Abstract
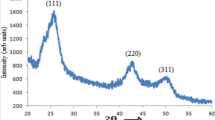
Cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized using a biodegradable starch [(C6H10O5)n] polymer as a capping and stabilizing agent. The as-synthesized CdS NPs were highly crystalline and had a hexagonal structure with an average particle size of ~ 10.5 nm. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis was used to examine the presence and interactions of starch on the surface of the nanoparticles. The electronic behavior of CdS NPs was analyzed using I–V measurements and impedance spectroscopy. These NPs exhibit semiconducting behavior with resistance and conductance values of 1.78 ×108 Ω, and 5.61 × 10−9 S, respectively. Photoresponse studies of CdS NPs showed significant photoresponse with improved photocurrent under light conditions. The dielectric measurements were done at different temperatures, during both the heating and cooling cycles, and the frequency dependence and temperature dependence of dielectric constant and dielectric loss were investigated.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Jia, J. Wu, J. Dong, L. Fan, M. Huang, J. Lin, and Z. Lan, Cadmium sulfide as an efficient electron transport material for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Chem. Commun. 54, 3170 (2018).
K.-J. Wu, K.-C. Chu, C.-Y. Chao, Y.-F. Chen, C.-W. Lai, C.-C. Kang, C.-Y. Chen, and P.-T. Chou, CdS nanorods imbedded in liquid crystal cells for smart optoelectronic devices. Nano Lett. 7, 1908 (2007).
E. Alkuam, E. Badradeen, and G. Guisbiers, Influence of CdS morphology on the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Omega 3, 13433 (2018).
A.K. Bansal, F. Antolini, S. Zhang, L. Stroea, L. Ortolani, M. Lanzi, E. Serra, S. Allard, U. Scherf, and I.D.W. Samuel, Highly luminescent colloidal CdS quantum dots with efficient near-infrared electroluminescence in light-emitting diodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 1871 (2016).
J. Xu, E. Oksenberg, R. Popovitz-Biro, K. Rechav, and E. Joselevich, Bottom-up tri-gate transistors and submicrosecond photodetectors from guided CdS nanowalls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 15958 (2017).
Y. Fang, Z. Li, Y. Jiang, X. Wang, H.-Y. Chen, N. Tao, and W. Wang, Intermittent photocatalytic activity of single CdS nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, 10566 (2017).
S. Smrithi, N. Kottam, A. Narula, G. Madhu, R. Mohammed, and R. Agilan, Carbon dots decorated cadmium sulphide heterojunction-nanospheres for the enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic dye degradation and hydrogen generation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 627, 956 (2022).
Y.A.E. Dahshoury, M. Ahmed, and M.G. Elmahgary, Photocatalytic hydrogen production on the surface of cadmium sulphide and other different doping nanomaterials dispersed on zinc oxide. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 7, 575 (2022).
D.B. Pal, A.K. Rathoure, and A. Singh, Investigation of surface interaction in rGO-Cds photocatalyst for hydrogen production: an insight from XPS studies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46, 26757 (2021).
S. Ghosh, P. Das, B. Bairy, R. Ghosh, S. Dam, and M.B. Sen, Exploration of photoreduction ability of reduced graphene oxide–cadmium sulphide hetero-nanostructures and their intensified activities against harmful microbes. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 16928 (2021).
Y. Ma, F. Yan, L. Liu, W. Wei, Z. Zhao, and J. Sun, The enhanced photo-thermal therapy of surface improved photoactive cadmium sulfide (CdS) quantum dots entrenched graphene oxide nanoflakes in tumor treatment. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 192, 34 (2019).
I. Uddin, Onsite visual detection of heavy metal contaminants using impregnated strip. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 421, 113512 (2021).
R.K. Sonker, B. Yadav, V. Gupta, and M. Tomar, Synthesis of CdS nanoparticle by sol–gel method as low temperature NO2 sensor. Mater. Chem. 239, 121975 (2020).
