Abstract
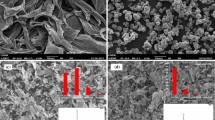
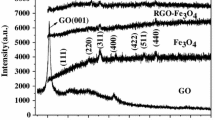
FeCoV alloy/graphene oxide (GO)/coupling agent composites were prepared by the ball-milling method. The microstructure and phase of the composites were detected by scanning electron microscope and x-ray diffraction. The electromagnetic parameters were characterized by the Agilent vector network analyzer in the frequency range of 1–18 GHz. The value of the minimum reflection loss (RLmin) for the FeCoV alloy/GO/coupling agent composites can reach − 17.1 dB at 2.8 GHz with a thickness of 2 mm, accompanied by a bandwidth (<− 10 dB) of 0.8 GHz. The impedance matching properties of the composites were greatly improved by the addition of the coupling agent. The superior absorption properties for the FeCoV/GO/coupling agent composites can be used widely as microwave absorption materials in the S band.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
P. Liu, T. Gao, W. He, and P. Liu, Electrospinning of hierarchical carbon fibers with multi-dimensional magnetic configurations toward prominent microwave absorption. Carbon 202, 244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.10.089.
H. Wu, G. Xie, Y. Zhu, N. Xie, and J. Chen, Improving impedance matching of flaky carbonyl iron based on the surface modification by binary coupling agents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 12 (2021).
L. Liang, Q. Li, X. Yan, Y. Feng, Y. Wang, H.B. Zhang, X. Zhou, C. Liu, C. Shen, and X. Xie, Multifunctional magnetic Ti 3 C 2 T x MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Nano 15, 4 (2021).
X. Liu, Y. Huang, L. Ding, X. Zhao, P. Liu, and T. Li, Synthesis of covalently bonded reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 72, 93 (2021).
B. Chen, D. Chen, Z. Kang, and Y. Zhang, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of Ni–Co nanoferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 618, 222 (2015).
Z. Yan, J. Cai, Y. Xu, and D. Zhang, Microwave absorption property of the diatomite coated by Fe-CoNiP films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 346, 77 (2015).
Y. Zhou, W. Zhou, R. Li, Y. Mu, and Y. Qing, Enhanced antioxidation and electromagnetic properties of Co-coated flaky carbonyl iron particles prepared by electroless plating. J. Alloys Compd. 637, 10 (2015).
Y. Zhai, D. Zhu, W. Zhou, D. Min, and F. Luo, Enhanced impedance matching and microwave absorption properties of the MAMs by using ball-milled flaky carbonyl iron-BaFe12O19 as compound absorbent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 467, 82 (2018).
P. Liu, Z. Yao, J. Zhou, Z. Yang, and L.B. Kong, Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C. 4, 41 (2016).
B. Wang, Q. Wu, Y. Fu, and T. Liu, A review on carbon/magnetic metal composites for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 86, 91 (2021).
C. Wang, V. Murugadoss, J. Kong, Z. He, X. Mai, Q. Shao, Y. Chen, L. Guo, C. Liu, S. Angaiah, and Z. Guo, Overview of carbon nanostructures and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding. Carbon 140, 696 (2018).
W.Q. Cao, X.X. Wang, J. Yuan, W.Z. Wang, and M.S. Cao, Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 38 (2015).
M. Lv, B. Zhou, Y. Liu, B. Ya, H. Jia, and X. Zhang, Study on electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of nanocrystalline Fe81.5Si3B9P3C1Cu1Ti1.5/Graphene oxide composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 575, 170704 (2023).
X. Chen, Y. Wu, W. Gu, M. Zhou, S. Tang, J. Cao, Z. Zou, and G. Ji, Research progress on nanostructure design and composition regulation of carbon spheres for the microwave absorption. Carbon 189, 617 (2022).
H. Xiaoyu, X. Guozhi, X. Ningyan, and J. Chen, Fabrication and microwave absorption properties of the flaky carbonyl iron/graphene oxide composite in S band. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 2 (2023).
S. Gao, S.H. Yang, H.Y. Wang, G.S. Wang, and P.G. Yin, Excellent electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of two-dimensional carbon-based nanocomposite supported by transition metal carbides Fe3C. Carbon 162, 438 (2020).
S. Das, G. Chandra Nayak, S.K. Sahu, and R. Oraon, Development of FeCoB/Graphene Oxide based microwave absorbing materials for X-Band region. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 384, 224 (2015).
J. Feng, F. Pu, Z. Li, X. Li, X. Hu, and J. Bai, Interfacial interactions and synergistic effect of CoNi nanocrystals and nitrogen-doped graphene in a composite microwave absorber. Carbon 104, 214 (2016).
