Abstract
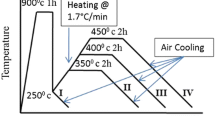
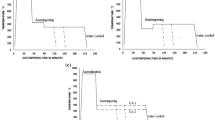
Austempered ductile iron is a heat treated form of as-cast ductile iron. The heat treatment process-austempering, was developed with the intent of improving the strength and toughness of ferrous alloys. It offers a range of mechanical properties superior to those of other cast iron, and shows excellent economic competitiveness with steels and aluminum alloys. The main aim is to analyze the mechanical properties and microstructural characteristics of as-cast ductile iron austenitized at 900 °C for 90 min and afterward austempered over a range of temperatures to obtain distinctive microstructures. The samples were austempered for durations of 60, 90 and 180 min at each austempering temperature of 340, 360, 380, and 400 °C. The influence of these austempering temperatures and times on the microstructure and tensile properties were investigated at room temperature.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walton C F, Iron Casting Handbook, Iron Casting Society Inc., New York (1981) p 323.
Loper C R Jr., Foundry Manage Technol 11 (1994) 32.
Jenkins L R, and Forrest R D, Ductile Iron properties and selection: Irons and steels. ASM metals handbook, Vol. 1, 10th ed., ASM International, Metals Park, (1990) p 33.
Elliott R, Cast Iron Technology, Butterworths, London (1988), p 13.
Labrecque C, and Gagne M, Can Metall Q 37 (1998) 343.
Moore D J, Rouns T N, and Rundman K B, AFS Trans 93 (1985) 705.
Rouns T N, Rundman K B, and Moore D M, AFS Trans 92 (1984) 815.
Gundlach R B, and Janowak J F, Proc. 2nd international conference on ADI, Ann Arbor: ASME, Gear Research Institute: Naperville, (1986) p 23.
Shah S M, and Verhoeven J D, Wear 113 (1986) 267.
Bartosiewicz L, Krause A R, Alberts F A, Singh I, and Puttunda S K, Mater Charact 30 (1993) 221.
Hayrynen K L, The Production of Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI), 2002 world Conference on ADI. (2002)
ASTM E-8, Annual book of ASTM standards, ASTM, 3.01 (1992) 542.
Anita Bisht, Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Nodular iron, M.Tech Thesis, http://ethesis.nitrkl.ac.in/1501/1/motu-thesis.pdf, Rourkela odisha (2009).
Ductile iron data for design engineers, Ductile iron society (DIS), Rio Tinto Iron & Titanium, Inc, Montreal (1990). http://www.ductile.org/didata/
Rao P P, and Putatunda S K, Metall Mater Trans A, 28 (1997) 1457.
Adel Nofal, J Metall Eng (ME) 2 (2013).
Harding R A, “Control of the retained austenite content of ADI,” in AFS Inc., 1991 world conference on Austempered ductile iron, Bloomingdale, Chicago p 22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K.M., Hariharan, P., Venkateshwaran, P. et al. Examination of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) As Per Austempering Temperature and Time. Trans Indian Inst Met 68 (Suppl 1), 67–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0608-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0608-7