Abstract
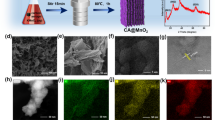
Fabrication of a highly active and robust electrocatalyst for alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) is important for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Here, we report an alkaline HOR electrocatalyst with PtRu nanoparticles uniformly dispersed on porous nitrogen-doped carbon via an ethylene glycol reduction method, where porous nitrogen-doped support (NC-ZG) is prepared by the low-temperature pyrolysis of an in situ-grown ZIF-8/graphene oxide nanocomposite. The obtained PtRu0.6/NC-ZG electrocatalyst shows a mass specific exchange current density (j0,m) of 1102 A gPtRu−1, superior to reference PtRu0.6/NC-Z with only ZIF-8 pyrolyzed as carbon support (312 A gPtRu−1) and the commercial Pt/C (224 A gPtRu−1). The splendid property contributes to the rich micro-mesopores structure, large specific surface area, high conductivity, and electronic effects between Pt and Ru for the optimization of OHads and Hads binding energy. Moreover, PtRu0.6/NC-ZG also displays good stability with 66.4% of j0,m remaining after the accelerated durability tests, outperforming commercial Pt/C (45.9%). This work demonstrates that engineering support structures and active components can obtain efficient HOR electrocatalysts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.P. Setzler, Z. Zhuang, J.A. Wittkopf, and Y. Yan, Activity targets for nanostructured platinum-group-metal-free catalysts in hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 1020 (2016).
L. Han, P. Ou, W. Liu, X. Wang, H.-T. Wang, R. Zhang, C.-W. Pao, X. Liu, W.-F. Pong, J. Song, Z. Zhuang, M.V. Mirkin, J. Luo, and H.L. Xin, Design of Ru-Ni diatomic sites for efficient alkaline hydrogen oxidation. Sci. Adv. 8, 3779 (2022).
X. Yang, B. Ouyang, P. Shen, Y. Sun, Y. Yang, Y. Gao, E. Kan, C. Li, K. Xu, and Y. Xie, Ru colloidosome catalysts for the hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 25, 11138 (2022).
Y. Cong, G. Xie, X. Meng, H. Wang, F. Meng, C. Li, and Q. Zhao, Melamine-assisted synthesis of atomically dispersed Fe sites anchored on crumple-rich carbon nanospheres as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Ionics 27, 5287 (2021).
J. Wang, Y. Zhao, B.P. Setzler, S. Rojas-Carbonell, C.B. Yehuda, A. Amel, M. Page, L. Wang, K. Hu, L. Shi, S. Gottesfeld, B. Xu, and Y. Yan, Poly(aryl piperidinium) membranes and ionomers for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Energy 4, 392 (2019).
W. Ni, T. Wang, F. Héroguel, A. Krammer, S. Lee, L. Yao, A. Schüler, J.S. Luterbacher, Y. Yan, and X. Hu, An efficient nickel hydrogen oxidation catalyst for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Mater. 21, 804 (2022).
X. Zhao, X. Li, L. An, L. Zheng, J. Yang, and D. Wang, Controlling the valence-electron arrangement of nickel active centers for efficient hydrogen oxidation electrocatalysis, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2022).
J. Cai, X. Liao, P. Li, Q. Wang, H. Huang, Z. Lyu, J. Lin, and S. Xie, Penta-twinned Rh@Pt core–shell nanobranches with engineered shell thickness for reversible and active hydrogen redox electrocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132414 (2022).
S. Lu, and Z. Zhuang, Investigating the influences of the adsorbed species on catalytic activity for hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 14, 5156 (2017).
D.J. Weber, C. Dosche, and M. Oezaslan, Tuning of Pt-Co nanoparticle motifs for enhancing the HOR performance in alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 15415 (2021).
Y. Wang, G. Wang, G. Li, B. Huang, J. Pan, Q. Liu, J. Han, L. Xiao, J. Lu, and L. Zhuang, Pt-Ru catalyzed hydrogen oxidation in alkaline media: oxophilic effect or electronic effect? Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 177 (2015).
