Abstract
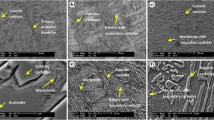
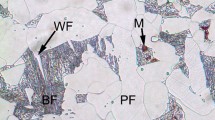
A statistical indentation method has been employed to study the hardness value of fire-refined high conductivity copper, using nanoindentation technique. The Joslin and Oliver approach was used with the aim to separate the hardness (H) influence of copper matrix, from that of inclusions and grain boundaries. This approach relies on a large array of imprints (around 400 indentations), performed at 150 nm of indentation depth. A statistical study using a cumulative distribution function fit and Gaussian simulated distributions, exhibits that H for each phase can be extracted when the indentation depth is much lower than the size of the secondary phases. It is found that the thermal treatment produces a hardness increase, due to the partly re-dissolution of the inclusions (mainly Pb and Sn) in the matrix.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Esparducer, M.A. Fernandez, M. Segarra, J.M. Chimenos, and F. Espiell, Characterization of Fire-Refined Copper Recycled from Scrap, J. Mater. Sci., 1999, 34, p 4239–4244
http://www.lfl.es/esp/default.asp. Accessed on 27 Dec 2012
http://www.copper.org/. Accessed on 27 Dec 2012
M. Martínez, A.I. Fernández, M. Segarra, H. Xuriguera, F. Espiell, and N. Ferrer, Comparative Study of Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Fire-Refined and Electrolytically Refined Cold-Drawn Copper Wires, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 7745–7749
L.E. Murr, Correlating Impact Related Residual Microstructures Through 2D Computer Simulations and Microindentation Hardness Mapping: Review, Mat. Sci. Technol., 2012, 28, p 1108–1126
Armstrong, R.W., Elban, W.L., and Walley, S.M. Elastic, Plastic, Cracking Aspects of the Hardness of Materials. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B., 2013, 27(8), p 1330004 (79 pp). doi:10.1142/S0217979213300041
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix, A Method for Interpreting the Data from Depth-Sensing Indentation Instruments, J. Mater. Res., 1986, 1, p 601–609
G.M. Pharr and W.C. Oliver, Measurement of Thin Film Mechanical Properties Using Nanoindentation, MRS Bull., 1992, 17, p 28–33
M.F. Doerner, D.S. Gardner, and W.D. Nix, Plastic Properties of Thin Films on Substrates as Measured by Submicron Indentation Hardness and Substrate Curvatures Techniques, J. Mater. Res., 1986, 1, p 845–851
D. Shuman, A. Costa, and M. Andrade, Calculating the Elastic Modulus from Nanoindentation and Microindentation Reload Curves, Mater. Charact., 2007, 58(4), p 380–389
M. Magnuson, M. Mattesini, C. Li, C. Höglund, M. Beckers, L. Hultman, and O. Eriksson, Bonding Mechanism in the Nitrides Ti2AlN and TiN: An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation, Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 76, p 195127/1–195127/9
K.W. McElhaney, J.J. Vlassak, and W.D. Nix, Determination of Indenter Tip Geometry and Indentation Contact Area for Depth-Sending Indentation Experiments, J. Mater. Res., 1998, 13, p 1300–1306
W.D. Callister, Jr., Introduccion a la Ciencia e Ingenieria de los Materiales, Ed. Reverté S.A, Barcelona, 2005
A. Esparducer, M. Segarra, F. Espiell, M. Garcia, and O. Guixà, Effects of Pre-heating Treatment on the Annealing Behaviour of Cold-Drawn Fire-Refined Coppers, J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36, p 241–245
D.L. Joslin and W.C. Oliver, A New Method for Analyzing Data from Continuous Depth-Sensing Microindentation Tests, J. Mater. Res., 1990, 5, p 123–126
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7, p 1564–1583
A. Esparducer, M. Segarra, F. Espiell, M. Garcia, and O. Guixà, Effects of Pre-heating Treatment on the Annealing Behaviour of Cold-Drawn Fire-Refined Coppers, J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36, p 241–245
J.S. Field and M.V. Swain, A Simple Predictive Model for Spherical Indentation, J. Mater. Res., 1993, 8, p 297–306
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, Review: Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology, J. Mater. Res., 2004, 19, p 3–20
G.M. Pharr, Measurement of Mechanical Properties by Ultra-Low Load Indentation, Mater. Sci. & Eng. A., 1998, 253, p 151–159
J.L. Hay and G.M. Pharr, Instrumented Indentation Testing, ASM Handbook, 2000, 8, p 232–243
S. Suresh, T.G. Nieh, and B.W. Choi, Nano-indentation of Copper Thin Films on Silicon Substrates, Scr. Mater., 1999, 41, p 951–957
A. Gouldstone, H.J. Koh, K.Y. Zeng, A.E. Giannakopoulos, and S. Suresh, Discrete and Continuous Deformation During Nanoindentation of Thin Films, Acta Mater., 2000, 48, p 2277–2295
J. Chen, W. Wang, L.H. Qian, and K. Lu, Critical shear stress for onset of plasticity in a nanocrystalline Cu determined by using nanoindentation. Scr. Mater., 2003, 49, pp. 645-650; 48, pp. 2277-2295
G. Constantinides, F.J. Ulm, and K. Van Vliet, On the use of nanoindentation for cementitious materials, Mater. Struct., 2003, 36, p 191–196
G. Constantinides and F.J. Ulm, The nanogranular nature of C-S-H, J. Mech. Phys. Sol., 2006, 55, p 679–690
G. Constantinides, K.S. Ravi Chandran, F.J. Ulm, and K. Van Vliet, Grid Indentation Analysis of Composite Microstructure and Mechanics: Principles and Validation, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 430, p 189–202
N.X. Randall, M. Vandamme, and F.-J. Ulm, Nanoindentation Analysis as a Two-Dimensional Tool for Mapping The Mechanical Properties of Complex Surfaces, J. Mater. Res., 2009, 24(3), p 679–690
V. Canseco, J.J. Roa, E. Rayón, A.I. Fernandez, and E. Palomo, Mechanical Characterization at Nanometric Scale for Heterogeneous Graphite-Salt Phase Change Materials with a Statistical Approach, Ceram. Inter., 2012, 38(1), p 401–409
F.J. Ulm, M. Vandamme, C. Bobko, J. Alberto Ortega, K. Tai, and C. Ortiz, Statistical Indentation Techniques for Hydrated Nanocomposites: Concrete, Bone, and Shale, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90, p 2677–2692
Y. Zhang, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu, Mechanical Properties and Rolling Behaviours of Nano-Grained Copper with Embedded Nano-twin Bundles, Acta Mater., 2008, 56, p 2429–2440
Acknowledgments
The corresponding authors would like to thank La Farga Lacambra Group for the materials supplied. Furthermore, the authors would like to thank the Linguistic Services at the University of Barcelona for linguistic and stylistic advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roa, J.J., Martínez, M., Rayón, E. et al. Hardness of FRHC-Cu Determined by Statistical Analysis. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 637–642 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0770-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0770-1