H. Wang, D. Zhu, W. Zhou, and F. Luo, Microwave electromagnetic properties of polyimide/carbonyl iron composites. J. Polym. Res. 21, 6 (2014).
X. Guozhi, W. Ping, Y. Liukui, Z. Baoshan, L. Pinghua, and L. Huaixian, The effect of coupling agent on the microwave properties of the melt-spun iron/earth nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 114, 4 (2009).
S. Mallakpour and V. Behranvand, Surface treatment of nano ZnO using 3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-N-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-phthalamic acid as novel coupling agent for the preparation of poly(amide–imide)/ZnO nanocomposites. Colloid Polym. Sci. 292, 9 (2014).
W. Zheng, Z. Yao, X. Zhang, and J. Zhou, Fabrication and properties of structural microwave absorption composites based on VARI process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 8 (2022).
L. Ye, G. Xie, N. Xie, H. Wang, J. Chen, and J. Chen, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of absorbing materials induced by complex coupling agents. IEEE Trans. Magn. 55, 2 (2019).
Z. Cui, G. Ma, M. Wang, C. Luo, Z. Chen, H. Ma, Q. Li, and W. Li, Enhanced microwave absorption for high filler content composite molded from polymer coated flaky carbonyl irons modified by silane coupling agents. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater Sci. Ed. 38, 1 (2023).
J. Pourahmadazar and V. Rafii, Broadband circularly polarised slot antenna array for L- and S band applications. Electron. Lett. 48, 10 (2012).
N. Shao, J. Li, S. Che, J. Zheng, L. Qiao, Y. Ying, J. Yu, and W. Li, L and S band microwave absorption properties of Z-type hexaferrite Ba3Co2Fe24O41 synthesized at low temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 968, 171926 (2023).
C. Zeng, Z. Jia, and W. Zhou, Effect of yttrium on the wave absorption properties of Fe95Si1B2P0.5Cu1.5 alloy powders in the S band and C band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 538, 168250 (2021).
Y. Zhu, G. Xie, H. Wu, N. Xie, X. Huang, and J. Chen, Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of tunable carbonyl iron absorbing materials prepared by self-composite treatment in 2–8 GHz band. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 20 (2022).
B. Zhang, Y. Feng, J. Xiong, Yi. Yang, and Lu. Huaixian, Microwave-absorbing properties of de-aggregated flake-shaped carbonyl-iron particle composites at 2–18 GHz. IEEE Trans. Magn. 42, 7 (2006).
R.B. Yang and W.F. Liang, Microwave properties of high-aspect-ratio carbonyl iron/epoxy absorbers. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 7 (2011).
Z. Zhang, J. Wei, W. Yang, L. Qiao, T. Wang, and F. Li, Effect of shape of Sendust particles on their electromagnetic properties within 0.1–18GHz range. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 406, 20 (2011).
K. Liang, X.J. Qiao, Z.G. Sun, X.D. Guo, L. Wei, and Y. Qu, Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of graphene oxides/ferrite composites. Appl. Phys. A 123, 6 (2017).
K.N. Gusak, N.G. Kozlov, R.D. Sauts, and V.A. Serzhanina, Reaction of benzylidene-2-naphthylamine with the ethyl ester of 3-pyridyl-?-oxopropionic acid. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 32, 6 (1996).
X. Tang, B.Y. Zhao, Q. Tian, and K.A. Hu, Synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of titania-coated barium ferrite composites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 67, 12 (2006).
L.J. Deng, P.H. Zhou, J.L. Xie, and L. Zhang, Characterization and microwave resonance in nanocrystalline FeCoNi flake composite. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 10 (2007).
T. Maeda, S. Sugimoto, T. Kagotani, N. Tezuka, and K. Inomata, Effect of the soft/hard exchange interaction on natural resonance frequency and electromagnetic wave absorption of the rare earth–iron–boron compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 281, 2–3 (2004).
J. Ding, P.G. McCormick, and R. Street, Remanence enhancement in mechanically alloyed isotropic Sm7Fe93-nitride. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 124, 1–2 (1993).
K. Huang, W. Liao, J. Yu, P. Li, and J. Xu, Microwave absorption performance of sandwich-like Ti3C2Tx@BFO composite material in C and X bands. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 584, 171047 (2023).
X. Deng, S. Gao, X. Qi, H. Dai, S. Fu, Q. Ni, and Y. Fu, Scalable 3D textile with hierarchically functionalized pyramidal units using nanostructured polyamide@carbon/Fe3O4 fibers for tunable microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 473, 145040 (2023).
T. Yu, J. Qiu, J. Liao, X. Wang, W. Chen, Y. Cheng, W. Wang, and Y.F. Song, Topological transformation strategy for layered double hydroxide@carbon nanofibers as highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. 867, 159046 (2021).
