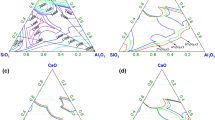
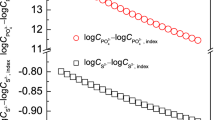
Abstract
Desulfurization behavior was investigated based on a wide slag composition and working temperature range. Moreover, the rate-controlling step (RCS) for desulfurization with regard to the ladle-refining conditions and the transition of the RCS by changing the slag composition was systematically discussed. The desulfurization ratio reached an equilibrium value within approximately 15 minutes irrespective of the CaO/Al2O3 (=C/A = 1.3 to 1.9) and CaO/SiO2 (=C/S = 3.8 to 6.3) ratios. However, the desulfurization behavior of less basic slags (C/A = 1.1 or C/S = 1.9) exhibited a relatively sluggish [S]-decreasing rate as a function of time. The equilibrium S partition ratio increased with an increase in slag basicity (C/A and C/S ratio), not only due to an increase in sulfide capacity but also due to a decrease in oxygen activity in the molten steel. There was a good correlation between the calculated and measured S partition ratios at various slag compositions. However, the measured S partition ratio increased by adding 5 pct CaF2, followed by a constant value. Multiphase slag exhibited a relatively slow desulfurization rate compared to that of fully liquid slag, possibly due to a decrease in the effective liquid slag volume, interfacial reaction area, and a relatively slow slag initial melting rate due to a high melting point. The activation energy of the desulfurization process was estimated to be 58.7 kJ/mol, from which it was proposed that the desulfurization reaction of molten steel via CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-MgO-CaF2 ladle slag was generally controlled by the mass transfer of sulfur in the metal phase. However, there was a transitional period associated with the rate-controlling mechanism due to a change in the physicochemical properties of the slag. For slag with a viscosity greater than about 1.1 dPa·s and an equilibrium S partition ratio lower than about 400, the overall mass-transfer coefficient was affected by the slag properties. Hence, it was theoretically and experimentally confirmed that the RCS of the desulfurization process under secondary refining conditions was strongly dependent on thermodynamic driving forces as well as the viscosity of the slag.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
FACTSAGE is a trademark of Thermfact-CRCT (Montreal, Canada) and GTT-Technologies (Aachen, Germany).
LECO is a trademark of LECO Corporation, St. Joseph, MI.
REFERENCES
L.J.P. Olund, T.B. Lund, and B.H. Hedberg: Proceedings of the 5th International. Clean Steel Conference, Hungarian Mining and Metallurgical Society, Hungary, 1999, pp. 137–43.
M. Hino, S. Kitagawa, and S. Ban-Ya: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 36–42.
S. He, G. Zhang, and Q. Wang: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 977–83.
M.K. Cho, J. Cheng, J.H. Park, and D.J. Min: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 215–21.
T.S. Kim and J.H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 2031–38.
S. Ban-ya, M. Hobo, T. Kaji, T. Itoh, and M. Hino: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 1810–16.
J. Ishida, K. Yamaguchi, S. Sugiura, K. Yamano, S. Hayakawa, and N. Demukai: Denki-Seiko, 1981, vol. 52, pp. 2–8.
T. Ebisawa, A. Ishii, H. Tenma, H. Kawakami, and K. Kikuchi: Proceedings of the 7th ICVM, Japan, 1985.
K. Schwerdtfeger: Arch. Eisenhuttenwes., 1983, vol. 54, p. 3.
R. Fruehan: Ladle Metallurgy, Principles and Practices, Iron & Steel Society (ISS), Warrendale, PA, 1985.
I. Sawada, T. Kitamura, and T. Ohashi: Proceedings of the Scaninject IV, MEFOS, Lulea, Sweden, 1986, p. 12.1.
Q. Ying, L. Yun, and L. Liu: Proceedings of the Scaninject III, Part I, MEFOS, Lulea, Sweden, 1983, paper no. 21.
T. Kitamura, K. Shibata, I. Sawada, and S. Kitamura: Proceedings of the 6th International Iron & Steel Congress (IISC), ISIJ, Japan, 1990, vol. 3, pp. 50–56.
H. Kataoka and T. Miyauchi: Kagaku-Kogaku, 1969, vol. 33, pp. 181–86.
J. Peter, K.D. Peaslee, D.G.C. Robertson, and B.G. Thomas: Proceedings of the AISTech 2005, AIST, Warrendale, PA, 2005, pp. 959–67.
D.G.C. Robertson and B.B. Staples: Process Engineering of Pyrometallurgy, IMM, London, 1974, pp. 51–59.
F. Oeters: Metallurgie der Stahlherstellung, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf, and Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1994.
M.G. Frohberg and A. Nillas: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1969, vol. 9, p. 355.
J.X. Deng and F. Oeters: Proceedings of the 7th Japan-Germany Seminar on Fundamentals of Iron and Steelmaking, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf, 1987, p. 33.
Y.H. Kim: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Strathclyde, Glasgow, United Kingdom, 1978.
