Abstract
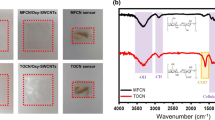
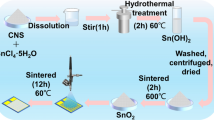
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF), a natural polymer material with a high specific surface area, is a potential candidate for gas sensors. Here, we report Au/SnO2 composites with excellent performance synthesized by a chemical precipitation method based on CNF-assisted synthesis, and a series of Au/SnO2 composites were prepared by adjusting the Au content. The sensitivity of the 1.5 wt.% Au/SnO2 sensor to a low concentration of 1 ppm NO2 was 53, nearly 17 times higher than that of pure SnO2 synthesized by CNF, under ultraviolet (UV) irradiation at a wavelength of 365 nm. The crystal structure of the composite was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), revealing that the composites had high crystallinity and particles reaching the nanoscale. Further experimental data showed that the CNF-assisted synthesis Au/SnO2 sensors had good selectivity, repeatability, and stability. Additionally, the sensor is able to maintain its excellent gas sensing performance even under varying humidity conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.W. Lee, W. Lee, Y. Hong, G. Lee, and D.S. Yoon, Recent advances in carbon material-based NO2 gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 255, 1788 (2018).
W. Yan, Y. Yun, T. Ku, G. Li, and N. Sang, NO2 inhalation promotes Alzheimer’s disease-like progression: cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E2 modulation and monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition-targeted medication. Sci. Rep. 6, 22429 (2016).
P. Zhou, Y. Shen, W. Lu, S. Zhao, T. Li, X. Zhong, B. Cui, D. Wei, and Y. Zhang, Highly selective NO2 chemiresistive gas sensor based on hierarchical In2O3 microflowers grown on clinoptilolite substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 828, 154395 (2020).
C. Copat, A. Cristaldi, M. Fiore, A. Grasso, P. Zuccarello, S.S. Signorelli, G.O. Conti, and M. Ferrante, The role of air pollution (PM and NO2) in COVID-19 spread and lethality: a systematic review. Environ. Res. 191, 110129 (2020).
J. Li, M. Yang, X. Cheng, X. Zhang, C. Guo, Y. Xu, S. Gao, Z. Major, H. Zhao, and L. Huo, Fast detection of NO2 by porous SnO2 nanotoast sensor at low temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 419, 126414 (2021).
S.M. Mali, S.S. Narwade, Y.H. Navale, S.B. Tayade, R.V. Digraskar, V.B. Patil, A.S. Kumbhar, and B.R. Sathe, Heterostructural CuO-ZnO nanocomposites: a highly selective chemical and electrochemical NO2 sensor. ACS Omega 4, 20129 (2019).
L. Čampara, N. Hasanspahić, and S. Vujičić, Overview of MARPOL ANNEX VI regulations for prevention of air pollution from marine diesel engines. SHS Web Conf. 58, 01004 (2018).
Y. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Z. Duan, Y. Wu, Q. Zhao, B. Liu, Q. Huang, Z. Yuan, X. Li, and H. Tai, Edge-enriched MoS2 nanosheets modified porous nanosheet-assembled hierarchical In2O3 microflowers for room temperature detection of NO2 with ultrahigh sensitivity and selectivity. J. Hazard. Mater. 434, 128836 (2022).
Q. Zhao, W. Zhou, M. Zhang, Y. Wang, Z. Duan, C. Tan, B. Liu, F. Ouyang, Z. Yuan, H. Tai, and Y. Jiang, Edge-enriched Mo2TiC2Tx/MoS2 heterostructure with coupling interface for selective NO2 monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2203528 (2022).
Z. Ying, X. He, C. Feng, L. Li, F. Wen, X. Zheng, P. Zheng, and G. Wang, Phenylalanine dipeptide-regulated Ag/In2O3 nanocomposites for enhanced NO2 gas sensing at room temperature with UV illumination. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 13018 (2021).
J.D. Prades, R. JimenezDiaz, F. HernandezRamirez, S. Barth, A. Cirera, A. RomanoRodriguez, S. Mathur, and J.R. Morante, Equivalence between thermal and room temperature UV light-modulated responses of gas sensors based on individual SnO2 nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 140, 337 (2009).
