Abstract
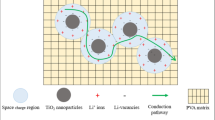
In this communication, the formation mechanism of the electroactive β phase, morphology and the dielectric activities of increasing doping concentration (0–1.2 M.W % of mullite) of Fe2+ ion-doped, mullite-impregnated polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanocomposite have been investigated. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) confirms the formation of an electroactive β phase, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed that the β phase increases simultaneously and attains the maximum increment of 2.6 times compared to pristine PVDF. X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra also agreed well with the β-phase increment behaviour and also confirmed the presence of required mullite phases. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images indicate the strong interaction between the polymer matrix and different concentrations of Fe2+ ion-doped mullite particles, resulting in enhanced electroactive β phase formation and large dielectric constant of the nanocomposite films followed by significant low dielectric loss with high ac conductivity compared to pristine PVDF films at room temperature. This doped polymer composite can be used as a high dielectric separator and, using this separator, we have successfully fabricated a high-charge-storage device. This paper also demonstrates that the loading of conductive Fe2+ ions within the highly insulating mullite matrix has a critical concentration for the enhancement and nucleation of the electroactive β phase of the PVDF polymer. In this critical concentration, the highest formation of a β network and maximum numbers of homogeneously distributed iron-doped mullite (FeM) particles in PVDF matrix improves the effective interfacial polarization by Maxwell–Wagner–Sillar (MWS) polarization effect which is responsible for the enhancement of dielectric constant and ac conductivity followed by significant tangent loss. So, it can be concluded that the incorporation of Fe2+-doped mullite into PVDF matrix is an effective way to fabricate a high dielectric separator of high-charge-storage electronic devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Treichel, B. Withers, Academic Press (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012513905-2/50003-0
M.J. Pan and C.A. Randall, IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 26, 44 (2010).
K. Hiroshi, M. Youichi, and C. Hirokazu, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 1 (2003).
D. Burks and G. Shirn, IEEE (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/APEC.1989.36988.
T. Homma, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 23, 243 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-796X(98)00012-6
X. Hao, J. Adv. Dielectr. 3, 1330001 (2013).
L. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Liu, and X. Yao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 1049 (2010).
F. Wen, Z. Xu, W. Xia, X. Wei, and Z. Zhang, J. Adv. Dielectr. 3, 1350010 (2013).
T. Kurihara, M. Horiuchi, Y. Takeuchi, and S. Wakabayashi, in 40th Conference Proceedings on Electronic Components and Technology (1990). 10.1109/ECTC.1990.122170.
R. Tummala, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74, 895 (1991).
L. Priya and J. Jog, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89, 2036 (2003).
N. Jahan, F. Mighri, D. Rodrigue, and A. Ajji, Appl. Clay Sci. 152, 93 (2018).
B.K. Paul, K. Halder, D. Roy, B. Bagchi, A. Bhattacharya, and S. Das, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 5218 (2014).
H. Schneider, J. Schreuer, and B. Hildmann, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 329 (2008).
T. Mah, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 66, 699 (1983).
I.A. Aksay, D.M. Dabbs, and M. Sarikaya, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74, 2343 (1991).
M.A. Camerucci, G. Urretavizcaya, M.S. Castro, and A.L. Cavalieri, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 2917 (2001).
B.K. Paul, D. Roy, S. Batabyal, A. Bhattacharya, P. Nandy, and S. Das, Mater. Chem. Phys. 187, 119 (2017).
P. Martins, C.M. Costa, M. Benelmekki, G. Botelho, and S.L. Mendez, Cryst. Eng. Comm. 14, 2807 (2012).
K. Halder, B.K. Paul, D. Roy, A. Bhattacharya, and S. Das, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2521-y.
T. Nestler, R. Schmid, W. Münchgesang, V. Bazhenov, J. Schilm, T. Leisegang, and D.C. Meyer, AIP Conf. Proc. 1597, 155 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4878486.
C.M. Costa, J.L. Gomez Ribelles, S. Lanceros-Méndez, G.B. Appetecchi, and B. Scrosati, J. Power Sources 245, 779 (2014).
B.K. Paul, D. Roy, S. Manna, P. Nandy, and S. Das, J. Electroceram. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-018-0136-z.
X. Yuan, S. Changgeng, G. Yan, and Z. Zhenghong, J. Phys Conf. Ser. 744, 012077 (2016).
E.I. Unuabonah and A. Taubert, Appl. Clay Sci. 99, 83 (2014).
Z. Dang, B. Peng, D. Xie, S. Yao, M. Jiang, J. Bai, Z. Dang, B. Peng, D. Xie, S. Yao, and M. Jiang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 112910 (2008).
P. Martins and A.C. Lopes, Prog. Polym. Sci. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.07.006.
A.L. Gayen, D. Mondal, D. Roy, P. Bandyopadhyay, S. Manna, R. Basu, S. Das, D.S. Bhar, B.K. Paul, and P. Nandy, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 14798 (2017).
C. Ribeiro, C.M. Costa, D.M. Correia, J.N. Pereira, J. Oliveira, P. Martins, R. Onçalves, V.F. Cardoso, and S.L. Méndez, Nat. Protoc. 13, 4 (2018).
M.S. Sebastian, RSC Adv. 6, 113007 (2016).
B.K. Paul, K. Haldar, D. Roy, B. Bagchi, A. Bhattacharya, and S. Das, J. Adv. Ceram. 3, 278 (2014).
B. Bagchi, S. Das, A. Bhattacharya, R. Basu, and P. Nandy, J. Sol–Gel. Sci. Technol. 55, 135 (2010).
M.M.S. Sanad, M.M. Rashad, E.A. Abdel-Aal, M.F. El-Shahat, and K. Powers, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 2487 (2014).
B. Bagchi, S. Das, A. Bhattacharya, R. Basu, and P. Nandy, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 748 (2009).
B. Wang and H. Huang, Compos. A 66, 16 (2014).
P. Martins, C. Caparros, R. Gonçalves, P.M. Martins, M. Benelmekki, G. Botelho, and S. Lanceros-Mendez, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 15790 (2012).
J. Nunes-Pereira, C.M. Costa, and S. Lanceros-Mendez, J. Power Sources 281, 378 (2015).
L. Yang, J. Qiu, H. Ji, K. Zhu, and J. Wang, Compos. A 65, 125 (2014).
G.M. Tsangaris, G.C. Psarras, and N. Kouloumbi, J. Mater. Sci. 33, 2027 (1998).
K. Meeporn, S. Maensiri, and P. Thongbai, Appl. Surf. Sci. 380, 67 (2016).
K.R. Reddy, W. Park, B.C. Sin, J. Noh, and Y. Lee, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 335, 34 (2009).
M. Panda, V. Srinivas, and A.K. Thakur, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 12 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to UGC, Government of India, for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, B.K., Mondal, D., Das, S. et al. Iron-Doped, Mullite-Impregnated PVDF Composite: An Alternative Separator for a High Charge Storage Ceramic Capacitor. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 7075–7084 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6635-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6635-5