Y.L. Wang, G.S. Wang, X.J. Zhang, and C. Gao, Porous carbon polyhedrons coupled with bimetallic CoNi alloys for frequency selective wave absorption at ultralow filler loading. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 103, 34 (2022).
Z. Jiao, J. Hu, M. Ma, Y. Liu, J. Zhao, X. Wang, S. Luan, and L. Zhang, One-dimensional core–shell CoC@CoFe/C@PPy composites for high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 650, 2014 (2023).
B. Quan, X. Liang, G. Xu, Y. Cheng, Y. Zhang, W. Liu, G. Ji, and Y. Du, A permittivity regulating strategy to achieve high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with compatibility of impedance matching and energy conservation. New J. Chem. 41, 3 (2017).
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, L. Zhou, and B. Zhang, Core–shell hybrid nanowires with Co nanoparticles wrapped in N-doped porous carbon for lightweight microwave absorption. Dalton Trans. 48, 40 (2019).
D. Xu, S. Yang, P. Chen, Q. Yu, X. Xiong, and J. Wang, Synthesis of magnetic graphene aerogels for microwave absorption by in-situ pyrolysis. Carbon 146, 301 (2019).
S.Y. Zhang, Q.X. Cao, Y.R. Xue, and Y.X. Zhou, Microwave absorption performance of the absorber based on epsilon-Fe3N/epoxy and carbonyl iron/epoxy composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 755 (2015).
G. Sun, B. Dong, M. Cao, B. Wei, and C. Hu, Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe 3 O 4, γ-Fe 2 O 3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem. Mater. 23, 6 (2011).
H.B. Zhao, J.B. Cheng, J.Y. Zhu, and Y.Z. Wang, Ultralight CoNi/rGO aerogels toward excellent microwave absorption at ultrathin thickness. J. Mater. Chem. C. 7, 2 (2019).
X. Jian, B. Wu, Y. Wei, S.X. Dou, X. Wang, W. He, and N. Mahmood, Facile synthesis of Fe 3 O 4 /GCs composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 9 (2016).
D. Ding, Y. Wang, X. Li, R. Qiang, P. Xu, W. Chu, X. Han, and Y. Du, Rational design of core-shell Co@C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 111, 722 (2017).
X.J. Zhang, G.S. Wang, W.Q. Cao, Y.Z. Wei, J.F. Liang, L. Guo, and M.S. Cao, Enhanced microwave absorption property of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)-MnFe2O4 nanocomposites and polyvinylidene fluoride. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 10 (2014).
S. He, G.S. Wang, C. Lu, J. Liu, B. Wen, H. Liu, L. Guo, and M.S. Cao, Enhanced wave absorption of nanocomposites based on the synthesized complex symmetrical CuS nanostructure and poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 15 (2013).
L. Huang, X. Liu, and R. Yu, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of rod-shaped Fe2O3/Fe3O4/MWCNTs composites. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 28, 3 (2018).
X. Qi, Y. Deng, W. Zhong, Y. Yang, C. Qin, C. Au, and Y. Du, Controllable and large-scale synthesis of carbon nanofibers, bamboo-like nanotubes, and chains of nanospheres over Fe/SnO2 and their microwave-absorption properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 2 (2010).
Y. Qin, R. Che, C. Liang, J. Zhang, and Z. Wen, Synthesis of Au and Au–CuO cubic microcages via an in situ sacrificial template approach. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 11 (2011).
S.S. Kim, S.T. Kim, Y.C. Yoon, and K.S. Lee, Magnetic, dielectric, and microwave absorbing properties of iron particles dispersed in rubber matrix in gigahertz frequencies. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10 (2005).
X. Zhao, Z. Zhang, L. Wang, K. Xi, Q. Cao, D. Wang, Y. Yang, and Y. Du, Excellent microwave absorption property of Graphene-coated Fe nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 3, 1 (2013).
J. Yan, Y. Huang, S. Zhou, X. Han, and P. Liu, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of Nanomesh Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) covalently functionalized graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 5 (2019).
R. Shu, Y. Wu, W. Li, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Shi, and M. Zheng, Fabrication of ferroferric oxide–carbon/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites derived from Fe-based metal–organic frameworks for microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 196, 108240 (2020).
B. Huang, J. Yue, Y. Wei, X. Huang, X. Tang, and Z. Du, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of carbon nanofibers functionalized by FeCo coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 483, 98 (2019).
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11974188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by NZ, XC and GX. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Xie, G. & Chen, X. Preparation and Microwave Absorption Properties of FeCoV/GO/Coupling Agent Composites in S Band. J. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11124-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11124-7