Abstract
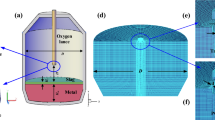
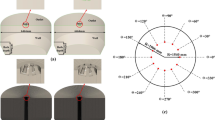
Numerical simulations are performed to explore the basic blowing characteristics of a dynamic free lance converter applied to hot metal dephosphorization technology, in which the sliding mesh model (SMM) is used to regulate the rotation motion of the top lance and the volume of fluid (VOF) model is inducted to simulate flows of gaseous oxygen, liquid slag and metal. The fundamental phenomena such as the motion of phase interfaces, slag–metal emulsion and mixing, and shape and magnitude of the velocity field inside the slag–metal bath are predicted reasonably well, and effects of lance designs including the lance twist angle and rotation speed on the blowing characteristics are evaluated. The results show that the rotation motion of the lance improves the flows inside the molten bath and induces remarkable circumferential and swirl flows around the hot spot. Such flows change the splashing mode and accelerate the dispersion of the splashed metal inside the slag layer, consequently producing a quite uniform distribution of metal phase in emulsion and promoting slag–metal emulsion and mixing. The slag–metal emulsion is strengthened when increasing the lance twist angle, but achieves its minimum at the lance rotation speed of 1.0472 rad/s. The effects of the lance twist angle and rotation speed on flow fields inside the molten bath vary with the bath depth.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
1.R. Sambasivam, S.N. Lenka, F. Durst, M. Bock, S. Chandra and S.K. Ajmani: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2007, Vol. 38, pp. 45-53.
2.M.M. Li, Q. Li, Z.S. Zou and X.Z. An: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, Vol. 48, pp. 713-25.
3.S. Banya, M. Hino, R. Nagabayashi and O. Terayama: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1989, vol. 75, pp. 66-73.
4.M. Miyata, T. Tamura, and Y. Higuchi: ISIJ Int. 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1751-55.
5.M. Miyata, T. Tamura, and Y. Higuchi: ISIJ Int. 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1756-61.
6.M. Miyata, and Y. Higuchi: ISIJ Int. 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1742-50.
M.M. Li, L. Li, B. Zhang, Q. Li, W. Wu and Z.S Zou, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 1718-30.
8.R. B. Banks and A. Bhavamai: J. Fluid Mech., 1965, vol. 23, pp. 229-40.
9.F. Qian, R. Mutharasan and B. Farouk: Metall. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 911-20.
10.M.J. Luomala, T.M.J. Fabritius, E.O. Virtanen, T.P. Siivola, T.L.J. Fabritius, H. Tenkku and J.J. Härkki: ISIJ Int. 2002, vol. 42, pp. 1219-24.
11.M.J. Luomala, T.M.J. Fabiritius, and J.J. Harkki: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 809-16.
12.S. Sabah and G.A. Brooks: ISIJ Int. 2014, vol. 54, pp. 836-44.
13.S. Sabah and G.A. Brooks: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 863-72.
M.M. Li, Q. Li, S.B. Kuang and Z.S. Zou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 116-26.
15.H.J. Odenthal, U. Falkenreck and J. Schlüter: ECCOMAS CFD Conference Proceedings, TU Delft, The Netherlands, 2006.
16.H.J. Odenthal, J. Kempken, J. Schluter and W.H. Emling: Iron Steel Technol. 2007, vol. 4, pp. 71-89.
17.M. Ersson, A. Tilliander, L. Jonsson and P. Jönsson: ISIJ Int. 2008, vol. 48, pp. 377-84.
18.H. Y. Hwang and G. A. Irons: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 575-91.
19.M. Alam, J. Naser, G. Brooks and A. Fontana: ISIJ Int. 2012, vol. 52, pp. 1026-35.
20.Y. Lytvynyuk, J. Schenk, M. Hiebler and A. Sormann: Steel Res. Int. 2014, vol. 85, pp. 537-43.
21.Y. Doh, P. Chapelle, A. Jardy, G. Djambazov, K. Pericleous, G. Ghazal and P. Gardin, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 653-70.
22.X.B. Zhou, M. Ersson, L.C. Zhong, J.K. Yu and P. Jönsson: Steel Res. Int., 2014, vol. 85, pp. 273-81.
23.Y. Li, W.T. Lou and M.Y. Zhu: Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, vol. 40B, pp. 505-14.
24.M. Lv, R. Zhu, Y.G. Guo and Y.W. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1560-71.
25.Q. Li, M.M. Li, S.B. Kuang and Z.S. Zou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1494-509.
26.M.M. Li, Q. Li, S.B. Kuang and Z.S. Zou: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, vol. 55, pp. 3630-40.
27.G.S. Wei, R. Zhu, T. Cheng, K. Dong, L.Z. Yang and X.T. Wu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 49B, pp. 361-74.
28.L.L. Cao, Y.N. Wang, Q. Liu and X.M. Feng: ISIJ Int. 2018, vol. 58, pp. 573-84.
29.C.W. Hirt and B.D. Nichols: J. Comput. Phys. 1981, vol. 39, pp. 201-25.
30.J.U. Brackbill, D.B. Kothe, and C. Zemach: J. Comput. Phys. 1992, vol. 100, pp. 335-54.
31.B.E. Launder and D.B. Spalding: Lectures in Mathematical Model of Turbulence, Academic Press, London, 1972, p. 124.
32.R. Steijl and G. Barakos: Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids, 2008, vol. 58, pp. 527-49.
A. Bakker, R.D. Laroche, M.H. Wang and R.V. Calabrese: Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1997, Vol. 75, pp. 42-44.
FLUENT 14.0 Manual. Ansys Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, 2011.
35.O. Ubbink and R.I. Isssa: J. Comput. Phys. 1999, vol. 153, pp. 26-50.
D. Price: Process Engineering of Pyrometallurgy, London: 1974, pp. 8–15.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51904062), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M650056) and the Fundamental Research Funds of the Central Universities of China (N2025015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted February 4, 2021; accepted March 15, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Shao, L., Li, Q. et al. A Numerical Study on Blowing Characteristics of a Dynamic Free Oxygen Lance Converter for Hot Metal Dephosphorization Technology Using a Coupled VOF-SMM Method. Metall Mater Trans B 52, 2026–2037 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02155-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02155-0