Abstract
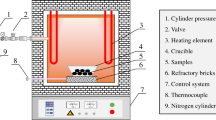
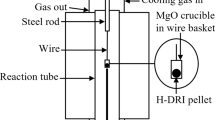
An experimental study was conducted to understand the decarburization and melting behavior of direct-reduced iron (DRI) pellets in SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-MgO-FeO slags with various FeO concentrations (10 to 25 wt pct) and basicities (Bs), ranging from 1.5 to 2.5. The behavior of the pellet in slag was observed using the X-ray fluoroscopy technique; the rate of decarburization was simultaneously measured with a constant volume pressure increase technique. The study shows that the decarburization of DRI in slag at 1600 °C takes place in two stages. The first stage is the reaction between the FeO and the carbon inside the pellet, which is controlled by heat transfer from the slag to the pellet; the second stage involves the decarburization reaction between the FeO in the slag and the remaining carbon in the DRI. The kinetics of this stage is determined by the mass transfer of FeO in the slag and is strongly dependent on the FeO concentration. Depending on the physicochemical properties of the slag and the rate of gas evolution, the DRI may sink through, float inside the slag, or remain on top before complete decarburization.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Direct Reduction Statistics–2007, Midrex, Charlotte, NC, 2006, pp. 2–4
S. Montague and W.D. Hausler: Direct from Midrex, Midrex, Charlotte, NC, 1999, 4th qu., pp. 3–7
R. Bailey: Direct from Midrex, Midrex, Charlotte, NC, 2001, 2nd qu., pp. 7–8
S.C. Montague and W.D. Haysler: Proc. 57th Electric Furnace Conf., Pittsburgh, PA, 1999, pp. 607–14
G. Whitten: Direct from Midrex, Midrex, Charlotte, NC, 1998, 3rd qu., pp. 3–5
D. Quintero Yanez: Proc. 4th Eur. Electric Steel Congr., Madrid, Spain, 1992, pp. 273–83
P.E. Duarte, R. Lopez: Iron Steel Eng., 1996, vol. 73 (11), pp. 38–41
F.M. Wheeler and Y.M. Gordon: Proc. 7th Eur. Electric Steelmaking Conf., Venice, Italy, Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, Italy, 2002, pp. 2.437–2.446
F.M. Wheeler and Y.M. Gordon: Proc. ISSTech Conf., Indianapolis, IN, Iron and Steel Society, Warrendale, PA, 2003, pp. 1033–41
Y. Gordon and F. Wheeler: U.S. Patent No. 6,785,251, 2005
F. Wheeler, F. Atkinson, Y. Gordon, S. Broek, V. So, and M. Barati: 3rd Int. Conf. Process Development in Iron and Steelmaking, MEFOS, Lulea, Sweden, 2008
J. Li, M. Barati, and Y. Yang: Proc. 4th Int. Congr. on the Science and Technology of Steelmaking (ICS 2008), Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, Gifu, Japan, Oct. 6–8, 2008
K. Sadrnezhaad, J.F. Elliott: Iron Steel Int., 1980, vol. 53 (6), pp. 327–39
K. Sadrnezhaad: Iron Steel Int., 1981, vol. 54 (6), pp. 309–14
D.A. Goldstein, R.J. Fruehan, B. Ozturk: Iron Steelmaker, 1999, vol. 26 (2), pp. 49–61
D.J. Min, R.J. Fruehan: Metall. Trans. B, 1992, vol. 23B, pp. 29–37
B. Sarma, A.W. Cramb, R.J. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 717–31
N. Siddiqi, B. Bhoi, R.K. Paramguru, V. Sahajwalla, O. Ostrovski: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2000, vol. 27 (5), pp. 367–72
R.D. Morales, R. Lule, F. Lopez, J. Camacho, J.A. Romero: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 1054–62
R.J. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 743–53
D.J. Min, J.W. Han, W.S. Chung: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 215–21
G. Urbain, F. Cambier, M. Deletter, M.R. Anseau: Trans. J. Br. Ceram. Soc., 1981, vol. 80, pp. 139–41
R. Roscoe: Br. J. Appl. Phys., 1952, vol. 3, pp. 267–69
K.C. Mills, B.J. Keene: Int. Mater. Rev., 1987, vol. 32, pp. 1–120
C.W. Bale, P. Chartrand, S.A. Degterov, G. Eriksson, K. Hack, R. Ben Mahfoud, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, S. Petersen: Calphad, 2002, vol. 26, pp. 189–228
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Hatch and Ontario Centres of Excellence, for providing funding of this research (Grant No. MP50479). The authors also appreciate the assistance by Dr. F. Ji and Ms. E. Chen from McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) for setting up the experimental furnace and the X-ray machine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 2, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Barati, M. Kinetics and Mechanism of Decarburization and Melting of Direct-Reduced Iron Pellets in Slag. Metall Mater Trans B 40, 17–24 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9195-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9195-x