Abstract
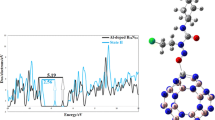
We investigated the potential application of Al24N24 nanocage (AlN-NC) as a drug delivery system for the anticancer drug cisplatin (CP) through density functional theory computations. Results indicate that CP drug very weakly interacts with the AlN-NC with the adsorption energy (AD-E) of around − 6.8 kcal/mol. This makes the AlN-NC inappropriate for the drug delivery. To overcome this problem, the AlN-NC has been decorated with Si impurity atoms. Decoration of the Si into the structure of the AlN-NC increased the AD-E of CP to − 33.4 kcal/mol. Based on the analysis of the partial density of states, the Si atom considerably contributed to the generation of the virtual orbitals of the Si-decorated AlN-NC (Si@AlN-NC), which showed that this atom was suitable for nucleophilic attack compared to the Al atoms. Finally, the adsorption performance and capacity of CP increased after decorating the Si, which made the AlN-NC more suitable for drug delivery. A mechanism of drug release was introduced into the cancerous tissues, which showed that, in cancerous cells with low pH, CP was significantly protonated, which led to the separation of CP from the surface of the Si@AlN-NC. The reaction nature of CP with the AlN-NC changed from covalent bonding in the natural environment to H-bonding in the acidic cancer cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ferrari, Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 5, 161–171 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1566.
J. Zhang, D.S. Thomas, M.S. Davies, S.J. Berners-Price, and N. Farrell, Effects of geometric isomerism in dinuclear platinum antitumor complexes on aquation reactions in the presence of perchlorate, acetate and phosphate. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 10, 652–666 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-005-0013-5.
E.L. Beard Jr., The american society of health system pharmacists. JONAS Healthc. Law Ethics Regul. 3, 78–79 (2001).
X. Duan, C. He, S.J. Kron, and W. Lin, Nanoparticle formulations of cisplatin for cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 8, 776–791 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1390.
S. Dasari and P. Bernard Tchounwou, Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 740, 364–378 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025.
R.-D. Kortmann, B. Timmermann, R.E. Taylor, G. Scarzello, L. Plasswilm, F. Paulsen, B. Jeremic, A.K. Gnekow, K. Dieckmann, S. Kay, and M. Bamberg, Current and future strategies in radiotherapy of childhood low-grade glioma of the brain. Strahlenther. Onkol. 179, 509–520 (2003).
L. Kong and G. Liu, Synchrotron-based infrared microspectroscopy under high pressure: An introduction. Matter Rad. Extrem. 6, 068202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0071856.
R.A. Alderden, M.D. Hall, and T.W. Hambley, The discovery and development of cisplatin. J. Chem. Educ. 83, 728–734 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/ed083p728.
F.H. Kasten, F.F. Strasser, and M. Turner, Inhibition of cell division in Escherichia coli by electrolysis products from a platinum electrode. Nature 207, 161–164 (1965).
R. Oun, Y.E. Moussa, and N.J. Wheate, The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: a review for chemists. Dalton Trans. 47, 6645–6653 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8dt00838h.
X. Wang, C. Li, Y. Zhang, H.M. Ali, S. Sharma, R. Li, M. Yang, Z. Said, and X. Liu, Tribology of enhanced turning using biolubricants: a comparative assessment. Tribol. Inter. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107766.
R. Langer, New methods of drug delivery. Science 249, 1527–1533 (1990).
R.S. Shawgo, A.C.R. Grayson, Y. Li, and M.J. Cima, BioMEMS for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 6, 329–334 (2002).
M.H. Smolensky and N.A. Peppas, Chronobiology, drug delivery, and chronotherapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 828–851 (2007).
S. Liu, B. Yang, Y. Wang, J. Tian, L. Yin, and W. Zheng, 2D/3D multimode medical image registration based on normalized cross-correlation. Appl. Sci. 12, 2828 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062828.
O. Pillai and R. Panchagnula, Polymers in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 447–451 (2001).
D. Arcos and M. Vallet-Regi, Bioceramics for drug delivery. Acta Mater. 61, 890–911 (2013).
C. Peetla, S. Vijayaraghavalu, and V. Labhasetwar, Biophysics of cell membrane lipids in cancer drug resistance: implications for drug transport and drug delivery with nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 65, 1686–1698 (2013).
S. Hossen, M.K. Hossain, M. Basher, M. Mia, M. Rahman, and M.J. Uddin, Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: a review. J. Adv. Res. 15, 1–18 (2019).
