Abstract
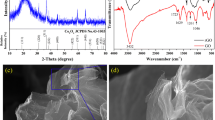
A commercial graphene-amine (CGA) and synthesized selenium nanoparticle (SSeNP) nanocomposite coated on the surface of fluorine-doped tin oxide (SSeNPs–CGA–FTO) substrate was developed by spin coating for H2O2 detection. The CGA–FTO and SSeNPs–CGA–FTO electrochemical sensors were characterized using FESEM with EDAX analysis. FESEM analysis showed nanotube and fluffy morphology of the SSeNPs and CGA, respectively. The developed CGA–FTO and SSeNPs–CGA–FTO electrochemical sensors were used for the sensing of hydrogen peroxide by chronoamperometry (CA) in NaOH (0.1 N) electrolyte. The sensors showed a linear response range from 0.1 mM to 20 mM with sensitivity of 101.7 mA mM−1 cm−2 (R2 = 0.9931) and 137.9 mA mM−1 cm−2 (R2 = 0.9956). The CGA–FTO and SSeNPs–CGA–FTO showed a very low detection limit of 0.1 mM and 0.05 mM, respectively, with a detection response time of less than 1 s. The interference study of the SSeNPs–CGA–FTO-based sensors showed higher selectivity towards H2O2 with interfering agents as compared with CGA–FTO.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Kumar, R.K. Gupta, R.K. Gundampati, D.K. Singh, S. Mohan, S.H. Hasan, and M. Malviya, Enhanced electron transfer mediated detection of hydrogen peroxide using a silver nanoparticle: reduced graphene oxide—polyaniline fabricated electrochemical sensor. RSC Adv. 8, 619 (2018).
Q. Wang, Y. Yun, and J. Zheng, Nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on a polyaniline-single walled carbon nanotubes composite in a room temperature ionic liquid. Microchim. Acta 167, 153 (2009).
M. Ma, Z. Minao, D. Zhang, X. Du, Y. Zhang, and C. Zhang, Highly-ordered perpendicularly immobilized FWCNTs on the thionine monolayer-modified electrode for hydrogen peroxide and glucose sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 64, 477 (2015).
S. Yang, X. Zhang, and H. Mi, Pd nanoparticles supported on functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and electrooxidation for formic acid. J. Power Sources 175, 26 (2008).
Y. Wang and Z. Iqbal, Functionalization of carbon nanotubes with amines and enzymes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 402, 96 (2005).
K.C. Lin, C.Y. Yang, and S.M. Chen, Fabrication of a nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with platinum and silver hybrid composite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 3726 (2014).
C. Xu, Y. Liu, F. Su, A. Liu, and H. Qiu, Nanoporous PtAg and PtCu alloys with hollow ligaments for enhanced electrocatalysis and glucose biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 27, 160 (2011).
S. Liu, B. Yu, F. Li, and Y. Ji, Coaxial electrospinning route to prepare Au-loading SnO2 hollow microtubes for non-enzymatic detection of H2O2. Electrochim. Acta 141, 161 (2014).
N.S. Dumore and M. Mukhopadhyay, Sensitivity enhanced SeNPs-FTO electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 878, 114544 (2020).
J. Wang and Y. Lin, Functionalized carbon nanotubes and nanofibers for biosensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 27, 619 (2008).
M. Zhou, Y. Zhai, and S. Dong, Electrochemical sensing and biosensing platform based on chemically reduced graphene oxide. Anal. Chem. 81, 5603 (2009).
C. Revathi, K. Rajavel, M. Saranya, and R.T.R. Kumar, MWCNT based non-enzymatic H2O2 sensor: influence of amine functionalization on the electrochemical H2O2 sensing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, B627 (2016).
T. Wang, L. Yang, B. Zhang, and J. Liu, Extracellular biosynthesis and transformation of selenium nanoparticles and application in H2O2 biosensor. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 80, 94 (2010).
U. Luesakul, S. Komenek, S. Puthong, and N. Muangsin, Shape-controlled synthesis of cubic-like selenium nanoparticles via the self-assembly method. Carbohydr. Polym. 153, 435 (2016).
N.S. Dumore and M. Mukhopadhyay, Antioxidant properties of aqueous selenium nanoparticles (ASeNPs) and its catalysts activity for 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl ( DPPH ) reduction. J. Mol. Struct. 1205, 127637 (2020).
W. Chen, Y. Li, S. Yang, L. Yue, Q. Jiang, and W. Xia, Synthesis and antioxidant properties of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 132, 574 (2015).
X. Jia, Q. Liu, S. Zou, X. Xu, and L. Zhang, Construction of selenium nanoparticles /β-glucan composites for enhancement of the antitumor activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 117, 434 (2015).
K. Kalishwaralal, S. Jeyabharathi, K. Sundar, and A. Muthukumaran, A novel one-pot green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and evaluation of its toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44, 471 (2014).
F. Lamberti, S. Agnoli, L. Brigo, G. Granozzi, M. Giomo, and N. Elvassore, Surface functionalization of fluorine-doped tin oxide samples through electrochemical grafting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 12887 (2013).
C. Lv, W. Di, Z. Liu, K. Zheng, and W. Qin, Luminescent CePO4: Tb colloids for H2O2 and glucose sensing. Analyst 139, 4547 (2014).
Y. Liu, M. Wang, F. Zhao, and Z. Xu, The direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase and glucose biosensor based on carbon nanotubes-chitosan matrix. Biosens. Bioelectron. 21, 984 (2005).
H. Zhao and H. Ju, Multilayer membranes for glucose biosensing via layer-by-layer assembly of multiwall carbon nanotubes and glucose oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 350, 138 (2006).
