Abstract
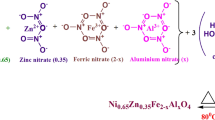
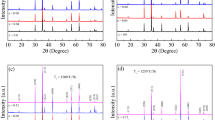
We report structural, morphological and elastic properties of NiXZn1-XFe2O4 (x = 0.28, 0.30, 0.32, 0.34, 0.36, 0.38, 0.40) ferrimagnetic oxides prepared using oxalate chemistry. The Rietveld refinement of the X-ray diffraction patterns confirm the formation of spinel cubic structure. The experimental and theoretical lattice constant is found to decrease with increasing Ni2+ content. The FTIR spectra exhibit two main fundamental absorption bands, one for the tetrahedral site around 575 to 580 cm-1 and the other for the octahedral site around 411–413 cm-1. The magnitude of elastic moduli is found to be independent with increasing Ni2+ content. The morphological analysis showed the formation of small and homogeneous particles, which is possible using an oxalate precursor. The elemental analysis confirmed the presence of Ni, Zn, Fe, and O as per their stoichiometric amounts. The structural, morphological and elastic properties are described with an interplay of oxalate precursor synthesis route of the ferrite development.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Cheng, J. Tian, J. Lin, S. Wang, S. Xie, Y. Pei, S. Yan, M. Qiao, H. Xu, and B. Zong, Potassium-promoted magnesium ferrite on 3D porous graphene as highly efficient catalyst for CO hydrogenation to lower olefins. J. Catal. 374, 24 (2019).
P.J. Jessy, V. Bambole, R.R. Deshmukh, and N. Patel, Reduced power consumption in nickel zinc ferrite nanoparticles doped blue phase chiral nematic liquid crystal devices. J. Mol. Liq. 281, 480 (2019).
S.Y. Srinivasan, K.M. Paknikar, D. Bodas, and V. Gajbhiye, Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 13, 10 (2018).
S. Chakma, G. K. Dinesh, S. Chakraborty, and V. S. Moholkar, Investigation in Sono-photocatalysis Process Using Doped Catalyst and Ferrite Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment, in ed. by A.A. Inamuddin, E. Lichtfouse, Nanophotocatalysis and Environmental Applications. Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World, vol 30 (Springer, 2020), p. 171-194.
M. Tahir Farid, I. Ahmad, M. Kanwal, G. Murtaza, M. Hussain, S.A. Khan, and I. Ali, Synthesis, electrical and magnetic properties of Pr-substituted Mn ferrites for high-frequency applications. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1826 (2017).
M. N. Akhtar, M. A. Khan, M. Ahmad, M.S. Nazir, M. Imran, A. Ali, A. Sattar, and G. Murtaza, Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (CuxZn0.5−xNi0.5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and MLCI’s applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421 (1), 260 (2017)
S.P. Dalawai, T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, and P.N. Vasambekar, Influence of Ni2+ and Sn4+ substitution on gas sensing behaviour of zinc ferrite thick films. J Solid State Electrochem 20, 2363 (2016).
N. Ikramullah, F. Ali, Z. Sheikh, M. Bilal, and I. Ahmad, Photocatalytic performance of zinc ferrite magnetic nanostructures for efficient eriochrome black-T degradation from the aqueous environment under unfiltered sunlight. Water Air Soil Pollut. 231, 59 (2020).
P. Gao, X. Hua, V. Degirmenci, D. Rooney, M. Khraisheh, R. Pollard, R. Bouiman, and E.V. Rebrav, Structural and magnetic properties of NiXZn1-XFe2O4 (x = 0, 0.5, 1) nanopowder prepared by sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 348, 44 (2013).
B.S. Badireddi, and V. Raghavendra, XRD, TEM, Magnetic studies on NixZn1-xFe2O4 (Where x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and 0.8) nano scale particles by chemical co-precipitation method. Int. Let. Chem. Phy. Astron. 60, 20 (2015).
D.H. Chen and X. Hea, Synthesis of nickel ferrite nanoparticles by sol-gel method. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 1369 (2001).
K. Sue, M. Aoki, T. Sato, D. Nishio-Hamane, S. Kawasaki, Y. Hakuta, Y. Takebayashi, S. Yoda, T. Furuya, T. Sato, and T. Hiaki, Continuous hydrothermal synthesis of nickel ferrite nanoparticles using a central collision-type micromixer: effects of temperature, residence time, metal salt molality, and NaOH addition on conversion, particle size, and crystal phase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 50, 9625 (2011).