P.P. Karmali and D. Simberg, Interactions of nanoparticles with plasma proteins: implication on clearance and toxicity of drug delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 8, 343–357 (2011).
Y. Dang and J. Guan, Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Smart Mater. Med. 1, 10–19 (2020).
W. Xu, C. Li, Y. Zhang, H.M. Ali, S. Sharma, R. Li, M. Yang, T. Gao, M. Liu, and X. Wang, Electrostatic atomization minimum quantity lubrication machining: from mechanism to application. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-7990/ac9652.
R. Li, Z. Du, X. Qian, Y. Li, J.-C. Martinez-Camarillo, L. Jiang, M.S. Humayun, Z. Chen, and Q. Zhou, High resolution optical coherence elastography of retina under prosthetic electrode. Quant. Image Med. Surg. 11, 918 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-1137.
H. Xu, Q. Wang, G. Fan, and X. Chu, Theoretical study of boron nitride nanotubes as drug delivery vehicles of some anticancer drugs. Theor. Chem. Acc. 137, 1–15 (2018).
A. Bianco, K. Kostarelos, and M. Prato, Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 9, 674–679 (2005).
Z. Liu, K. Chen, C. Davis, S. Sherlock, Q. Cao, X. Chen, and H. Dai, Drug delivery with carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer treatment. Can. Res. 68, 6652–6660 (2008).
J. Dobson, Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Drug Dev. Res. 67, 55–60 (2006).
M. Arruebo, R. Fernández-Pacheco, M.R. Ibarra, and J. Santamaría, Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2, 22–32 (2007).
M. Kumar and K. Raza, C60-fullerenes as drug delivery carriers for anticancer agents: promises and hurdles. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 5, 169–179 (2017).
F. Kamali, G. Ebrahimzadeh Rajaei, S. Mohajeri, A. Shamel, and M. Khodadadi-Moghaddam, Adsorption behavior of metformin drug on the C60 and C48 nanoclusters: a comparative DFT study. Monatshefte für Chemie-Chem. Mon. 151, 711–720 (2020).
R. Li, X. Qian, C. Gong, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, B. Xu, M.S. Humayun, and Q. Zhou, Simultaneous assessment of the whole eye biomechanics using ultrasonic elastography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2022.3215498.
E. Golipour-Chobar, F. Salimi, and G. Ebrahimzadeh-Rajaei, Sensing of lomustine drug by pure and doped C48 nanoclusters: DFT calculations. Sensors 9, 17 (2022).
J. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Zhang, M. Yang, D. Jia, G. Liu, Y. Hou, R. Li, N. Zhang, and Q. Wu, Experimental assessment of an environmentally friendly grinding process using nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication with cryogenic air. J. Clean. Prod. 193, 236–248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.009.
X. Wang, C. Li, Y. Zhang, Z. Said, S. Debnath, S. Sharma, M. Yang, and T. Gao, Influence of texture shape and arrangement on nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 119, 631–646 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08235-4.
X. Cui, C. Li, Y. Zhang, Z. Said, S. Debnath, S. Sharma, H.M. Ali, M. Yang, T. Gao, and R. Li, Grindability of titanium alloy using cryogenic nanolubricant minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Process. 80, 273–286 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.06.003.
X. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Zhang, D. Jia, B. Li, Y. Wang, M. Yang, Y. Hou, and X. Zhang, Performances of Al2O3/SiC hybrid nanofluids in minimum-quantity lubrication grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 86, 3427–3441 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8453-3.
Y. Zhang, C. Li, M. Yang, D. Jia, Y. Wang, B. Li, Y. Hou, N. Zhang, and Q. Wu, Experimental evaluation of cooling performance by friction coefficient and specific friction energy in nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication grinding with different types of vegetable oil. J. Clean. Prod. 139, 685–705 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.073.
M. Yang, C. Li, Y. Zhang, D. Jia, R. Li, Y. Hou, H. Cao, and J. Wang, Predictive model for minimum chip thickness and size effect in single diamond grain grinding of zirconia ceramics under different lubricating conditions. Ceram. Int. 45, 14908–14920 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.226.
A.A. Peyghan, and H. Soleymanabadi, Adsorption of H2S at Stone–Wales defects of graphene-like BC3: a computational study. Mol. Phys. 112, 2737–2745 (2014).
X. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. Zhang, and C.S. Lee, A novel aluminum–graphite dual-ion battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502588 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201502588.
M. Wang, C. Jiang, S. Zhang, X. Song, Y. Tang, and H.-M. Cheng, Reversible calcium alloying enables a practical room-temperature rechargeable calcium-ion battery with a high discharge voltage. Nat. Chem. 10, 667–672 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0045-4.
