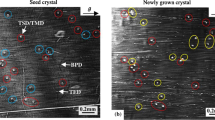
Electron–hole recombination-activated partial dislocations in 4H silicon carbide homoepitaxial layers and their behavior have been studied using synchrotron X-ray topography and electroluminescence. Stacking faults whose expansion was activated by electron–hole recombination enhanced dislocation glide were observed to be bounded by partial dislocations, which appear as white stripes or narrow dark lines in back-reflection X-ray topographs recorded using the basal plane reflections. Such contrast variations are attributable to the defocusing/focusing of the diffracted X-rays due to the edge component of the partial dislocations, which creates a convex/concave distortion of the basal planes. Simulation results based on the ray-tracing principle confirm our argument. Observations also indicate that, when an advancing partial dislocation interacts with a threading screw dislocation, a partial dislocation dipole is dragged behind in its wake. This partial dislocation dipole is able to advance regardless of the immobility of the C-core segment. A kink pushing mechanism is introduced to interpret the advancement of this partial dislocation dipole.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Koga, Y. Fujikawa, Y. Ueda, T. Yamaguchi, Springer Proc. Phys. 71, 96 (1992)
H. Chen, B. Raghothamachar, W. Vetter, M. Dudley, Y. Wang, B. Skromme, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 911, 0911-B05-24 (2006)
Y. Chen, G. Dhanaraj, W. Vetter, R. Ma, M. Dudley, Mater. Sci. Forum. 556–557, 231 (2007)
H. Lendenmann, F. Dahlquist, N. Johansson, R. Soderholm, P.A. Nilsson, J.P. Bergman, P. Skytt, Mater. Sci. Forum. 353–356, 727 (2001)
A. Galeckas, J. Linnros, P. Pirouz, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 883 (2002)
S. Ha, M. Benamara, M. Skowronski, H. Lendinmann, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4957 (2003)
S. Ha, M. Skowronski, J.J. Sumakeris, M.J. Paisley, M.K. Das, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 175504 (2004)
R.E. Stahlbush, M. Fatemi, J.B. Fedison, S.D. Arthur, L.B. Rowland, W. Wang, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 370 (2002)
Y. Chen, G. Dhanaraj, M. Dudley, E.K. Sanchez, and M.F. MacMillan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 071917 (2007)
Y. Chen and M. Dudley, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 141918 (2007)
X.R. Huang, D.R. Black, A.T. Macrander, J. Maj, Y. Chen, and M. Dudley, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2007) (in press)
K.X. Liu, R.E. Stahlbush, K.B. Hobart, J.J. Sumakeris, Mater. Sci. Forum. 527–529, 387 (2006)
R.E. Stahlbush, M. Fatemi, J.B. Fedison, S.D. Arthur, L.B. Rowland, S. Wang, J. Elec. Mater. 31, 370 (2002)
Y. Chen, M. Dudley, E.K. Sanchez, and M.F. MacMillan, J.␣Electron. Mater. (in press)
M. Dudley, X.R. Huang, W. Huang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 32, A139 (1999)
X.R. Huang, M. Dudley, W.M. Vetter, W. Huang, S. Wang, C.H. Carter Jr., Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 353 (1999)
P. Pirouz, M. Zhang, A. Galeckas, J. Linnros, Mater. Sci. Forum. 815, J6.1.1 (2004)
The core structure can be verified by using the right-hand rule to determine the position of the extra half-plane associated with the PD: assuming the line direction of the Shockley PD loop bounding the SF is clockwise, one can determine that the extra half-planes for segments AB, CD, and EF lie on the same side of the dislocation line (above the plane of the pictures); therefore they have the same core structure. On the contrary, the extra half-planes of segment BC and DE lie underneath the plane of the pictures, indicating the opposite core structure
P. Pirouz, J.L. Demenet, M.H. Hong, Phil. Mag. A 81, 1207 (2001)
Y. Chen, M. Dudley, K.X. Liu, R.E. Stahlbush, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 171930 (2007)
S. Ha, H.J. Chung, N.T. Nuhfer, M. Skowronski, J. Cryst. Growth 262, 130 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by ONR Grants N0001140010348, N000140110302, and N000140 211014 (Contract Monitor Dr. Colin Wood) and by Dow Corning Corporation under Contract Nos. N0001405C0324 and DAAD1701C0081. Topography experiments were carried out at the Stony Brook Synchrotron Topography Facility, beamline X-19C, at the NSLS (Contract No. DE-AC02-76CH00016) and beamline XOR-33BM, Advance Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, which is supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Contract No. W-31-109-ENG-38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhang, N., Dudley, M. et al. Investigation of Electron–Hole Recombination-Activated Partial Dislocations and Their Behavior in 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layers. J. Electron. Mater. 37, 706–712 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-007-0328-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-007-0328-9