Abstract
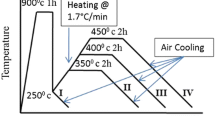
A ductile iron containing 0.6% copper as the main alloying element was austenitized at 850 °C for 120 min and was subsequently austempered for 60 min at austempering temperatures of 270, 330, and 380 °C. The samples were also austempered at 330 °C for austempering times of 30–150 min. The structural parameters for the austempered alloy austenite (Xγ), average carbon content (Cγ), the product XγCγ, and the size of the bainitic ferrite needle (dα) were determined using x-ray diffraction. The effect of austempering temperature and time has been studied with respect to tensile properties such as 0.2% proof stress, ultimate tensile strength (UTS), percentage of elongation, and quality index. These properties have been correlated with the structural parameters of the austempered ductile iron microstructure. Fracture studies have been carried out on the tensile fracture surfaces of the austempered ductile iron (ADI).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.L. Hayrynen, D.J. Moore, and K.B. Eundan, Tensile and Fatigue Properties of Relatively Pure ADI, Trans. AFS, Vol 100, 1992, p 93–104
T.N. Rouns, D.J. Moore, and K.B. Eundan, On the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Ductile Iron, Trans. AFS, Vol 92, 1984, p 815–840
D.J. Moore, T.N. Rouns, and K.B. Eundan, The Relationship Between Microstructure and Tensile Properties in ADI, Trans. AFS, Vol 95, 1987, p 765–774
D. Krishnaraj, H.N.L. Narasimhan, and S. Seshan, Structure and Properties of ADI as Affected by Low Alloy Additions, Trans. AFS, Vol 100, 1992, p 105–112
A.S. Hamid Ali, K.I. Uzlov, N. Darwish, and R. Elliot, Austempering of Low Manganese Ductile Irons: Part 4. Relationship Between Mechanical Properties and Microstructure, Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol 10, 1994, p 35–40
K.D. Mills, Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron: Its Development and Future, Br. Foundryman, Vol 65, 1972, p 34
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, Addison Wesley Publishing Company, 1956, p 390–396
U. Batra, S. Ray, and S.R. Prabhakar, Austempering and Austempered Ductile Iron Microstructure in Copper Alloyed Ductile Iron, J. Mater. Eng. Perf., Vol 12 (No. 4), 2003, p 426–429
K.L. Hayrynen, D.J. Moore, and K.B. Eundan, Tensile Properties and Microstructure of a Clean ADI, Trans. AFS, Vol 98, 1990, p 471–476
Ductile Iron Data for Design Engineers, QIT-Fer et Titane and Miller & Company, Montreal, Quebec, Canada 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batra, U., Ray, S. & Prabhakar, S.R. Tensile properties of copper alloyed austempered ductile iron: Effect of austempering parameters. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 13, 537–541 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-004-0001-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-004-0001-x