Y. Liang, J. Li, Y. Xue, T. Tan, Z. Jiang, Y. He, W. Shangguan, J. Yang, and Y. Pan, Benzene decomposition by non-thermal plasma: a detailed mechanism study by synchrotron radiation photoionization mass spectrometry and theoretical calculations. J. Hazardous Mater. 420, 126584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126584.
X. Feng, L. Jiang, D. Li, S. Tian, X. Zhu, H. Wang, C. He, and K. Li, Progress and key challenges in catalytic combustion of lean methane. J. Energy Chem. 75, 173–215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2022.08.001.
X.-Y. Li, Y. Song, C.-X. Zhang, C.-X. Zhao, and C. He, Inverse CO2/C2H2 separation in a pillared-layer framework featuring a chlorine-modified channel by quadrupole-moment sieving. Sep. Purif. Technol. 279, 119608 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119608.
Q. Zhong, Y. Chen, B. Zhu, S. Liao, and K. Shi, A temperature field reconstruction method based on acoustic thermometry. Measurement 200, 111642 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111642.
Y. Wei, C. Chen, C. Tan, L. He, Z. Ren, C. Zhang, S. Peng, J. Han, H. Zhou, and J. Wang, High-performance visible to near-infrared broadband Bi2O2Se nanoribbon photodetectors. Adv. Opt. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202201396.
W. Hao and J. Xie, Reducing diffusion-induced stress of bilayer electrode system by introducing pre-strain in lithium-ion battery. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage (2021). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4049238.
Y. Xu, X. Chen, H. Zhang, F. Yang, L. Tong, Y. Yang, D. Yan, A. Yang, M. Yu, and Z. Liu, Online identification of battery model parameters and joint state of charge and state of health estimation using dual particle filter algorithms. Int. J. Energy Res. 46, 19615–19652 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.8541.
E. Mehrjouei, H. Akbarzadeh, A.N. Shamkhali, M. Abbaspour, S. Salemi, and P. Abdi, Delivery of cisplatin anti-cancer drug from carbon, boron nitride, and silicon carbide nanotubes forced by Ag-nanowire: a comprehensive molecular dynamics study. Mol. Pharm. 14, 2273–2284 (2017).
H. Fang, Z. Wang, Q. Chen, and Y. Wang, C@ZnO Self-assembly composite nanostructure with a strong absorption capacity in UV–visible light and its optical properties. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 7263–7269 (2019).
R.G. Mendes, A. Bachmatiuk, B. Büchner, G. Cuniberti, and M.H. Rümmeli, Carbon nanostructures as multi-functional drug delivery platforms. J. Mater. Chem. B 1, 401–428 (2013).
N. Kumar, P. Chamoli, M. Misra, M.K. Manoj, and A. Sharma, Advanced metal and carbon nanostructures for medical, drug delivery and bio-imaging applications. Nanoscale 14, 3987–4017 (2022).
G.A. Hughes, Nanostructure-mediated drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 1, 22–30 (2005).
S. Sayhan, and A. Kinal, Computational investigation and comparison of hydrogen storage properties of B24N24 and Al24N24 nanocages. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42, 14166–14180 (2017).
M.M.R. Nayini, H. Sayadian, N. Razavipour, and M. Rezazade, Chemical-sensing of Amphetamine drug by inorganic AlN nanocage: a DFT/TDDFT study. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 121, 108237 (2020).
Y. Yang, Y. Zhao, M. Xing, C. Tian, and F. Ahmadi Peyghan, Effects of Ag-decoration on the adsorption and detection of toxic OF2 gas on a GaN nanotube. Mol. Simulation 48, 1426–1434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/08927022.2022.2095375.
Z. Al-Sawaff, S. Dalgic, and F. Kandemirli, Theoretical study of the adsorption of BMSF-BENZ drug for osteoporosis disease treatment on Al-doped carbon nanotubes (Al-CNT) as a drug delivery vehicle. Eur. J. Chem. 12, 314–322 (2021).
L. Zhao, M.-H. Chai, H.-F. Yao, Y.-P. Huang, and Z.-S. Liu, Molecularly imprinted polymers doped with carbon nanotube with aid of metal-organic gel for drug delivery systems. Pharm. Res. 37, 1–14 (2020).
S. Mu, Q. Liu, P. Kidkhunthod, X. Zhou, W. Wang, and Y. Tang, Molecular grafting towards high-fraction active nanodots implanted in N-doped carbon for sodium dual-ion batteries. Natl. Sci. Rev. 8, 178 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa178.