B. Deo and P. Grieveson: Steel Res., 1986, vol. 57, pp. 514–19.
B. Deo and P. Grieveson: Steel Res., 1988, vol. 59, pp. 263–68.
J.C. Fulton and J. Chipman: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1959, vol. 215, p. 113.
K.M. Goldman, G. Derge, and W.D. Philbrook: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1954, vol. 200, pp. 534–40.
S. Ramachandran, T.B. King, and N.J. Grant: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1956, vol. 206, pp. 1549–53.
F. Patsiogiannis, U.B. Pal, and R.S. Bogan: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 140–49.
R.J. Fruehan: Trans. Iron Steel Soc, 1985, vol. 6, pp. 43–49.
T.B. King: in Electric Furnace Steelmaking, C.R. Taylor, ed., Iron and Steel Society (ISS), Warrendale, PA, 1985.
D. Roy, P.C. Pistorius, and R.J. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1086–94.
B. Deo and R. Boom: Fundamentals of Steelmaking Metallurgy, Prentice Hall, New York, NY, 1993.
P. Yan, X. Guo, S. Huang, J.V. Dyck, M. Guo, and B. Blanpain: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 459–67.
X. Chushao and T. Xin: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 1081–83.
V. Seshadri, C.A. da Silva, I.A. da Silva, and P. von Kruger: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 21–30.
G.G. Roy, P.N. Chaudhary, R.K. Minj, and R.P. Goel: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 558–61.
J.K. Jung and J.J. Pak: J. Kor. Inst. Met. Mater., 2000, vol. 38, pp. 585–90.
J.Y. Choi, D.J. Kim, and H.G. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 216–24.
E.T. Turkdogan: Physical Chemistry of High Temperature Technology, Academic Press, New York, NY, 1980.
M. Hino and K. Ito: Thermodynamic Data for Steelmaking, The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, The 19th Committee on Steelmaking, Tohoku University Press, Sendai, 2010.
www.factsage.com. Accessed Dec. 2015.
C.W. Bale, E. Belisle, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, K. Hack, I.H. Jung, Y.B. Kang, J. Melancon, A.D. Pelton, C. Robelin, and S. Petersen: Calphad, 2009, vol. 33, pp. 295–311.
J.S. Park and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 953–60.
J.S. Park and J.H. Park: Steel Res. Int., 2014, vol. 85, pp. 1303–09.
S.K. Kwon, Y.M. Kong, and J.H. Park: Met. Mater. Int., 2014, vol. 20, pp. 959–66.
Y.S. Han and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 235–42.
J.H. Heo, Y. Chung, and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1154–61.
J.S. Park, D.H. Kim, and J.H. Park: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, vol. 98, pp. 1974–81.
Y.S. Han, D.R. Swinbourne, and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 2449–2557.
S.K. Kwon, J.S. Park, and J.H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 2589–96.
E.H. Jeong, C.W. Nam, K.H. Park, and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 1103–12.
J.H. Shin and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. E, 2016, vol. 3E, pp. 218–26.
J.A. Duffy and M.D. Ingram: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1971, vol. 93, 6448–54.
J.A. Duffy: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1989, vol. 109, pp. 35–39.
J.A. Duffy: J. Chem. Educ., 1996, vol. 73, pp. 1138–42.
T. Nakamura, Y. Ueda, and J.M. Toguri: J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1986, vol. 50, pp. 456–61.
D.J. Sosinsky and I.D. Sommerville: Metall. Trans. B, 1986, vol. 17B, pp. 331–37.
R.W. Young, J.A. Duffy, G.J. Hassall, and Z. Xu: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1992, vol. 19, pp. 201–19.
J.H. Park and D.J. Min: Mater. Trans., 2006, vol. 47, pp. 2038–43.
J.H. Park, G.H. Park, and Y.E. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 1078–83.
G.H. Park, Y.B. Kang, and J.H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1375–82.
G.J.W. Kor and F.D. Richardson: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1969, vol. 245, pp. 319–27.
A. Bronson and G.R.S.T. Pierre: Metall. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 375–80.
J.H. Park, D.J. Min, and H.S. Song: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 33B, pp. 723–29.
J.H. Park and D.J. Min: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 223–28.
J.H. Park and D.J. Min: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2004, vol. 337, pp. 150–56.
A. Ghosh: Secondary Steelmaking—Principles and Applications, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2001.
K.J. Graham and G.A. Irons: Proceedings of the SCANMET III, June 8–11, 2008, MEFOS, Lulea, Sweden, 2008, vol. 1, pp. 385–96.
S. Seetharaman: Fundamentals of Metallurgy, Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2005.
J.W. Robinson, Jr. and R.D. Pehlke: Metall. Trans. B, 1974, vol. 5B, pp. 1041–51.
S. Asai, M. Kawachi, and I. Muchi: Proceedings of the Scaninject III, June 15–17, 1983, MEFOS, Lulea, Sweden, 1983, Part 1, paper no. 12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 3, 2016.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0980-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J.G., Shin, J.H., Chung, Y. et al. Effect of Slag Chemistry on the Desulfurization Kinetics in Secondary Refining Processes. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 2123–2135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0948-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0948-2