Abstract
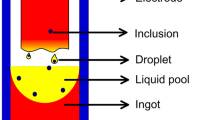
The electronic scanning microscope is applied to analyze the inclusion distribution in the ingot middle part. It is observed that the large-size inclusions are mainly located at a distance of 1.6 mm from side surface. With the distance increasing, the area fraction, number density, and diameter of inclusion decrease clearly. As the inclusion is assumed as spherical, the melt flow, solidification, and particle redistribution are simulated by a coupled model. With the electric power applied, the electromagnetic force shows a maximum in the ingot edge part, which pushes liquid from the edge part to the inner part. The particle movement is both affected by fluid flow and particle buoyancy force. In the earlier remelting stage, fluid flow is dominated by electromagnetic force and it drives the particle moving from the inner top part to the ingot bottom, where it can be captured. As the liquid pool depth increases in the later stage, the thermal flow drives the particle moving along the solidification front. Due to particle buoyancy, the 50 μm diameter particle floats up, and it is mainly located in the ingot side surface. For the 2 or 10 μm particle, it still exists in the inner part.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Van Den Avyle, J.A. Brooks, and A.C. Powell: JOM, 1998, vol. 50, pp. 22–5.
K.O. Yu, J.A. Domingue, G.E. Maurer, and H.D. Flanders: JOM, 1986, vol. 38, pp. 46–50.
S. Tin, P.D. Lee, A. Kermanpur, M. McLean, and M. Rist: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 2493–504.
H.C. Kou, Y.J. Zhang, Z.J. Yang, P.F. Li, J.S. Li, and L. Zhou: Int. J. Eng. Technol., 2014, vol. 12, pp. 50–6.
M. Revil-Baudard, A. Jardy, H. Combeau, F. Leclerc, and V. Rebeyrolle: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 51–7.
D. Zagrebelnyy and M.J.M. Krane: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 281–88.
K. Pericleous, G. Djambazov, M. Ward, L. Yuan, and P.D. Lee: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 5365–76.
X. Wang, M.D. Barratt, R.M. Ward, and M.H. Jacobs: J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 7169–4.
J. Valdés, P. King, and X. Liu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 2408–16.
J. Cui, B. Li, Z. Liu, F. Qi, J. Xu, and J. Zhang: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, vol. 18, pp. 3991–4006.
J.F. Grignard, A. Soller, J. Jourdan, J.P. Bellot, and A. Jardy: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2011, vol. 13, pp. 563–69.
W. Zhang, P.D. Lee, and M. McLean: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 443–54.
X. Wang, R.M. Ward, M.H. Jacobs, and M.D. Barratt: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 2981–89.
A. Jardy and D. Ablitzer: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2009, vol. 25, pp. 163–69.
G. Ghazal, A. Jardy, P. Chapelle, and Y. Millet: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41B, pp. 646–59.
Z. Chen, S. Yang, J. Qu, J. Li, A. Dong, and Y. Gu: Materials, 2018, vol. 11, p. 1838.
E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, M. Wu, A. Ludwig, and J. Bohacek: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 222–35.
Y. Yin and J. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2021, vol. 61, pp. 853–64.
Z. Liu, B. Li, L. Xiao, and Y. Gan: Acta Metall. Sin., 2022, vol. 58, pp. 1236–52.
Z.Y. Xin, H.N. Cui, T. Li, G.Z. Tang, Y.L. Zhu, J.C. Yan, and J.G. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, vol. 53B, pp. 2570–86.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful for the support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904024 and U22A20171), the High Steel Center (HSC) at North China University of Technology and University of Science and Technology Beijing.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, D., Ren, Y. & Zhang, L. Numerical Simulation of Inclusion Distribution in Vacuum Arc Remelting Ingot. Metall Mater Trans B 54, 1342–1351 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02765-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02765-w