Abstract
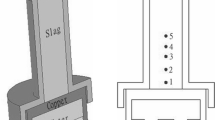
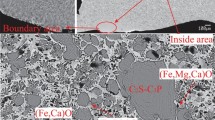
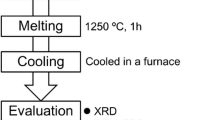
EAF slag constitutes a major waste in the steel industry, which necessitates the development of processes to recover its valuable compounds and thermal energy values. A promising method involves the modification of the composition of EAF slag melts to utilize its waste heat and recover more valuable elements by controlled crystallization of spinel under a cooling process. In this study, crystallization behaviors of modified EAF slag melts with a basicity of 1.2 were investigated, with the aim of precipitating more magnetic spinel phases, and leaving a matrix with the amorphous phase, which favors subsequent utilization in the cement industry. Samples were prepared at different cooling temperatures, for different holding times, or quenched by air or water. Results show that two kinds of spinel phases were found during the cooling process of the melts. One was bulky spinel (BS) in granular form with size > 40 μm, and the other was dendritic spinel (DS) with arms < 20 μm. Three stages existed in the crystallization process of the melts. It is crucial to keep the slag melts in stage one for less than 30 minutes and then rapidly cool it to stage three. More and larger BS was obtained when this method was applied.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Energy Agency: Energy Balance Flows, https://www.iea.org. Accessed 5 June 2019.
M. Barati and S. Jahanshahi: in: 3rd Slag Valorization Symposium, Unpublished Research, Mechelen Belgium, 2019.
G. Bisio: Energy, 1997, vol. 22, pp. 501-9.
Y. Li and W. B. Dai: J. Cleaner Prod., 2018, vol. 175, pp. 176-89.
S. C. Tian, J. C. Jiang, F. Yan, K. M. Li and X. Chen: Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, vol. 49, pp. 7464-72.
S. Sorlini, A. Sanzeni and L. Rondi: J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, vol. 209-10, pp. 84-91.
P. E. Tsakiridis, G. D. Papadimitriou, S. Tsivilis and C. Koroneos: J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, vol. 152, pp. 805-11.
S. N. Lekakh, C. H. Rawlins, D. G. C. Robertson, V. L. Richards and K. D. Peaslee: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39, pp. 125-34.
J. H. Park, J. J. Wang, S. H. Kim, J. S. Cho, S. W. Kang, R. D. Delaune and D. C. Seo: Chem. Eng. J., 2017, vol. 327, pp. 713-24.
X. Lu, Y. Li, S. Ma, W. B. Dai and D. Q. Cang: Chin. J. Eng., 2016, vol. 38, pp. 1386-92.
R. Sarkar, N. Singh and S. D. Kumar: Bull. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 33, pp. 293-8.
G. Kim and I. Sohn: J. Hazard. Mater., 2018, vol. 359, pp. 174-85.
Y. J. Tu, C. F. You and C. K. Chang: J. Hazard. Mater., 2013, vol. 258-9, pp. 102-8.
A. Semykina and S. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. 2011, vol. 42, pp. 2-4.
V. Shatokha, A. Semykina, J. Nakano, S. Sridhar and S. Seetharaman: J. Min. Metal. B, 2013, vol. 49, pp. 169-74.
K. K. Cui, Z. J. Wu, W. Huang, Z. F. Gao, X. M. Shen and W. M. Liu: ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2014, vol. 2, pp. 344-7.
X. Peng, D. He, A. Xu, Z. Gu, Q. Yang, F. Engström and B. Bo: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 712, pp. 640-8.
A. Semykina, V. Shatokha, and S. Seethareama: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2011, vol. 37, pp. 536–40.
Y. Li, X. M. Liu, H. H. Sun and D. Q. Cang: Sci. China Technol. Sci., 2011, vol. 54, pp. 105-9.
C. Pellegrino and V. Gaddo: Cem. Concr. Compos., 2009, vol. 31, pp. 663-71.
O. Bretcanu, S. Spriano, E. Verné, M. Cöisson, P. Tiberto and P. Allia: Acta Biomater., 2005, vol. 1, pp. 421-9.
V. D. Eisenhuttenleute: Slag Atlas, 2nd ed., Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Duesseldorf, 1995, pp. 126.
S. Hara, K. Irie and K. Ogino: Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1988, vol. 29, pp. 977-89.
S. S. Jung and I. Sohn: Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 48, pp. 1886-92.
T. Osugi, S. Sukenaga, Y. Inatomi, Y. Gonda, N. Saito and K. Nakashima: ISIJ Int., 2013 vol. 53, pp. 185-90.
B. O. Mysen: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2006, vol. 70, pp. 3121-38.
Z. Wang, Y. Sun, S. Sridhar, Z. Mei and Z. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 2246-54.
X. Lu: Study on the effects of EAF slag hot modification on its iron recovery and the cementitious activity, Doctoral Dissertation, University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017.
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1960201) and by the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFB0601304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted August 18, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Meng, X., Chen, K. et al. Crystallization Behaviors of Spinel During Cooling Process of Modified EAF Slag. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 1027–1038 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01802-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01802-2