X. Feng, L. Xia, Z. Jiang, M. Tian, S. Zhang, and C. He, Dramatically promoted toluene destruction over Mn@ Na-Al2O3@ Al monolithic catalysts by Ce incorporation: Oxygen vacancy construction and reaction mechanism. Fuel 326, 125051 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125051.
Z. Zhang, F. Yang, H. Zhang, T. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. Xu, and Q. Ma, Influence of CeO2 addition on forming quality and microstructure of TiCx-reinforced CrTi4-based laser cladding composite coating. Mater. Charact. 171, 110732 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110732.
C. Wang, L. Sheng, M. Jiang, X. Lin, Q. Wang, M. Guo, G. Wang, X. Zhou, X. Zhang, and J. Shi, Flexible SnSe2/N-doped porous carbon-fiber film as anode for high-energy-density and stable sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 555, 232405 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232405.
T. Gao, Y. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Wang, Y. Chen, Q. An, S. Zhang, H.N. Li, H. Cao, and H.M. Ali, Fiber-reinforced composites in milling and grinding: machining bottlenecks and advanced strategies. Front. Mech. Eng. 17, 1–35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-022-0680-8.
S. Grimme, Accurate description of van der Waals complexes by density functional theory including empirical corrections. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1463–1473 (2004).
M.W. Schmidt, K.K. Baldridge, J.A. Boatz, S.T. Elbert, M.S. Gordon, J.H. Jensen, S. Koseki, N. Matsunaga, K.A. Nguyen, S. Su, T.L. Windus, M. Dupuis, and J.A. Montgomery, J. Comp. Chem. 14, 1347–1363 (1993).
Y. Yang, M.N. Weaver, and K.M. Merz Jr., Assessment of the “6-31+ G**+ LANL2DZ” mixed basis set coupled with density functional theory methods and the effective core potential: prediction of heats of formation and ionization potentials for first-row-transition-metal complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 113, 9843–9851 (2009).
N. O’Boyle, A. Tenderholt, and K. Langner, Cclib: a library for package-independent computational chemistry algorithms. J. Comput. Chem. 29, 839–845 (2008).
J. Beheshtian, A.A. Peyghan, M.B. Tabar, and Z. Bagheri, DFT study on the functionalization of a BN nanotube with sulfamide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 266, 182–187 (2013).
M. Noei and A.A. Peyghan, A DFT study on the sensing behavior of a BC2N nanotube toward formaldehyde. J. Mol. Model. 19, 3843–3850 (2013).
H. Li, Y. Zhang, C. Li, Z. Zhou, X. Nie, Y. Chen, H. Cao, B. Liu, N. Zhang, and Z. Said, Cutting fluid corrosion inhibitors from inorganic to organic: progress and applications. Korean J. Chem. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-1057-0.
S.F. Boys and F. Bernardi, The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 19, 553–566 (1970).
B. Mennucci, J. Tomasi, R. Cammi, J. Cheeseman, M. Frisch, F. Devlin, S. Gabriel, and P. Stephens, Polarizable continuum model (PCM) calculations of solvent effects on optical rotations of chiral molecules. J. Phys. Chem. A 106, 6102–6113 (2002).
I. Parolini, C. Federici, C. Raggi, L. Lugini, S. Palleschi, A. De Milito, C. Coscia, E. Iessi, M. Logozzi, and A. Molinari, Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 34211–34222 (2009).
A.J. Thistlethwaite, D.B. Leeper, D.J. Moylan, and R.E. Nerlinger, pH distribution in human tumors. Int. J. Rad. Oncol*. Biol*. Phys. 11, 1647–1652 (1985).
J. Shi, Y. Liu, L. Wang, J. Gao, J. Zhang, X. Yu, R. Ma, R. Liu, and Z. Zhang, A tumoral acidic pH-responsive drug delivery system based on a novel photosensitizer (fullerene) for in vitro and in vivo chemo-photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 10, 1280–1291 (2014).
K. Nobusawa, M. Akiyama, A. Ikeda, and M. Naito, pH responsive smart carrier of [60] fullerene with 6-amino-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 22610–22613 (2012).
Funding
The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have participated in (a) conception and design, or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (c) approval of the final version. This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal or other publishing venue.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kadhim, M.M., Taha, A., Abdullaha, S.A. et al. Delivery of Cisplatin Anti-cancer Drug by Si-Decorated Al24N24 Nanocage: DFT Evaluation of Electronic and Structural Features. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 3281–3290 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10289-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10289-x