Abstract
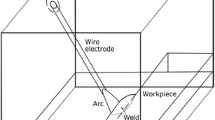
A numerical model of the welding arc is coupled to a model for the heat transfer and fluid flow in the weld pool of a SUS304 stainless steel during a moving GTA welding process. The described model avoids the use of the assumption of the empirical Gaussian boundary conditions, and at the same time, provides reliable boundary conditions to analyze the weld pool. Based on the two-dimensional axisymmetric numerical modeling of the argon arc, the heat flux to workpiece, the input current density, and the plasma drag stress are obtained. The arc temperature contours, the distributions of heat flux, and current density at the anode are in fair agreement with the reported experimental results. Numerical simulation and experimental studies to the weld pool development are carried out for a moving GTA welding on SUS304 stainless steel with different oxygen content from 30 to 220 ppm. The calculated result show that the oxygen can change the Marangoni convection from outward to inward direction on the liquid pool surface and make the wide shallow weld shape become narrow deep one. The calculated result for the weld shape and weld D/W ratio agrees well with the experimental one.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Gurevich and V.N. Zamkov, Nekotorye Osovennosti Svarki Titana Neplaviachinsia Zlektrodom S Primeneniem Flynsov, Avtom. Svarka, 1966, 12, p 13–16
M.M. Savitskii and G.I. Leskov, Mechanizm Vliyamia Dzlektrootrida Tepvnykh Zpementov Na Proplavlauchyu Sposovnosti Luqi S Voliframoym Katodm, Avtom. Svarka, 1980, 9, p 17–22
W. Lucas and D.S. Howse, Activating Flux-Increasing the Performance and Productivity of the TIG and Plasma Processes, Weld. Metal Fabr., 1996, 64, p 11–17
D.S. Howse and W. Lucas, Investigation into Arc Constriction by Active Fluxes for Tungsten Inert Gas Welding, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2000, 5, p 189–193
D. Fan, R.H. Zhang, Y.F. Gu, and M. Ushio, Effect of Flux on A-TIG Welding of Mild Steel, Trans. JWRI, 2001, 30, p 35–40
C.R. Heiple and J.R. Roper, Mechanism for Minor Effect on GTA Fusion Zone Geometry, Weld. J., 1982, 61, p 97s–102s
C.R. Heiple and J.R. Roper, Surface Active Element Effects on the Shape of GTA, Laser, and Electron Beam Welds, Weld. J., 1983, 62, p 72s–77s
M. Tanaka, T. Shimizu, H. Terasaki, M. Ushio, F. Koshi-ishi, and C.L. Yang, Effects of Activating Flux on Arc Phenomena in Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2000, 6, p 397–402
P.J. Modenesi, E.R. Apolinario, and I.M. Pereira, TIG Welding with Single Component Fluxes, J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 2000, 99, p 260–265
S.P. Lu, H. Fujii, H. Sugiyama, M. Tanaka, and K. Nogi, Weld Penetration and Marangoni Convection with Oxide Fluxes in GTA Welding, Mater. Trans., 2002, 43, p 2926–2931
J.J. Lowke, M. Tanaka, and M. Ushio, Insulation Effects of Flux Layer in Producing Greater Weld Depth, Proc. 57th Ann. Assembly Int. Inst. Weld., July 2004 (Osaka, Japan), International Institute of Welding, IIW Doc. 212-1053-04
G.M. Oreper and J. Szekely, A Comprehensive Representation of Transient Weldpool Development in Spot Welding Operations, Metall. Trans. A, 1987, 18, p 1325–1332
T. Zacharia, S.A. David, J.M. Vitek, and T. Debroy, Weld Pool Development During GTA and Laser Beam Welding of Type 304 Stainless Steel, Part I. Theoretical Analysis, Weld. J., 1989, 68, p 499s–509s
T. Zacharia, S.A. David, J.M. Vitek, and T. Debroy, Weld Pool Development During GTA and Laser Welding of Type 304 Stainless Steel, Part II. Experimental Correlation, Weld. J., 1989, 68, p 510s–519s
Y. Wang, Q. Shi, and H.L. Tsai, Modeling of the Effects of Surface-Active Elements on Flow Patterns and Weld Penetration, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, 32, p 145–161
R.H. Zhang and D. Fan, Effects of Activating Flux on Flow Patterns and Weld Penetration in ATIG Welding, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2007, 12(1), p 15–23
