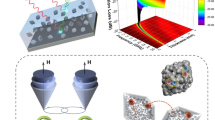
Abstract
The primary aim of the present investigation is to develop a novel method for a magnetic system as high-performance microwave absorbing material, particularly in the K and Ka band (18–42 GHz) frequencies. A simple cost-effective pulsed-DC electrochemical method has been developed to synthesize Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The particle size of the as-synthesized nanoparticles was analyzed by x-ray diffraction and the magnetic properties were verified by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). It was found that a higher wt% of nanoparticles in paraffin wax corresponds to the higher microwave absorbing performance in terms of reflection loss (RL). Moreover, the γ-Fe2O3 (70 wt%) nanoparticles show the maximum RL of − 40.6 dB at 30.2 GHz, whereas the Fe3O4 (70 wt%) nanoparticles show the maximum RL of − 13.5 dB at 42 GHz at an absorber layer thickness of 2 mm. Compared to Fe3O4, the γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles have greater \(\varepsilon^{\prime}\) and \(\varepsilon^{\prime\prime}\) values, which can be ascribed to the improved conductivity and more polarization sites being responsible for their enhanced microwave absorption. The excellent microwave absorption performance of the γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles in the K and Ka bands endows its application in advanced communication systems and stealth technology.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Yu, F. Chi, Y. Sun, J. Guo, and X. Liu, Assembled porous Fe3O4@g-C3N4 hybrid nanocomposites with multiple interface polarization for stable microwave absorption. Ceram. Int. 44, 19207 (2018).
X. Zhang, X. Su, B. Zhang, and J. Wang, Facile synthesis of graphene oxide-wrapped CNFs as high-performance microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 45, 12895 (2019).
Y. Wang, D. Sun, G. Liu, Y. Wang, and W. Jiang, Size-controllable synthesis of Fe3O4 nanospheres for electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 2292 (2015).
P. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Chen, G. Wang, D. Wang, T. Wang, and F. Li, Magnetism and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4 microflake-paraffin composites without and with magnetic orientation. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 721 (2018).
M.A. Aslam, K. Hu, W. Ding, A. Hassan, Y. Bian, K. Qiu, L. Qiangchun, and Z. Sheng, Dimensionality determined microwave absorption properties in ferrite/bio-carbon composites. Ceram. Int. 47, 27496 (2021).
N. Aggarwal and S.B. Narang, Comparison of Ku (12.4–18 GHz) and K (18–26.5 GHz) band microwave absorption characterization of Co-Zr Co-substituted Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 5338 (2021).
T. Liu and S.-S. Kim, Ultrawide bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorbers composed of double-layer frequency selective surfaces with different patterns. Sci. Rep. 8, 13889 (2018).
J. Ning, S. Dong, X. Luo, K. Chen, J. Zhao, T. Jiang, and Y. Feng, Ultra-broadband microwave absorption by ultra-thin metamaterial with stepped structure induced multi-resonances. Results Phys. 18, 103320 (2020).
A. Arora and S.B. Narang, Tuning of microwave absorptive behavior of double substituted barium hexaferrites with change in thickness in 26.5–40.0 GHz band. Appl. Phys. A 123, 520 (2017).
S.B. Narang and K. Pubby, Electromagnetic characterization of Co-Ti-doped Ba-M ferrite-based frequency-tunable microwave absorber in 124–40 GHz. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 30, 511 (2017).
Y. Ge, C. Li, G.I.N. Waterhouse, Z. Zhang, and L. Yu, ZnFe2O4@SiO2@Polypyrrole nanocomposites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties in the K and Ka band regions. Ceram. Int. 47, 1728 (2021).
F. Liu, C. Li, G.I.N. Waterhouse, X. Jiang, Z. Zhang, and L. Yu, Lightweight PVDF/γ-Fe2O3/PANI foam for efficient broadband microwave absorption in the K and Ka bands. J. Alloys Compd. 876, 159983 (2021).
M.S. Saeed, J. Seyed-Yazdi, and S.H. Hekmatara, Surface modification of MWCNT with cluster form of Fe2O3/Fe3O4 NPs for improving their microwave absorption performance. Chem. Phys. Lett. 756, 137823 (2020).
G. Tong, W. Wu, J. Guan, H. Qian, J. Yuan, and W. Li, Synthesis and characterization of nanosized urchin-like α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4: microwave electromagnetic and absorbing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4320 (2011).
S. Wang, Q. Jiao, Q. Shi, H. Zhu, T. Feng, Q. Lu, C. Feng, H. Li, D. Shi, and Y. Zhao, Synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by γ-Fe2O3 nanorings for enhancing microwave absorbing performance. Ceram. Int. 46, 1002 (2020).
L.L. Adebayo, H. Soleimani, N. Yahya, Z. Abbas, F.A. Wahaab, R.T. Ayinla, and H. Ali, Recent advances in the development OF Fe3O4-based microwave absorbing materials. Ceram. Int. 46, 1249 (2020).
A. Feng, Z. Jia, Y. Zhao, and H. Lv, Development of Fe/Fe3O4@C composite with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 745, 547–554 (2018).
G. Wang, Y. Chang, L. Wang, L. Liu, and C. Liu, Facilely preparation and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1007 (2013).
C. Shang, G. Ji, W. Liu, X. Zhang, H. Lv, and Y. Du, One-pot in situ molten salt synthesis of octahedral Fe3O4 for efficient microwave absorption application. RSC Adv. 5, 80450 (2015).
F. Wang, X. Li, Z. Chen, W. Yu, K.P. Loh, B. Zhong, Y. Shi, and Q.-H. Xu, Efficient low-frequency microwave absorption and solar evaporation properties of γ-Fe2O3 nanocubes/graphene composites. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126676 (2021).