D. Strmcnik, M. Uchimura, C. Wang, R. Subbaraman, N. Danilovic, D. van der Vliet, A.P. Paulikas, V.R. Stamenkovic, and N.M. Markovic, Improving the hydrogen oxidation reaction rate by promotion of hydroxyl adsorption. Nat. Chem. 5, 300 (2013).
Y. Cong, I.T. Mccrum, X. Gao, Y. Lv, S. Miao, Z. Shao, B. Yi, H. Yu, M.J. Janik, and Y. Song, Uniform Pd0.33Ir0.67 nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon with remarkable activity toward the alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 3161 (2019).
Y. Zhao, X. Wang, Z. Li, P. Zhao, C. Tao, G. Cheng, and W. Luo, Enhanced catalytic activity of Ru through N modification toward alkaline hydrogen electrocatalysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 33, 1065 (2021).
Y. Zhou, D. Ma, A.C. Foucher, L. Xiong, J. Zhang, E.A. Stach, Q. Yue, and Y. Kang, Atomic Fe dispersed hierarchical mesoporous Fe-N-C nanostructures for an efficient oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Catal. 11, 74 (2021).
X. Guo, X. Wan, Q. Liu, Y. Li, W. Li, and J. Shui, Phosphated IrMo bimetallic cluster for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Escience 2, 304 (2022).
L. Zhao, Y. Liu, X. Han, Y. Ding, W. Kong, Y. Tong, J. Xu, and W. Xing, Theoretical study of the alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction on Ni-based nanocluster catalysts: effects of graphene supports and dopants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 567, 150895 (2021).
E.B. Boz, A. Taşdemir, E. Biçer, A. Yürüm, and S.A. Gürsel, Emergent hierarchical porosity by ZIF-8/GO nanocomposite increases oxygen electroreduction activity of Pt nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 46, 32858 (2021).
H. Liu, J. Fu, H. Li, J. Sun, X. Liu, Y. Qiu, X. Peng, Y. Liu, H. Bao, L. Zhuo, R. Cao, S. Zhang, and J. Luo, Single palladium site in ordered porous heteroatom-doped carbon for high-performance alkaline hydrogen oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 306, 121029 (2021).
R. Li, X. Wang, Y. Dong, X. Pan, X. Liu, Z. Zhao, and J. Qiu, Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes decorated with cobalt nanoparticles derived from zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysis. Carbon 132, 580 (2018).
P. Su, H. Xiao, J. Zhao, Y. Yao, Z. Shao, C. Li, and Q. Yang, Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes derived from Zn-Fe-ZIF nanospheres and their application as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts with in situ generated iron species. Chem. Sci. 4, 2941 (2013).
L. Ge, Y. Yang, L. Wang, W. Zhou, R. De Marco, Z. Chen, J. Zou, and Z. Zhu, High activity electrocatalysts from metal–organic framework-carbon nanotube templates for the oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 82, 417 (2015).
D. Kim, D.W. Kim, W.G. Hong, and A. Coskun, Graphene/ZIF-8 composites with tunable hierarchical porosity and electrical conductivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 7710 (2016).
J. Li, Y. Xie, S. Li, Y. Bai, X. Guo, B. Yi, and Y. Song, Graphene supported foam-like platinum electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Mater. Res. Express 1, 025045 (2014).
S. Liu, H. Zhang, Q. Zhao, X. Zhang, R. Liu, X. Ge, G. Wang, H. Zhao, and W. Cai, Metal–organic framework derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon@graphene sandwich-like structured composites as bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Carbon 106, 74 (2016).
Y. Cong, C. Chai, X. Zhao, B. Yi, and Y. Song, Pt0.25Ru0.75/N-C as highly active and durable electrocatalysts toward alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 7, 2000310 (2020).
L. Zheng, S. Yu, X. Lu, W. Fan, and S. Liao, 2D bimetallic Zn/Fe-MOF-derived porous carbon nanosheets with high density of single/paired Fe atoms as high-performance oxygen reduction catalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 13878 (2020).
S. Zhao, L. Ban, J. Zhang, W. Yi, and Z. Zhu, Cobalt and nitrogen co-doping of porous carbon nanosphere as highly effective catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction and Zn-air battery. Chem. Eng. J. 409, 128171 (2020).