T. Senasu, K. Hemavibool, and S. Nanan, Hydrothermally grown CdS nanoparticles for photodegradation of anionic azo dyes under UV-visible light irradiation. RSC Adv. 8, 22592 (2018).
M. Kristl, I. Ban, A. Danč, V. Danč, and M. Drofenik, A sonochemical method for the preparation of cadmium sulfide and cadmium selenide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 17, 916 (2010).
A. Singh, D. Singh, B. Ahmed, and A.K. Ojha, Sun/UV-light driven photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye by Zn doped CdS nanostructures as photocatalyst. Mater. Chem. Phys. 277, 125531 (2022).
M. Darwish, A. Mohammadi, and N. Assi, Microwave-assisted polyol synthesis and characterization of pvp-capped CdS nanoparticles for the photocatalytic degradation of tartrazine. Mater. Res. Bull. 74, 387 (2016).
M. Ganiga and J. Cyriac, Detection of PETN and RDX using a FRET-based fluorescence sensor system. Anal. Methods 7, 5412 (2015).
J. Wang, X. Wu, Y. He, W. Guo, Q. Zhang, Y. Wang, and Z. Wang, Investigation of the electronic structure of CdS nanoparticles with sum frequency generation and photoluminescence spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 27712 (2019).
M. Martins, C. Toste, and I.A. Pereira, Enhanced light-driven hydrogen production by self-photosensitized biohybrid systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 9055 (2021).
H. Chauhan, Y. Kumar, and S. Deka, New synthesis of two-dimensional CdSe/CdS core@ shell dot-in-hexagonal platelet nanoheterostructures with interesting optical properties. Nanoscale 6, 10347 (2014).
A. Alipour, M. Mansour Lakouraj, and H. Tashakkorian, Study of the effect of band gap and photoluminescence on biological properties of polyaniline/CdS QD nanocomposites based on natural polymer. Sci. Rep. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79139-8.
S. Bano, S.I. Raj, A. Khalilullah, A. Jaiswal, and I. Uddin, Selective and sensitive cation exchange reactions in the aqueous starch capped ZnS nanoparticles with tunable composition, band gap and color for the detection and estimation of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 405, 112925 (2021).
F.J. Warren, M.J. Gidley, and B.M. Flanagan, Infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterise starch ordered structure – a joint FTIR–ATR, NMR, XRD and DSC study. Carbohydr. Polym. 139, 35 (2016).
N.V. Deshmukh, T.M. Bhave, A.S. Ethiraj, S. Sainkar, V. Ganesan, S. Bhoraskar, and S. Kulkarni, Photoluminescence and IV characteristics of a CdS-nanoparticles-porous-silicon heterojunction. Nanotechnology 12, 290 (2001).
M.Z. Nawaz, L. Xu, X. Zhou, K.H. Shah, J. Wang, B. Wu, and C. Wang, CdS nanobelt-based self-powered flexible photodetectors with high photosensitivity. Mater. Adv. 2, 6031 (2021).
L. Ma, X. Ai, X. Yang, X. Song, and X. Wu, Dielectric and conductivity relaxation of rGO@CdS nanocomposites via in situ assembly of CdS nanoparticles on an rGO layer. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 25133 (2020).
J.C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1873).
S. Suresh, Studies on the dielectric properties of CdS nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 4, 325 (2014).
Acknowledgments
JKD and KK would like to acknowledge the UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Kolkata Centre for the Collaborative Research Scheme (CRS) project (Grant No. UGC-DAE-CSR-KC/CRS/19/IBMS04/0465). IU acknowledges SRM University-AP for the timely financial support to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uddin, I., Abzal, S.M., Kalyan, K. et al. Starch-Assisted Stable Synthesis of CdS Nanoparticles for Enhanced Electrical and Optical Properties. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 1710–1716 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10198-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10198-5