Abstract
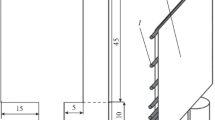
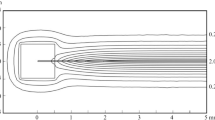
The electromagnetic probe of Ricou and Vives for measurement of velocity in liquid metals is well known. This probe incorporates a permanent magnet. Consequently, the use of the probe at temperatures approaching the Curie temperature of the magnet is difficult. Above that temperature, the probe is inoperable. This article describes a modification of the probe; the permanent magnet was replaced by an electromagnet. The article treats the theory of using an electromagnet and gives an account of experiments in which the principle of the probe was demonstrated by velocity measurements in an alloy with a low melting point. Circuits for measurements with the electromagnet driven by both alternating and direct current are described; better results were obtained with the latter. Two types of probes were examined, one intended for complete submersion in the melt and the other for measurements near the surface of the melt. An air-cooled version was found to withstand external temperatures of 970 K, while the internal temperature remained below 390 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ricou and C. Vives: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1982, vol. 25, p. 1579.
H.-C. Lee, J.W. Evans, and C. Vives: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 734–36.
S.K. Banerjee and J.W. Evans: Metall. Trans. B, 1990, vol. 21B, pp. 59–69.
B.Q. Li, D.P. Cook, and J.W. Evans: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1989, vol. 29, p. 1048.
D.P. Cook, S. Nishioka, and J.W. Evans, Metall. Trans. B, 1995, vol. 26B, pp. 1271–80.
E. Takeuchi, H. Harada, H. Tanaka, and H. Kajioka: in Magnetohydrodynamics in Process Metallurgy, J. Szekley, J.W. Evans, K. Blazek, and N. El-Kaddah, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1991, pp. 261–66.
C. Vives and R. Ricou: Light Metals 1986, R.E. Miller, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 873–82.
J.A. Shercliff: A Textbook of Magnetohydrodynamics, Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1965.
R. Moreau: Magnetohydrodynamics, Kluwer, Dordrecht, Germany, 1990.
H. Hayashi: Master’s Thesis University of California, Berkeley, CA, 1997.
W.R. Smythe: Static and Dynamic Electricity, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1950.
M. Iguchi, H. Kawabata, Y. Demoto, and Z. Morita: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1994, vol. 34, p. 461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, H., Becker, A. & Evans, J.W. Toward a probe for velocity measurement in molten metals at high temperatures. Metall Mater Trans B 30, 623–630 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-999-0023-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-999-0023-8