Abstract
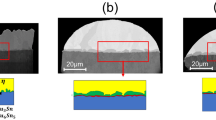
The spalling phenomenon on under bump metallization (UBM) is one of the current urgent reliability issues for the Pb-free solder implementation in flip chip technology. In this paper, we report that spalling of Ni thin UBM can be prevented during the soldering reaction, if a Cu reservoir is introduced into the structure of controlled collapse chip connections (C4) solder joints. Once molten Sn-3.5Ag solder was saturated with Cu atoms, Cu precipitated out as a layer of Cu-Sn compound on Ni thin UBM. The Cu-Sn compound layer served as a reaction barrier to retard the consumption of Ni thin UBM. So, spalling was retarded. After prolonged reflowing, Ni thin UBM was converted to ternary Cu-Sn-Ni compounds. Unlike interfaces of the Ni-Sn compound/Cr, the interface of the Cu-Sn-Ni compound/Cr was very stable and no spalling was found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The International Technology Road Map for Semiconductors (San Jose, CA: Semiconductors Industry Association, 2000), pp. 215–235.
J.H. Lau, Flip Chip Technologies (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1996), pp. 42–63.
Rao R. Tummala, Fundamentals of Microsystems Packaging, Chapter 7 (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001).
Ann A. Liu, H.K. Kim, and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 80, 2774 (1996).
C.Y. Liu, H.K. Kim, K.N. Tu, and P.A. Totta, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 4014 (1996).
B.S. Berry and I. Ames, IBM J. Res. Dev. 13, 286 (1969).
P.A. Totta and R.P. Sopher, IBM J. Res. Dev. 13, 226 (1969).
C.Y. Liu, Chih Chen, A.K. Mal, and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 3882 (1999).
C.Y. Liu, K.N. Tu, T.T. Sheng, C.H. Tung, D.R. Frear, and P. Elenius, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 11 (1999).
Database for Solder Properties on New Lead-Free Solders (CO: National Institute of Standards & Technology, 2000), pp. 2–30.
National Electronics Manufacturing Initiative (NEMI) Lead-Free Readiness Task Force Report (Herdon, VA: NEMI, 1999), pp. 5–10.
Lead-Free Solder Project (National Center for Manufacturing Sciences [NCMS], website: www.ncms.org).
M. Li, F. Zhang, W.T. Chen, K. Zeng, K.N. Tu, H. Balkan, and P. Elenius, J. Mater. Res. 17, 1612 (2002).
P.G. Kim, J.W. Jang, T.Y. Lee, and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 6746 (1999).
J.W. Jang, P.G. Kim, K.N. Tu, D.R. Frear, and P. Thompson, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 8456 (1999).
J.W. Jang, D.R. Frear, and T.Y. Lee, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 6359 (2000).
J.W. Jang, private communication with the authors, Motorola, Phoenix, AZ, Oct., 2001.
T.M. Korhonen, P. Su, S.J. Hong, M.A. Korhonen, and C.-Y. Li, J. Electron. Mater. 28, 1146 (1999).
C.-H. Lin (M.S. Thesis, National Tsing-Hua University, 2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C.Y., Wang, S.J. Prevention of spalling by the self-formed reaction barrier layer on controlled collapse chip connections under bump metallization. J. Electron. Mater. 32, L1–L3 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-003-0251-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-003-0251-7