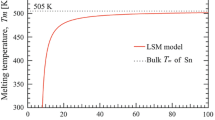
Due to the toxicity of lead (Pb), Pb-containing solder alloys are being phased out from the electronics industry. This has lead to the development and implementation of lead-free solders. Being an environmentally compatible material, the lead-free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (wt.%) solder alloy is considered to be one of the most promising alternatives to replace the traditionally used Sn-Pb solders. This alloy composition possesses, however, some weaknesses, mainly as a result of its higher melting temperature compared with the Sn-Pb solders. A possible way to decrease the melting temperature of a solder alloy is to decrease the alloy particle size down to the nanometer range. The melting temperature of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu lead-free solder alloy, both as bulk and nanoparticles, was investigated. The nanoparticles were manufactured using the self-developed consumable-electrode direct current arc (CDCA) technique. The melting temperature of the nanoparticles, with an average size of 30 nm, was found to be 213.9°C, which is approximately 10°C lower than that of the bulk alloy. The developed CDCA technique is therefore a promising method to manufacture nanometer-sized solder alloy particles with lower melting temperature compared with the bulk alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Suganuma, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 5, 55 (2001).
M. Amagai, M. Watanabe, M. Omiya, K. Kishimoto, T. Shibuya. Microelectron. Reliab. 42, 951 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0026-2714(02)00017-3
F.L. Zhu, H.H. Zhang, R.F. Guan, and S. Liu, J. Alloy. Compd. 438, 100 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.08.009
W.B. Guan, S.C. Verma, Y.L. Gao, C. Andersson, Q.J. Zhai, and J. Liu, Proceedings of the 1st IEEE CPMT Electronics Systemintegration Technology Conference (ESTC2006), September 5–7, Dresden, Germany, 2006, p. 7.
J. Liu, T. Wang, W.B. Guan, M.O. Olorunyomi, M. Jonsson, W.X. Wang, T. Aronsson, X.Z. Lu, Y.L. Gao, Q.J. Zhai, E.B.C. Eleanor, and D.K. Shangguan, Proceedings of International Microelectronics and Packaging Conference (IMAPS), Nordic, September 17–19, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2006, p. 212.
W. Liu, X.Y. Deng, and Z.K. Zhang, Phys. Chem. Test. A Phys. Test 40, 64 (2004) (in Chinese)
L.H. Xin, R.M. Zhou, B.G. Ekoko, O.F. Adeleke. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Processe. 22, 69 (2004)
M.L. Lavčević, Z. Ogorelec, Mater. Lett. 57, 4134 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00278-7
W. Liu, X.P. Zhang, Z.L. Cui, and Z.K. Zhang, Chin. J. Rare Met. 28, 1082 (2004) in Chinese
L.F. He, R.M. Zou, L.H. Xin, O.F. Adeleke, C.W. Pan. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 23, 6 (2005)
L.Y. Hsiao, J.G. Duh. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, J105–J109 (2005) doi:10.1149/1.1954928
H.J. Jiang, K. Moon, F. Hua, C.P. Wong. Chem. Mater. 19, 4482 (2007) doi:10.1021/cm0709976
Q.J. Zhai, Y.L. Gao, W.B. Guan, Y.Y. Gong, R.X. Li, X. Hou, and J. Liu, Chinese patent 200610026216.0 (2006) (in Chinese).
X.Z. Xia, C.D. Zou, Y.L. Gao, J. Liu, and Q.J. Zhai, Proceedings of 2007 International Symposium on High Density Packaging and Microsystem Integration (HDP’07), Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, June 27–30, 2007, p. 302.
P.R. Couchman, W.A. Jesser. Nature 269, 481 (1977) doi:10.1038/269481a0
C.R.M. Wronski, Br. J. Appl. Phys. 18, 1731 (1967) doi:10.1088/0508-3443/18/12/308
P. Buffat, J. Borel, Phys. Rev. A 13, 2287 (1976) doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.13.2287
Q.S. Mei, K. Lu, Prog. Mater. Sci. 52, 1175 (2007) doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2007.01.001
W.A. Jesser, R.Z. Shneck, W.W. Gile. Phys. Rev. B 69, 144121 (2004) doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.69.144121
C.T. Schamp, W.A. Jesser. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1825 (2006) doi:10.1007/s11661-006-0125-8
M. Abtew, G. Selbaduray. Mater. Sci. Eng. Rep. 27, 95 (2000) doi:10.1016/S0927-796X(00)00010-3
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) with Contract No. 2006AA 03Z339. The authors would also like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50571057, 50401023), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (Grant No. 06QA14020), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission Program (Grant No. 2006AZ002), and the National Swedish Research Council for support of the project “Nanointerconnect” with contract No. 621-2007-4660.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, C.D., Gao, Y.L., Yang, B. et al. Nanoparticles of the Lead-free Solder Alloy Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu with Large Melting Temperature Depression. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 351–355 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-008-0591-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-008-0591-4