Abstract
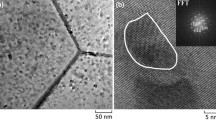
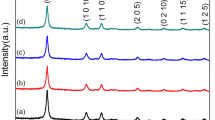
In this work, silicon and higher manganese silicide (HMS) bulk nanocomposites were synthesized, Si100-x(HMS)x, where x is 10–50, and their thermoelectric properties were studied. The powders of Si and Mn in a stoichiometric ratio were mixed by a ball milling, followed by hot-pressing to obtain the Si + HMS bulk nanocomposite samples. Every bulk sample was highly dense, with a density of over 90% of its theoretical value. The x-ray diffraction analysis revealed that only the Si and HMS phases, without any impurity phase, were obtained. The fractured surface morphology showed that the composites consisted of micro-sized Si matrix grains with the HMS nanodots homogenously distributed within the grains. The thermoelectric studies showed that thermal conductivity decreased with a higher concentration of HMS, mainly due to the reduction of lattice thermal conductivity. It was believed to be the presence of the HMS nanodots which effectively scattered phonon transport. Furthermore, the addition of HMS increased charge carrier concentration. Hence, the Seebeck coefficient decreased, and the electrical conductivity increased with increasing HMS content. However, the presence of the HMS nanodots also contributed to strong scattering of charge carriers. The charge mobility was reduced significantly for the composite samples compared to the bulk Si sample. Therefore, the electrical conductivity is relatively low compared to the reported values in the literature. The dimensionless figure-of-merit (ZT) was improved in the nanocomposite samples compared to the bulk Si sample, and the values were largest for the sample with x = 50.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.J. Snyder and E.S. Toberer, Nat. Mater. 7, 105 (2008).
T.M. Tritt and M.A. Subramanian, MRS Bull. 31, 188 (2006).
S.K. Bux, R.G. Blair, P.K. Gogna, H. Lee, G. Chen, M.S. Dresselhaus, R.B. Kaner, and J. Fleurial, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 2445 (2009).
T. Fu, X. Yue, H. Wu, C. Fu, T. Zhu, X. Liu, L. Hu, P. Ying, J. He, and X. Zhao, J. Materiomics 2, 141 (2016).
K. Kurosaki, A. Yusufu, Y. Miyazaki, Y. Ohishi, H. Muta, and S. Yamanaka, Mater. Trans. 57, 1018 (2016).
J.R. Sootsman, D.Y. Chung, and M.G. Kanatzidis, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48, 8616 (2009).
J.A. Minnich, M.S. Dresselhaus, Z.F. Ren, and G. Chen, Energy Environ. Sci. 2, 466 (2009).
D.M. Rowe, CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics (Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1995)
R.H. Shanks, D.P. Maycock, H.P. Sidles, and C.G. Danielson, Phys. Rev. 130, 1743 (1963).
L. Weber and E. Gmelin, Appl. Phys. A 53, 136 (1991).
N. Mingo, D. Hauser, P.N. Kobayashi, M. Plissonnier, and A. Shakouri, Nano Lett. 9, 711 (2009).
Y. Ohishi, K. Kurosaki, T. Suzuki, H. Muta, S. Yamanaka, N. Uchida, T. Tada, and T. Kanayama, Thin Solid Films 534, 238 (2013).
N. Uchida, T. Tada, Y. Ohishi, Y. Miyazaki, K. Kurosaki, and S. Yamanaka, J. Appl. Phys. 114, 134311 (2013).
A. Yusufu, K. Kurosaki, Y. Ohishi, H. Muta, and S. Yamanaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 061301 (2016).
S. Tanusilp, K. Kurosaki, A. Yusufu, Y. Ohishi, H. Muta, and S. Yamanaka, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 3249 (2017).
W.D. Lui, X.L. Shi, R. Moshwan, Q. Sun, L. Yang, Z.G. Chen, and J. Zou, J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 7212 (2019).
W. Luo, H. Li, Y. Yan, Z. Lin, X. Tang, Q. Zhang, and C. Uher, Intermetallics 19, 404 (2011).
Y. Sadia and Y. Gelbstein, J. Electro. Mater. 41, 1504 (2012).
X. Shi, X. Shi, Y. Li, Y. He, L. Chen, and Q. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 116, 245104 (2014).
D. Shin, K. Jang, S. Ur, and I. Kim, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 1756 (2013).
N.Y.D. Truong, Ph. D. thesis, the Waterloo, (2015).
M. Yoshikura and T. Itoh, J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 57, 242 (2010).
W.D. Lui, Z.G. Chen, and J. Zou, Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 18000056 (2018).
A.B. Gokhale and R. Abbaschian, Phase Equilibria 11, 468 (1990).
J. Sakurai, Y. Yamamoto, and Y. Komura, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 57, 24 (1987).
G.S. Nolas, J. Sharp, and J. Goldsmid, Thermoelectrics: Basic Principles and New Materials Developments (Berlin: Springer, 2001).
X.W. Wang, H. Lee, Y.C. Lan, G.H. Zhu, G. Joshi, D.Z. Wang, J. Yang, A.J. Muto, M.Y. Tang, J. Klatsky, S. Song, S.M. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, and Z.F. Gen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 193121 (2008).
A. Nozariasbmarz, A. Agarwal, Z.A. Coutant, M.J. Hall, J. Liu, R. Liu, A. Malhortra, and P. Norouzzadeh, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 56, 05DA04 (2017).
R.J. Drabble and J.H. Goldsmid, Thermal Conduction in Semiconductors (Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1961).
B. Yu, M. Zebarjadi, H. Wang, K. Lukas, H. Wang, D. Wang, C. Opeil, M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, and Z.F. Ren, Nano Lett. 12, 2077 (2012).
M. Zebarjadi, G. Joshi, G. Zhu, B. Yu, J.A. Minnich, Y.C. Lan, X. Wang, M.S. Dresselhaus, Z.F. Ren, and G. Chen, Nano Lett. 11, 2225 (2011).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) in cooperation with Synchrotron Light Research Institute (public organization) and Khon Kaen University (RSA6280020), the Research Network NANOTEC (RNN) program of the National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC), NSTDA, Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation and Khon Kaen University, and the National Research Council of Thailand through Khon Kaen University (6200071). D.P. would like to thank the Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palaporn, D., Parse, N., Tanusilp, a. et al. Synthesis of Silicon and Higher Manganese Silicide Bulk Nano-composites and Their Thermoelectric Properties. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 2920–2927 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-07983-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-07983-5