W. You, H. Bi, W. She, Y. Zhang, and R. Che, Dipolar-distribution cavity γ-Fe2O3@C@α-MnO2 nanospindle with broadened microwave absorption bandwidth by chemically etching. Small 13, 1602779 (2017).
S. Parveen and A. Manju, Microwave absorption and EMI shielding behavior of nanocomposites based on intrinsically conducting polymers, graphene and carbon nanotubes, New Polymers for Special Applications. ed. A.D.S. Gomes (Rijeka: IntechOpen, 2012), p. 3.
S. Wang, Q. Jiao, X. Liu, Y. Xu, Q. Shi, S. Yue, Y. Zhao, H. Liu, C. Feng, and D. Shi, Controllable synthesis of γ-Fe2O3 nanotube/porous rGO composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 7004 (2019).
G. Sun, B. Dong, M. Cao, B. Wei, and C. Hu, Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem. Mater. 23, 1587 (2011).
H. Cui, Y. Liu, and W. Ren, Structure switch between α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4, during the large scale and low temperature sol–gel synthesis of nearly monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 24, 93 (2013).
M. Aliahmad and N. Nasiri Moghaddam, Synthesis of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles by thermal-decomposition of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Pol. 31, 264 (2013).
K. Iraj and S. Mosivand, Phase transition of electrooxidized Fe3O4 to gamma and alpha-Fe2O3 nanoparticles using sintering treatment. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. A 125, 1210 (2014).
A.M. Ali, N. Yahya, and S. Qureshi, Interactions of ferro-nanoparticles (hematite and magnetite) with reservoir sandstone: implications for surface adsorption and interfacial tension reduction. Pet. Sci. 17, 1037 (2020).
X. Zhang, D. Han, Z. Hua, and S. Yang, Porous Fe3O4 and gamma-Fe2O3 foams synthesized in air by sol-gel autocombustion. J. Alloys Compd. 684, 120 (2016).
B. Yadav, R. Singh, A. Vishwakarma, and N. Kumar, Facile synthesis of substantially magnetic hollow nanospheres of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) originated from magnetite (Fe3O4) via solvothermal method. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 2199 (2020).
N. Zhang, Y. Huang, and M. Wang, 3D ferromagnetic graphene nanocomposites with ZnO nanorods and Fe3O4 nanoparticles co-decorated for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos. B Eng. 136, 135 (2018).
X. Zeng, X. Cheng, R. Yu, and G.D. Stucky, Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers. Carbon 168, 606 (2020).
J. Li, Y. Xie, W. Lu, and T.-W. Chou, Flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing composite based on 3D rGO-CNT-Fe3O4 ternary films. Carbon 129, 76 (2018).
L. Huang, X. Liu, and R. Yu, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of rod-shaped Fe2O3/Fe3O4/MWCNTs composites. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 28, 288 (2018).
N. Li, G.-W. Huang, Y.-Q. Li, H.-M. Xiao, Q.-P. Feng, N. Hu, and S.-Y. Fu, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of coated carbon nanotubes by optimizing the Fe3O4 nanocoating structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 2973 (2017).
Y. Qing, D. Min, Y. Zhou, F. Luo, and W. Zhou, Graphene nanosheet- and flake carbonyl iron particle-filled epoxy–silicone composites as thin–thickness and wide-bandwidth microwave absorber. Carbon 86, 98 (2015).
J. Wei, J. Liu, and S. Li, Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4 magnetic films plated on hollow glass spheres. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312, 414 (2007).
K. Jia, R. Zhao, J. Zhong, and X. Liu, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of loose nanoscale Fe3O4 spheres. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2167 (2010).
S. Ni, X. Sun, X. Wang, G. Zhou, F. Yang, J. Wang, and D. He, Low temperature synthesis of Fe3O4 micro-spheres and its microwave absorption properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 124, 353 (2010).
S. Ni, S. Lin, Q. Pan, F. Yang, K. Huang, and D. He, Hydrothermal synthesis and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4 nanocrystals. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 055004 (2009).
M. George, S.S. Nair, K.A. Malini, P.A. Joy, and M.R. Anantharaman, Finite size effects on the electrical properties of sol–gel synthesized CoFe2O4 powders: deviation from Maxwell–Wagner theory and evidence of surface polarization effects. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 1593 (2007).
H. Wu, G. Wu, and L. Wang, Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 269, 443 (2015).
N. Gill, A.L. Sharma, V. Gupta, M. Tomar, O.P. Pandey, and D.P. Singh, Enhanced microwave absorption and suppressed reflection of polypyrrole-cobalt ferrite-graphene nanocomposite in X-band. J. Alloys Compd. 797, 1190 (2019).
S.S. Batsanov and D.A. Dan’kin, Size effect on dielectric properties of synthetic diamond. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 49, 275301 (2016).
S. Narang and K. Pubby, Electromagnetic characterization of Co-Ti-DOPED Ba-M ferrite-based frequency-tunable microwave absorber in 12.4–40 GHz. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 30, 511 (2017).
P. Kaur, S. Bindra Narang, and S. Bahel, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ni-Zr doped La-Sr hexagonal ferrites in 18–40 GHz frequency range. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 268, 115141 (2021).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by (I) DST-AMT Grants (ii) MHRD-IMPRINT grant and (iii) DST-SERB grant of Government of India.
Funding
The funding was provided by Department of Science & Technology (IN) (Grant No. SERB), Department of Science and Technology (IN) (Grant No. AMT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Kumar, N., Chaudhary, D. et al. Dual-Band Microwave/mm-Wave Absorption Properties of γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Stealth Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2762–2771 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10238-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10238-8