Abstract
The interfacial reaction is a factor that plays an important role in governing the rate of many metallurgical processes. In the direct iron smelting process, interfacial reactions of carbonaceous materials, such as coals, with molten iron is one of the key factors that dictate the rate of carbon transfer from the carbonaceous materials into molten iron and establish a carbon concentrated melt to reduce iron oxide in the slag phase.
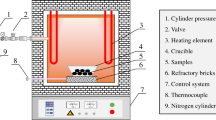
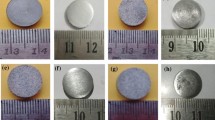
In the current investigation, wetting of natural graphite, which contains 8.8 pct ash, by iron was studied in a horizontal tube furnace at 1600 °C using the sessile drop approach to establish a fundamental understanding of the influence of ash on interactions between graphite and iron. The mass-transfer phenomena between the solid substrate and the iron droplet were studied by withdrawing the assembly at different time intervals. After the wetting experiment, the contacting surface of the iron droplet was observed by a field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM). The components of the interfacial layer formed during the experiment were examined by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The change in the carbon and sulfur contents of the droplet at different time intervals during the wetting experiment was analyzed by a LECO carbon and sulfur analyzer. It was found that the formation of an ash interfacial layer between the carbonaceous materials and the liquid iron has a strong influence on the mass transfer and interfacial reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.R. Belton and R.J. Fruehan: Turkdogan Symp. Proc., 1994, pp. 3–22.
B.L. Cusack, G.J. Hardie, and P.D. Burke: Eur. Ironmaking Congr., Glasgow, Sept. 1991.
V.O. Dahlke and O. Knacke: Arch Eisenhuettenwes., 1955, vol. 26, pp. 373–78.
R.G. Olsson, V. Koump, and T.F. Perzak: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 426–29.
S. Orsten and F. Oeters: 5th Int. Iron Steel Congr., Book 3, Process Technology Proc., ISS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1986, vol. 6, pp. 143–55.
S. Orsten and F. Oeters: 1988 W.O. Pilbrook Memorial Symp. Conf. Proc., 1988, pp. 27–38.
C. Wu and V. Sahajwalla: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29B, pp. 471–77.
C. Wu and V. Sahajwalla: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 249–51.
F. Neumann, H. Scheneck, and W. Pattrson: Giesserei, 1960, vol. 47, pp. 25–95.
L.A. Aksay, C.E. Hoge, and J.A. Pask: J. Phys. Chem., 1974, vol. 78 (12), pp. 1178–83.
J.V. Naidich: Progr. Surf. Membrane Sci., 1981, vol. 14, pp. 353–485.
B.J. Keene: Slag Atlas, 2nd ed., VDEh, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, 1995 pp. 513–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation made in the “Geoffrey Belton Memorial Symposium,” held in January 2000, in Sydney, Australia, under the joint sponsorship of ISS and TMS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Wiblen, R. & Sahajwalla, V. Influence of ash on mass transfer and interfacial reaction between natural graphite and liquid iron. Metall Mater Trans B 31, 1099–1104 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-000-0085-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-000-0085-0