E. Espid and F. Taghipour, UV-LED photo-activated chemical gas sensors: a review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 42, 416 (2017).
A. Dey, Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 206 (2018).
M. Balci Leinen, D. Dede, M.U. Khan, M. Çaǧlayan, Y. Koçak, H.V. Demir, and E. Ozensoy, CdTe quantum dot-functionalized P25 titania composite with enhanced photocatalytic NO2 storage selectivity under UV and Vis irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 865 (2019).
Z. Yuan, Q. Zhao, Z. Duan, C. Xie, X. Duan, S. Li, Z. Ye, Y. Jiang, and H. Tai, Ag2Te nanowires for humidity-resistant trace-level NO2 detection at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 363, 131790 (2022).
E. Wu, Y. Xie, B. Yuan, H. Zhang, X. Hu, J. Liu, and D. Zhang, Ultra-sensitive and fully reversible NO2 gas sensing based on p-type MoTe2 under ultraviolet illumination. ACS Sens. 3, 1719 (2018).
Y. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Z. Duan, Q. Huang, Y. Wu, B. Liu, Q. Zhao, S. Wang, Z. Yuan, and H. Tai, Highly sensitive and selective NO2 sensor of alkalized V2CTx MXene driven by interlayer swelling. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 344, 130150 (2021).
J. Liang, W. Li, J. Liu, and M. Hu, Room temperature NO2 Sensing performance of free-standing mesh-structure vanadium dioxide nanorods by a chemical vapour deposition method. J. Alloys Compd. 687, 845 (2016).
A. Giampiccolo, D.M. Tobaldi, S.G. Leonardi, B.J. Murdoch, M.P. Seabra, M.P. Ansell, G. Neri, and R.J. Ball, Sol-gel graphene/TiO2 nanoparticles for the photocatalytic-assisted sensing and abatement of NO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 243, 183 (2019).
D. Klemm, E.D. Cranston, D. Fischer, M. Gama, S.A. Kedzior, D. Kralisch, F. Kramer, T. Kondo, T. Lindström, S. Nietzsche, K. Petzold-Welcke, and F. Rauchfuß, Nanocellulose as a natural source for groundbreaking applications in materials science: today’s state. Mater. Today 21, 720 (2018).
K. Heise, E. Kontturi, Y. Allahverdiyeva, T. Tammelin, M.B. Linder, Nonappa, and O. Ikkala, Nanocellulose: recent fundamental advances and emerging biological and biomimicking applications. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004349 (2021).
T. Abitbol, A. Rivkin, Y. Cao, Y. Nevo, E. Abraham, T. Ben-Shalom, S. Lapidot, and O. Shoseyov, Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 39, 76 (2016).
S. Sulaiman, M.N. Mokhtar, M.N. Naim, A.S. Baharuddin, A. Sulaiman, and A. Review, Potential usage of cellulose nanofibers (CNF) for enzyme immobilization via covalent interactions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 175, 1817 (2015).
J.T. Korhonen, P. Hiekkataipale, J. Malm, M. Karppinen, O. Ikkala, and R.H.A. Ras, Inorganic hollow nanotube aerogels by atomic layer deposition onto native nanocellulose templates. ACS Nano 5, 1967 (2011).
W. Xiao, J. Xu, X. Liu, Q. Hu, and J. Huang, Antibacterial hybrid materials fabricated by nanocoating of microfibril bundles of cellulose substance with titania/chitosan/silver-nanoparticle composite films. J. Mater. Chem. B 1, 3477 (2013).
X. Kou, F. Meng, K. Chen, T. Wang, P. Sun, F. Liu, X. Yan, Y. Sun, F. Liu, K. Shimanoe, and G. Lu, High-performance acetone gas sensor based on Ru-doped SnO2 nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 320, 128292 (2020).
G. Li, Y. Fan, Q. Hu, D. Zhang, Z. Ma, Z. Cheng, X. Wang, and J. Xu, Morphology and size effect of Pd nanocrystals on formaldehyde and hydrogen sensing performance of SnO2 based gas sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 906, 163765 (2022).