W.C. Dong, S.P. Lu, D.Z. Li, and Y.Y. Li, Numerical Simulation of Effects of the Minor Active-Element Oxygen on the Marangoni Convection and the Weld Shape, Acta Metall. Sin., 2008, 44, p 249–256 (in Chinese)
M. Tanaka, H. Terasaki, M. Ushio, and J.J. Lowke, Numerical Study of a Free-Burning Argon Arc with Anode Melting, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2003, 23(3), p 585–606
M.A. Ramirez, G. Trapaga, and J. McKelliget, A Comparison Between Two Different Numerical Formulations of Welding Arc Simulation, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2003, 11, p 675–695
F. Lago, J.J. Gonzalez, P. Freton, and A. Gleizes, A Numerical Modeling of an Electrode Arc and Its Interaction with the Anode: Part I. The Two-Dimensional Model, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2004, 37, p 883–897
Y.M. Zhang, Z.N. Cao, and R. Kovacevic, Numerical Analysis of Fully Penetrated Weld Pools in GTA Welding, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part C. J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 1996, 210, p 187–195
V.R. Voller, M. Cross, and N.C. Markatos, An Enthalpy Method for Convection Diffusion Phase-Change, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 1987, 24, p 271–284
J.J. Gonzalez, F. Lago, P. Freton, M. Masquere, and X. Franceries, Numerical Modelling of an Electric Arc and Its Interaction with the Anode: Part II. The Three-Dimensional Model-Influence of External Forces on the Arc Column, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2005, 38, p 306–318
J. McKelliget and J. Szekely, Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow in the Welding Arc, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1986, 17, p 1139–1148
C.S. Wu and J.Q. Gao, Analysis of the Heat Flux Distribution at the Anode of a TIG Welding Arc, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2002, 24(3), p 323–327
P. Sahoo, T. DebRoy, and M.J. McNallan, Surface Tension of Binary Metal-Surface Active Solute Systems Under Conditions Relevant to Welding Metallurgy, Metall. Trans. B, 1988, 19, p 483–491
M.I. Boulos, P. Fauchais, and E. Pfender, Thermal Plasmas—Fundamentals and Applications, Vol 1, Plenum, New York, 1994, p 388
D.L. Evans and R.S. Tankin, Measurement of Emission and Absorption of Radiation by an Argon Plasma, Phys. Fluids, 1967, 10(6), p 1137–1144
R.T.C. Choo, J. Szekely, and S.A. David, On the Calculation of the Free Surface Temperature of Gas-Tungsten-Arc Weld Pools from First Principles: Part II. Modeling the Weld Pool and Comparison with Experiments, Metall. Trans. B, 1992, 23, p 371–384
H.G. Fan, H.L. Tsai, and S.J. Na, Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow in a Partially or Fully Penetrated Weld Pool in Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2001, 44, p 417–428
Fluent Inc., FLUENT User’s Manual, Lebanon, NH, 2005
S.V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1980
K.C. Hsu, K. Etemadi, and E. Pfender, Study of the Free-Burning High-Intensity Argon Arc, J. Appl. Phys., 1982, 54(3), p 1293–1301
O.H. Nestor, Heat Intensity and Current Density Distributions at the Anode of High Current, Inert Gas Arcs, J. Appl. Phys., 1962, 33(5), p 1638–1648
S.P. Lu, H. Fujii, H. Sugiyama, M. Tanaka, and K. Nogi, Effects of Oxygen Additions to Argon Shielding Gas on GTA Weld Shape, ISIJ Int., 2003, 43(10), p 1590–1595
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 50874101 and the Science Program of Shenyang City under Grant No. 1071275-0-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, W., Lu, S., Li, D. et al. Modeling of the Weld Shape Development During the Autogenous Welding Process by Coupling Welding Arc with Weld Pool. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 19, 942–950 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9570-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9570-z