Abstract
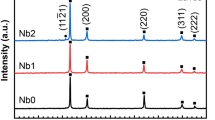
Application of novel low-temperature ionic liquid electrolytes for the extraction of Ti-Al alloys was investigated. The study was focused on the production of Ti-Al alloys from AlCl3-1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride (BmimCl) (molar ratio of AlCl3 and BmimCl is 2:1) at different temperatures between 70 °C and 125 °C ± 3 °C. The Ti-Al alloys were deposited on titanium sheet (>99.9 wt pct) cathodes at various voltages between 1.5 and 3.0 V. Titanium sheet was used as the anode and its dissolution served the source of Ti ion in the electrolyte. Morphology and composition of deposited Ti-Al alloys were investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and an inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES). The phase analysis was carried out using X-ray diffraction (XRD). This study was focused to determine the effect of process variables such as applied voltage and temperature on cathode current density, current efficiency, composition, and morphology of Ti-Al alloys. The Ti-Al alloys containing about 13 to 25 atom pct Ti were produced with a current efficiency of about 79 to 87 pct. This study shows that uniform and fine particle size with high titanium content Ti-Al alloy was obtained in the voltage range of 1.5 to 2.0 V and temperature between 70 °C to 100 °C.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Labconco is a trademark of Labconco Corporation, Kansas City, MO.
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronic Instruments, Mahwah, NJ.
References
D.M. Ferry, G.S. Picard, and B.L. Tremillion: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1988, vol. 135, p. 1443
R.B. Head: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1961, vol. 108, p. 806
A. Robin, and R.B. Ribeiro: J. Appl. Electrochem., 2000, vol. 30, pp. 239–46.
F. Lantelme, K. Kuroda, and A. Barhoun: Electrochim. Acta, 1998, vol. 44, pp. 421–31
G.M. Haarberg, W. Rolland, Å. Sterten, and J. Thonstad: J. Appl. Electrochem., 1993, vol. 23, pp. 217–24
L. Langrand, A. Chausse, and R. Messina: Electrochim. Acta, 2001, vol. 46, pp. 2407–13
E. Chassaing, F. Basile, and G. Lorthioir: J. Less-Common Met., 1979, vol. 68, pp. 153–58
G.M. Janowski, and G.R. Stafford: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, p. 2715
M.R. Ali, A. Nishikata, and T. Tsuru: Indian J. Chem. Technol., 2003, vol. 10, pp. 21–26
T. Tsuda, C.L. Hussey, G.R. Stafford, and J.E. Bonevich: J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, vol. 150 (4), pp. C234–C243
K.W. Fung, and G. Mamantov: J. Electroanal. Chem., 1972, vol. 35, pp. 27–34
G.R. Stafford, and T.P. Moffat: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1995, vol. 142 (10), pp. 3288–96
G.R. Stafford: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, vol. 141, p. 945
R.T. Carlin, R.A. Osteryoung, J.S. Wilkes, and J. Rovng: Inorg. Chem., 1990, vol. 29, p. 3003
T. Takenaka, A. Hoshikawa, and M. Kawakami: Proc. Int. Symp. on Molten Salt Technol., 1993, pp. 184–92
I. Mukhopadhyay, C.L.R. Aravinda, D. Borissov, and W. Freyland: Electrochim. Acta, 2005, vol. 50, pp. 1275–81
R.T. Carlin, W. Crawford, and M. Bersch: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1992, vol. 139 (10), pp. 2720–27
Q. Liao, W.R. Pitner, G. Stewart, C.L. Hussey, and G.R. Stafford: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, vol. 144 (3), pp. 936–43
P.K. Lai, and M. Skyllas-Kazacos: J. Electroanal. Chem., 1998, vol. 248, pp. 431–40
P.K. Lai, and M. Skyllas-Kazacos: Electrochim. Acta, 1987, vol. 32, pp. 1443–49
J. Robinson, and R.A. Osteryoung: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1980, vol. 127 (1), pp. 122–28
V. Kamavaram, and R.G. Reddy: Light Metals 2005, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005, pp. 501–05
M. Zhang, V. Kamavaram, and R.G. Reddy: JOM, 2003, vol. 55 (11), pp. 54–57
V. Kamavaram, and R.G. Reddy: in Metal Separation Technologies III, R.E. Aune, and M. Kekkonen, eds., Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo, Finland, 2004, pp. 143–51
V. Kamavaram, D. Mantha, and R.G. Reddy: Electrochim. Acta, 2005, vol. 50, pp. 3286–95
Z.J. Karpinski, and R.A. Osteryoung: Inorg. Chem., 1984, vol. 23, pp. 1491–94
D. Pradhan, and R.G. Reddy: in Innovation in Titanium Technology: Novel Materials and processes I, M.N. Gungor, M.A. Imam, and F.H. Froes, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2007, pp. 79–86
D. Pradhan and R.G. Reddy: Electrochim. Acta, 2008, in press
A. Dent, K. Seddon, and T. Welton: J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1990, vol. 4, pp. 315–16
A. Abdur-Saha, A. Greenway, K.R. Sodden, and T. Walton: Org. Mass Spectrum, 1992, vol. 27, p. 648
T. Takenaka, and M. Kawakami: Int. J. Mater. Product Technol., Special Issue, SPMI, 2001, pp. 500–06
A. Brenner: Electrodeposition of Alloys—Principles and Practice, vol. I, Academic Press, New York, NY, 1963, pp. 75–85 and 139–46
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Science Foundation, ACIPCO, and The University of Alabama.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 11, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pradhan, D., Reddy, R. & Lahiri, A. Low-Temperature Production of Ti-Al Alloys Using Ionic Liquid Electrolytes: Effect of Process Variables on Current Density, Current Efficiency, and Deposit Morphology. Metall Mater Trans B 40, 114–122 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9214-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9214-y