S. Seetharaman, S.V. Selvaganesh, and R. Chetty, Tailored synthesis of hybrid iron-nitrogen-graphene with reduced carbon xerogel as an efficient electrocatalyst towards oxygen reduction. Ionics 26, 6255 (2020).
Y. Zhao, F. Yang, W. Zhang, Q. Li, X. Wang, L. Su, X. Hu, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, L. Zhuang, S. Chen, and W. Luo, High-performance Ru2P anodic catalyst for alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells. CCS Chem. 4, 1732 (2022).
F. Yang, P. Han, N. Yao, G. Cheng, S. Chen, and W. Luo, Inter-regulated D-band centers of the Ni3B/Ni heterostructure for boosting hydrogen electrooxidation in alkaline media. Chem. Sci. 11, 12118 (2020).
Y. Huang, K. Liu, S. Kan, P. Liu, R. Hao, W. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Liu, M. Liu, and K. Liu, Highly dispersed Fe-Nx active sites on graphitic-N dominated porous carbon for synergetic catalysis of oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 171, 1 (2021).
X. Wang, X. Li, T. Cai, Y. Cui, D. Kong, J. Xu, H. Hu, Y. Wang, H. Hu, X. Gao, Y. Li, Q. Xue, Z. Yan, L. Zhao, and W. Xing, Enhancing hydrogen oxidation electrocatalysis of nickel-based catalyst by simultaneous chemical anchoring and electronic structure regulation. Chem. Eng. J. 425, 130654 (2021).
X. Wang, L. Zhao, X. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Q. Yao, J. Xie, Q. Xue, Z. Yan, X. Yuan, and W. Xing, Atomic-precision Pt6 nanoclusters for enhanced hydrogen electro-oxidation. Nat. Commun. 13, 1596 (2022).
J.J. Ogada, A.K. Ipadeola, P.V. Mwonga, A.B. Haruna, F. Nichols, S. Chen, H.A. Miller, M.V. Pagliaro, F. Vizza, J.R. Varcoe, D.M. Meira, D.M. Wamwangi, and K.I. Ozoemena, CeO2 modulates the electronic states of a palladium onion-like carbon interface into a highly active and durable electrocatalyst for hydrogen oxidation in anion-exchange-membrane fuel cells. ACS Catal. 12, 7014 (2022).
W. Sheng, M.N. Myint, J.G. Chen, and Y. Yan, Correlating the hydrogen evolution reaction activity in alkaline electrolytes with the hydrogen binding energy on monometallic surfaces. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 1509 (2013).
S. Deng, X. Liu, X. Guo, T. Zhao, Y. Lu, J. Cheng, K. Chen, T. Shen, Y. Zhu, and D. Wang, Insight into the hydrogen oxidation electrocatalytic performance enhancement on Ni via oxophilic regulation of MoO2. J. Energy Chem. 54, 202 (2021).
Y.-F. Xing, Y. Zhou, Y.-B. Sun, C. Chi, Y. Shi, F.-B. Wang, and X.-H. Xia, Bifunctional mechanism of hydrogen oxidation reaction on atomic level tailored-Ru@Pt core–shell nanoparticles with tunable Pt layers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 872, 114348 (2020).
Y. Zhao, X. Wang, Z. Li, P. Zhao, C. Tao, G. Cheng, and W. Luo, Enhanced catalytic activity of Ru through N modification toward alkaline hydrogen electrocatalysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 33, 1065 (2022).
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22262018), Young Science and Technology Fund in Gansu Province of China (Grant No. 21JR7RA252), Natural Research Fund of Gansu Province (Grant No. 20JR5RA441), Lanzhou Open Competition Mechanism, Merit Based Admission Project Major Fund (Grant No. 2021-JB-6) and National Engineering & Fund for National Nickel and Cobalt Advanced Materials Engineering Research Center (GCZX2021JSKF001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cong, Y., Meng, F., Wang, X. et al. Uniform PtRu0.6 Nanoparticles Supported on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Obtained from ZIF-8/GO Hybrid with Remarkable Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation Activity. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2388–2395 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10184-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10184-x