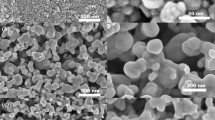
We propose use of Ag/Sn-3.0 (wt.%) Ag-0.5 Cu (SAC305) composite ink to reduce sintering temperature, sintering time, and material costs. The SAC305 nanoparticle (NP) surfaces were not capped by any stabilizers, which are detrimental to the resistivity of the sintered tracks. Compared with commercial pure Ag ink, use of Ag/3.2 (vol.%) SAC305 composite ink containing ultrafine SAC305 NPs resulted in outstandingly enhanced processability, enabling faster sintering at low temperatures. The average sheet resistance of composite ink samples sintered for 25 min at 170°C was as low as 0.011 Ω/□, comparable with that of a pure Ag sample sintered for over 30 min at 220°C. The morphology and the differential scanning calorimetry curves enabled explanation of the changes in the sintering behavior and sheet resistance. The Ag/SAC305 clusters in the composite ink sintered at 170°C grew, on average, to ~201.1–226.1 nm as a result of faster local liquid-phase sintering, and most of the Ag particles were mutually linked, dramatically changing the microstructure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Sirringhaus, T. Kawase, R.H. Friend, T. Shimoa, M. Inbasekaran, W. Wu, and E.P. Woo, Science 290, 2123 (2000).
D. Huang, F. Liao, S. Molesa, D. Redinger, and V. Subramanian, J. Electron. Soc. 150, G412 (2003).
Q. Cao, H.-S. Kim, N. Pimparkar, J.P. Kulkarni, C. Wang, M. Shim, K. Roy, M.A.A. Alam, and J.A. Rogers, Nature 454, 495 (2008).
E. Fisslthaler, S. Sax, U. Scherf, G. Mauthner, E. Moderegger, K. Landfester, and E.J.W. List, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 183305 (2008).
J. Perelaer, M. Klokkenburg, C.E. Hendriks, and U.S. Schubert, Adv. Mater. 21, 4830 (2009).
J.D. Kim, J.S. Choi, B.S. Kim, Y.C. Choi, and Y.W. Cho, Polymer 51, 2147 (2010).
Y. Li, Y. Wu, and B.S. Ong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 3266 (2005).
K.J. Lee, B.H. Jun, T.H. Kim, and J. Joung, Nonotechnology 17, 2424 (2006).
S. Joo and D.F. Baldwin, Proceedings of 57th ECTC (EIA/IEEE, 2007), pp. 219–226.
J. Perelaer, A.W.M. de Laat, C.E. Hendriks, and U.S. Schubert, J. Mater. Chem. 18, 3209 (2008).
S. Magdassi, M. Grouchko, O. Berezin, and A. Kamyshny, ACS Nano 4, 1943 (2010).
K. Woo, D. Kim, J.S. Kim, S. Lim, and J. Moon, Langmuir 25, 429 (2009).
C.D. Zou, Y.L. Gao, B. Yang, X.Z. Xia, Q.J. Zhai, C. Andersson, and J. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 351 (2009).
Y. Gao, C. Zou, B. Yang, Q. Zhai, J. Liu, E. Zhuravlev, and C. Schick, J. Alloys Compd. 484, 777 (2009).
Y.H. Jo, I. Jung, C.S. Choi, I. Kim, and H.M. Lee, Nanotechnology 22, 225701 (2011).
S–.S. Chee and J.-H. Lee, Appl. Mech. Mater. 249–250, 939 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (2011-0009088). The authors thank Able Metal Co., Ltd (http://www.ablemetal.co.kr) for the SAC305 NPs and the Korean Basic Science Institute (Seoul) for the TEM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, Y.M., Kim, HJ., Jang, S.P. et al. Enhancement of Processability and Electrical Resistance by Use of Ag-Based Composite Inks Containing Ultrafine SAC305 Alloy Nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 3372–3378 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3245-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3245-8