L. Hao, Y. Zhao, Q. Jiao, and P. Chen, Synthesis of zinc–nickel ferrite nanorods and their magnetic properties. RSC Adv. 4, 15650 (2014).
A. Verma and R. Chatterjee, Effect of zinc substitution on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of mixed Mn-Zn and Ni-Zn ferrites synthesized by citrate precursor techniques. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 306, 313 (2006).
S. Kumar, V. Singh, S. Aggrawal, U. Mandal, and R.K. Kotnala, Synthesis of nanocrystalline Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 ferrite and study of its magnetic behavior at different temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. (B) 166, 76 (2010).
Y. Koseoglu, Structural and magnetic properties of Cr doped Ni-Zn ferrite nano particles prepared by surfactant assisted hydrothermal technique. Ceram. Inter. 41, 6417 (2015).
A.S. Dzunuzovic, N.I. IIice, M.M. Vijatovic Petrovic, J.D. Bobic, B. Stojadinovic, Z. Dohcevic Mitrovic, and B.D. Stojanorvic, Structure and properties of Ni-Zn ferrites obtained by auto combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 245 (2015)
V.D. Sudheesh, J. Nehra, A. Vinesh, V. Sebastian, N. Lukshmi, D.P. Dutta, V.R. Reddy, K. Venugopalan, and A. Gupta, Investigations of structural and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nano powders prepared by self combustion method. Mat. Res. Bull. 48, 698 (2013).
K. Velmurugan, V.S.K. Venkatachalapathy, and S. Sendhilnathan, Thermogravimetric and magnetic properties of Ni1-XZnXFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation. J. Mater. Res. 12, 529 (2009).
L. Rezlescu, E. Rezlescu, P.D. Popa, and N. Rezlescu, Fine barium hexaferrite powder prepared by crystallization of glass. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 193, 288–290 (1999).
J. Massoudi, M. Smari, K. Nouri, E. Dhahri, K. Khirouni, S. Bertaina, L. Bessaisc, and E.K. Hlilf, Magnetic and spectroscopic properties of Ni-Zn-Al ferrite spinel: from the nanoscale to microscale. RSC Adv. 10, 34556 (2020).
K.H. Maria, S. Choudhary, and M.A. Hakim, Structural transformation and hysteresis behavior of Cu-Zn ferrites. Int. Nano Lett. 3, 1 (2013).
A.R. Das, V.S. Ananthan, and D.C. Khan, Lattice parameter variation and magnetization studies on titanium-, zirconium-, and tin-substituted nickel-zinc ferrites. J. Appl. Phy. 57, 4189 (1985).
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 1727 (1955).
S. Dabagh, K. Chaudhary, Z. Haider, and J. Ali, Study of structural phase transformation and hysteresis behavior of inverse-spinel α-ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Res. Phys. 8, 93 (2018).
T.K. Pathak, J.J.U. Buch, U.N. Trivedi, H.H. Joshi, and K.B. Modi, Infrared spectroscopy and elastic properties of nanocrystalline Mg-Mn ferrites prepared by co-precipitation technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 4181 (2008).
A. Goldman, Understanding ferrites. ACS. Bulletin 63, 582 (1984).
P. Ravindranathan and K.C. Patil, Novel solid solution precursor method for the preparation of ultrafine Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Mat. Sci. 22, 3261 (1987).
H. Igarash, and K. Okazaki, Effects of porosity and grain size on the magnetic properties of NiZn ferrite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 60, 54 (1977).
M.P. Reddy, W. Madhuri, N.R. Reddy, K.V. Siva Kumar, V.R.K. Murthy, and R.R. Reddy, Magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrites prepared by microwave sintering method. J. Electroceram. 28, 1–9 (2012).
K. Zipare, J. Dhumal, S. Bandgar, V. Mathe, and G. Shahane, Superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticle: synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 1, 178 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhari, N.D., Nadargi, D.Y., Kabbur, S.M. et al. Investigation of Structural, Morphological and Elastic Properties of Ni-Zn Ferrite Grown with an Oxalate Precursor. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 2732–2740 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09582-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09582-y