B. Bhangare, N.S. Ramgir, S. Jagtap, A.K. Debnath, K.P. Muthe, C. Terashima, D.K. Aswal, S.W. Gosavi, and A. Fujishima, XPS and Kelvin probe studies of SnO2/RGO nanohybrids based NO2 sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 487, 918 (2019).
R. Abdelghani, H. Shokry Hassan, I. Morsi, and A.B. Kashyout, Nano-architecture of highly sensitive SnO2–based gas sensors for acetone and ammonia using molecular imprinting technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 297, 126668 (2019).
H. Huang, C.Y. Ong, J. Guo, T. White, M.S. Tse, and O.K. Tan, Pt surface modification of SnO2 nanorod arrays for CO and H2 sensors. Nanoscale 2, 1203 (2010).
R. Yogamalar, V. Mahendran, R. Srinivasan, A. Beitollahi, R.P. Kumar, A.C. Bose, and A. Vinu, Gas-sensing properties of needle-shaped Ni-doped SnO2 nanocrystals prepared by a Simple sol-gel chemical precipitation method. Chem. Asian J. 5, 2379 (2010).
A. Katoch, J.H. Byun, S.W. Choi, and S.S. Kim, One-pot synthesis of Au-loaded SnO2 nanofibers and their gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 202, 38 (2014).
D. Liu, J. Pan, J. Tang, W. Liu, S. Bai, and R. Luo, Ag decorated SnO2 nanoparticles to enhance formaldehyde sensing properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 124, 36 (2019).
X. He, Z. Ying, X. Zhou, L. Li, F. Wen, X. Zheng, P. Zheng, and G. Wang, A sensitive SO2 gas sensor based on nanocellulose prepared tin dioxide under UV excitation. J. Mater. Sci. 58, 3249 (2023).
S.S. Shendage, V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, S.P. Patil, N.S. Harale, J.L. Bhosale, J.H. Kim, and P.S. Patil, Sensitive and selective NO2 gas sensor based on WO3 nanoplates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 240, 426 (2017).
Y. Tie, S.Y. Ma, S.T. Pei, Q.X. Zhang, K.M. Zhu, R. Zhang, X.H. Xu, T. Han, and W.W. Liu, Pr doped BiFeO3 hollow nanofibers via electrospinning method as a formaldehyde sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 308, 127689 (2020).
Z. Lu, Q. Zhou, L. Xu, Y. Gui, Z. Zhao, C. Tang, and W. Chen, Synthesis and characterization of highly sensitive hydrogen (H2) sensing device based on Ag doped SnO2 nanospheres. Materials (Basel) 11, 492 (2018).
S. Zhang, L. Zhao, B. Huang, and X. Li, Enhanced sensing performance of Au-decorated TiO2 nanospheres with hollow structure for formaldehyde detection at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 358, 131465 (2022).
Z. Niu, P. Zheng, Y. Xiao, C. Luo, K. Zhang, J. Zhang, L. Zheng, Y. Zhang, and W. Bai, Bi0.5K0.5TiO3-based lead-free relaxor ferroelectric with high energy storage performances via the grain size and bandgap engineering. Mater. Today Chem. 24, 100898 (2022).
C. Cui, Y. Pu, and R. Shi, High-energy storage performance in lead-free (0.8–x)SrTiO3-0.2Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-XBaTiO3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 740, 1180 (2018).
L. Guo, Z. Shen, C. Ma, C. Ma, J. Wang, and T. Yuan, Gas sensor based on MOFs-derived Au-loaded SnO2 nanosheets for enhanced acetone detection. J. Alloys Compd. 906, 164375 (2022).
H. Fu, X. Yang, Z. Zhang, W. Wang, X. An, Y. Dong, and X. Li, Preparation of plasmonic porous Au@AgVO3 belt-like nanocomposites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Nanotechnology 29, 295706 (2018).
Z. Ying, T. Zhang, C. Feng, F. Wen, L. Li, and X. Zheng, UV-enhanced NO2 gas sensors based on In2O3/ZnO composite material modified by polypeptides. Nanotechnology 33, 155501 (2022).
