1953
C.B. Fuller, Friction Stir Tooling: Tool Materials and Design, Friction Stir Welding And Processing, ed. by R.S. Mishra, M.W. Mahoney (ASM International, 2007), p. 7–35.
G.M. Xie, Z.Y. Ma, and L. Geng, Development of a Fine-Grained Microstructure and the Properties of a Nugget Zone in Friction Stir Welded Pure Copper, Scripta Mater., 2007, 57(2), p 73–76
H.J. Liu, J.J. Shen, Y.X. Huang, L.Y. Kuang, C. Liu, and C. Li, Effect of Tool Rotation Rate on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Copper, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2009, 14(6), p 577–583
H.S. Park, T. Kimura, T. Murakami, Y. Nagano, K. Nakata, and M. Ushio, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welds of 60% Cu-40% Zn Copper Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, A371(1–2), p 160–169
W.B. Lee and S.B. Jung, The Joint Properties of Copper by Friction Stir Welding, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58(6), p 1041–1046
C. Meran, The Joint Properties of Brass Plates by Friction Stir Welding, Mater. Des., 2006, 27(9), p 719–726
G. İpekoğlu and G. Çam, Effects of Initial Temper Condition and Postweld Heat Treatment on the Properties of Dissimilar Friction-Stir-Welded Joints between AA7075 and AA6061 Aluminum Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45A(7), p 3074–3087
G. İpekoğlu, S. Erim, and G. Çam, Investigation into the Influence of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on the Friction Stir Welded AA6061 Al-Alloy Plates with Different Temper Conditions, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45A(2), p 864–877
G. İpekoğlu, S. Erim, and G. Çam, Effects of Temper Condition and Post Weld Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Butt-Welded AA7075 Al Alloy Plates, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, 70(1–4), p 201–213
G. İpekoğlu, S. Erim, and B. Gören, Kıral, and G. Çam, Investigation into the Effect of Temper Condition on Friction Stir Weldability of AA6061 Al-Alloy Plates, Kovove Mater., 2013, 51(3), p 155–163
G. İpekoğlu, B. Gören Kıral, S. Erim, and G. Çam, Investigation of the Effect of Temper Condition on the Friction Stir Weldability of AA7075 Al-Alloy Plates, Mater. Tehnol., 2012, 46(6), p 627–632
G. Çam, G. İpekoğlu, and H. Tarık Serindağ, Effects of Use of Higher Strength Interlayer and External Cooling on Properties of Friction Stir Welded AA6061-T6 Joints, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2014, 19(8), p 715–720
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küçükömeroğlu, T., Şentürk, E., Kara, L. et al. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Nickel-Aluminum Bronze (NAB) Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 320–326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1838-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1838-x