X. Luo, A.J. Killard, and M.R. Smyth, Reagentless glucose biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on carbon nanotube-modified electrodes. Electroanalysis 18, 1131 (2006).
N.S. Dumore and M. Mukhopadhyay, Electroanalytical performance of non-enzymatical electrochemical sensor based on PtNPs-SeNPs-SnO2NPs@BFTO nanocomposites for the detection of hydrogen peroxide. Electrocatalysis (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-023-00828-9.
M.M. Rahman, A.J.S. Ahammad, J.H. Jin, S.J. Ahn, and J.J. Lee, A comprehensive review of glucose biosensors based on nanostructured metal-oxides. Sensors 10, 4855 (2010).
K.E. Toghill and R.G. Compton, Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: a perspective and an evaluation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 5, 1246 (2010).
A. Ahmad, S. Ullah, A. Khan, W. Ahmad, A.U. Khan, U.A. Khan, A.U. Rahman, and Q. Yuan, Graphene oxide selenium nanorod composite as a stable electrode material for energy storage devices. Appl. Nanosci. (Switzerland) 10, 1243 (2020).
C. Liang, T. Zhai, W. Wang, J. Chen, W. Zhao, X. Lu, and Y. Tong, Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide with enhanced electrochemical performance towards lithium storage. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2, 7214 (2014).
T. Ramanathan, F.T. Fisher, R.S. Ruoff, and L.C. Brinson, Amino-functionalized carbon nanotubes for binding to polymers and biological systems. Chem. Mater. 17, 1290 (2005).
H. Liu, A. Wang, Q. Sun, T. Wang, and H. Zeng, Cu nanoparticles/fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) nanocomposites for photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Catalysts 7, 385 (2017).
Y. Huang, Y.E. Miao, J. Fu, S. Mo, C. Wei, and T. Liu, Perpendicularly oriented few-layer MoSe2 on SnO2 nanotubes for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 3, 16263 (2015).
K. Wang, Q. Liu, X.Y. Wu, Q.M. Guan, and H.N. Li, Graphene enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdS nanocrystal for H2O2 sensing. Talanta 82, 372 (2010).
J. Cai, S. Ding, G. Chen, Y. Sun, and Q. Xie, In situ electrodeposition of mesoporous aligned α-Fe2O3 nanoflakes for highly sensitive nonenzymatic H2O2 sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 456, 302 (2018).
A. Levine, R. Tenhaken, R. Dixon, and C. Lamb, H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 79, 583 (1994).
N.S. Dumore and M. Mukhopadhyay, Development of novel electrochemical sensor based on PtNPs-SeNPs-FTO nanocomposites via electrochemical deposition for detection of hydrogen peroxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10, 107058 (2022).
Y. Li, J. Zhang, J. Xuan, L. Jiang, and J. Zhu, Fabrication of a novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on Se/Pt nanocomposites. Electrochem. Commun. 12, 777 (2010).
K.S.S. Prasad, J.V. Vaghasiya, S.S. Soni, J. Patel, R. Patel, M. Kumari, and F. Jasmani, Microbial selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) and their application as a sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 177, 1386 (2015).
K.J. Huang, D.J. Niu, X. Liu, Z.W. Wu, Y. Fan, Y.F. Chang, and Y.Y. Wu, Direct electrochemistry of catalase at amine-functionalized graphene/gold nanoparticles composite film for hydrogen peroxide sensor. Electrochim. Acta 56, 2947 (2011).
S. Woo, Y.R. Kim, T.D. Chung, Y. Piao, and H. Kim, Synthesis of a graphene-carbon nanotube composite and its electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Electrochim. Acta 59, 509 (2012).
G. Yu, W. Wu, X. Pan, Q. Zhao, X. Wei, and Q. Lu, High sensitive and selective sensing of hydrogen peroxide released from pheochromocytoma cells based on Pt-Au bimetallic nanoparticles electrodeposited on reduced graphene sheets. Sensors 15, 2709 (2015).
P. Chakraborty, S. Dhar, K. Debnath, and S.P. Mondal, Glucose and hydrogen peroxide dual-mode electrochemical sensing using hydrothermally grown CuO nanorods. J. Electroanal. Chem. 833, 213 (2019).
H. Lu, S. Yu, Y. Fan, C. Yang, and D. Xu, Nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide electrochemical sensor based on carbon-coated SnO2 supported Pt nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 101, 106 (2013).
Y. Zhang, X. Wang, Y. Zhu, H. Jiang, X. Bai, and K.-K. Shiu, highly sensitive graphene-Pt nanocomposites amperometric biosensor and its application in living cell H2O2 detection. Anal. Chem. 86, 9459 (2014).
D. Lu, Y. Zhang, S. Lin, L. Wang, and C. Wang, Synthesis of PtAu bimetallic nanoparticles on graphene–carbon nanotube hybrid nanomaterials for nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor. Talanta 112, 111 (2013).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (SAIF), IIT Bombay, Mumbai, Central Research Facility (CRF), IIT Delhi, New Delhi, and Materials Research Centre, MNIT Jaipur, for providing the research facility for the characterization of samples. We also thank the Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India, India, for providing fellowship and the Chemical Engineering Department, SVNIT, Surat, for providing research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NSD: formal analysis, data curation, investigation, methodology, writing- original draft. MM: data curation, conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dumore, N.S., Mukhopadhyay, M. Electroanalytical Study of SSeNPs–CGA–FTO Electrochemical Sensor Towards the Detection of H2O2. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 6800–6814 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10612-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10612-6