Abstract
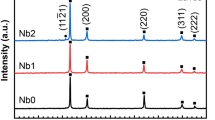
Chromium, nickel, and manganese are common alloying elements in stainless steels. Additionally, titanium and niobium are added as microalloying elements to certain stainless steel grades. A double-stabilized stainless steel sample was dissolved in electrolyte using an electrolytic extraction method. Inclusions were separated from the electrolyte with vacuum filtration and put through a separate elemental analysis. Steel-soluble alloying elements were determined from the electrolyte after the extraction, and the elemental analysis of inclusions was performed. The results were compared to the ones obtained from the surface analysis commonly used in the steel industry. It was concluded that the alloying elements were distributed between inclusions and the steel matrix. Therefore, optical emission analysis from a solid steel sample can be misleading. The results might not accurately depict the composition of the steel matrix. Electrolytic extraction methods combined with elemental analysis provide accurate information about the real matrix composition of microalloying elements in steel. The method is also a tool for the simultaneous analysis of inclusions in 3D and soluble alloying elements.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, B. G. Thomas: Metallurgical and materials transaction B, Vol.37 B, 2006, 733-761.
L. Zhang, B. G. Thomas: ISIJ International, Vol. 43, 2003, No. 3, pp. 271-291.
P. Kaushik, H. Pielet, H. Yin: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2009, Vol.36, No 8, 572-582.
S. Kinoshiro, T. Ishida, M. Inose, K. Fujimoto: ISIJ International, Vol.54, 2014, No. 4, pp.880-884.
J. Janis, K. Nakajima, A. Karasev, S. Jonsson, R. Inoue, P. G. Jönsson: ISIJ International, Vol. 53, 2013, No.2, pp.221-229.
J. Janis, A. Karasev, K. Nakajima, P. G. Jönsson: ISIJ International, 53(3), 2013, 476-483.
Y. Bi, A. Karasev, P G. Jönsson, ISIJ International, Vol. 53, 2013, No. 12, pp.2099-2109.
H. Ohta, H. Suito: ISIJ International, Vol. 46, 2006, No.1, pp. 14-21.
K. Sakata, H. Suito: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, 1053–63.
P. Kaushik, J. Lehmann, M. Nadif: Metallurgical and Materials Transaction B, Vol 43 B, 2012, 710-725.
V. Kuzucu, M. Aksoy, M. H. Korkut: Journal of Materials Processing Technology 82, 1998, 165-171.
M. Aksoy, O. Yilmaz, M. H. Korkut: Wear 249, Issue 8, 2001, 639-646.
H. Yan, H. Bi, X. Li, Z. Xu: Materials Characterization 59, 2008¸1741-1746.
A.L. Rivas, E. Vidal, D.K. Matlock, and J.G. Speer: Rev. Met. Madr., 2008, vol. 44(5), 447–56.
S. G. Hong, K.B. Kang, C. G. Park: Scripta Materialia 46, 2002, 163-168.
M. Fernandes, N. Cheung, A. Garcia: Materials Characterization 48, 2002, 255-261.
C. Peiffert, C. Nguyen-Trung, D. A. Palmer, J. P. Laval, E. Giffaut: J-Solution Chem, 2010, 39, 197-218.
T. Kawai, H. Nishihara, and K. Aramaki: Corros. Sci., 1995, vol. 37(5), pp. 823–31.
J. L. Cavazos: Materials Characterization 56, 2006, 96-101.
H. J. Jun, K. B. Kang, C. G. Park: Scripta Material 49, 2003, 1081-1086.
Acknowledgments
This research is a part of the System Integrated Metal Processing (SIMP) research program coordinated by the Finnish Metals and Engineering Competence Cluster (FIMECC). Outokumpu Stainless Oy and the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (TEKES) are acknowledged for funding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 12, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sipola, T., Alatarvas, T., Heikkinen, EP. et al. Determination of Alloying Elements Ti, Nb, Mn, Ni, and Cr in Double-Stabilized Ferritic Stainless Steel Process Sample Using an Electrolytic Extraction Method and Separate Analysis of Inclusions. Metall Mater Trans B 46, 1775–1781 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0364-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0364-4