G. Li, Z. Sun, D. Zhang, Q. Xu, L. Meng, and Y. Qin, Mechanism of sensitivity enhancement of a ZnO nanofilm gas sensor by UV light illumination. ACS Sens. 4, 1577 (2019).
X. Zhang, J. Sun, K. Tang, H. Wang, T. Chen, K. Jiang, T. Zhou, H. Quan, and R. Guo, Ultralow detection limit and ultrafast response/recovery of the H2 gas sensor based on Pd-doped RGO/ZnO-SnO2 from hydrothermal synthesis. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 8, 67 (2022).
Y. Wang, L. Liu, F. Sun, T. Li, T. Zhang, and S. Qin, Humidity-insensitive NO2 sensors based on SnO2/RGO composites. Front. Chem. 9, 681313 (2021).
M. Ul Haq, Z. Zhang, Z. Wen, S. Khan, S. Ud Din, N. Rahman, and L. Zhu, Humidity sensor based on mesoporous Al-doped NiO ultralong nanowires with enhanced ethanol sensing performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 7121 (2019).
X. Ma, Z. Ying, F. Wen, L. Li, X. Zheng, P. Zheng, and G. Wang, Gas-sensitive properties of ZnO/ZnCo2O4 made from sodium citrate against formaldehyde. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 7009 (2022).
Z. Duan, Y. Jiang, M. Yan, S. Wang, Z. Yuan, Q. Zhao, P. Sun, G. Xie, X. Du, and H. Tai, Facile, flexible, cost-saving, and environment-friendly paper-based humidity sensor for multifunctional applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 21840 (2019).
W. Li, X. Zhang, and X. Guo, Electrospun Ni-doped SnO2 nanofiber array for selective sensing of NO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 244, 509 (2017).
H.-S. Jeong, M.-J. Park, S.-H. Kwon, H.-J. Joo, S.-H. Song, and H.-I. Kwon, Low temperature NO2 sensing properties of RF-sputtered SnO-SnO2 heterojunction thin-film with p-type semiconducting behavior. Ceram. Int. 44, 17283 (2018).
S. Bai, D. Li, D. Han, R. Luo, A. Chen, and C.L. Chung, Preparation, characterization of WO3-SnO2 nanocomposites and their sensing properties for NO2,. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 150, 749 (2010).
H. Zhang, L. Wang, and T. Zhang, Reduced graphite Oxide/SnO2/Au hybrid nanomaterials for NO2 sensing Performance at relatively low operating temperature. RSC Adv. 4, 57436 (2014).
H.W. Kim, H.G. Na, Y.J. Kwon, S.Y. Kang, M.S. Choi, J.H. Bang, P. Wu, and S.S. Kim, Microwave-assisted synthesis of graphene-SnO2 nanocomposites and their applications in gas sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 31667 (2017).
M. Modak and S. Jagtap, Low temperature operated highly sensitive, selective and stable NO2 gas sensors using N-doped SnO2-RGO nanohybrids. Ceram. Int. 48, 19978 (2022).
L. Zhou, Z. Hu, H.-Y. Li, J. Liu, Y. Zeng, J. Wang, Y. Huang, L. Miao, G. Zhang, Y. Huang, J. Jiang, S. Jiang, and H. Liu, Template-free construction of tin oxide porous hollow microspheres for room-temperature gas sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 25111 (2021).
F.H. Saboor, T. Ueda, K. Kamada, T. Hyodo, Y. Mortazavi, A.A. Khodadadi, and Y. Shimizu, Enhanced NO2 gas sensing performance of bare and Pd-loaded SnO2 thick film sensors under UV-light irradiation at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 223, 429 (2016).
N.M. Hung, C.M. Hung, N. Van Duy, N.D. Hoa, H.S. Hong, T.K. Dang, N.N. Viet, L.V. Thong, P.H. Phuoc, and N. Van Hieu, Significantly enhanced NO2 gas-sensing performance of nanojunction-networked SnO2 nanowires by pulsed UV-radiation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 327, 112759 (2021).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province [Grant No. 2019C04003].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Ying, Z., He, X. et al. Enhanced Sensing Performance of Au-decorated Cellulose Nanofiber-SnO2 for NO2 Detection Under UV Light. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 5964–5974 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10531-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10531-6