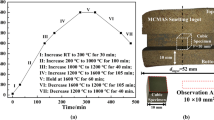
Abstract
Te is sulfide inclusion morphology optimization element in steel, and Te doping in MnS inclusions is considered the main mechanism for modification, but the mechanism of Te doping behavior itself is not clear. Te-doped MnS inclusion behavior in steel was investigated using optical microscope, electron probe microanalysis, transmission electron microscopy, thermomechanical simulator, and first-principles calculations. After Te treatment, the amount of type II sulfides was decreased, the size of sulfides was increased, and the sulfides were strengthened. The aspect ratio of hot deformed sulfides was decreased significantly through Te doping. The atomic ratio of S to Te for MnS inclusions with MnTe adhesion was determined to be between 66 and 49 through the energy and wavelength spectra. The crystal structure of the Te-doped MnS inclusions retained the rock-salt structure, and no ordered structure was formed. The first-principles calculation results showed that the doping of Te led to the replacement of S atoms from MnS. Lattice distortion was observed after Te doping, and the lattice constant increased; Te doping mainly affected the position of the nearest Mn atoms, and the lattice distortion can affect about three layers of atoms along the < 100 > direction. Considering the cost-effectiveness of adding Te, the mass ratio of Te to S should be controlled at approximately 0.063 during actual production.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.V. Popova, D.V. Lebedev, and A.G. Nasibov: Properties of steel 16G2AF with microadditions of tellurium. Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1983, vol. 25(3), pp. 184–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00805969.
I.V. Popova, A.G. Nasibov, G.G. Gulei, and G.A. Sveshnikova: Nonmetallic inclusions and austenite grains of steel containing tellurium. Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1986, vol. 28(1), pp. 52–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735548.
Q. Huang, Y. Ren, Y. Luo, S. Ji, and L. Zhang: Deformation of MnS–MnTe inclusions in a sulfur-containing free-cutting steel with tellurium treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02698-w.
P. Shen, Q. Yang, D. Zhang, S. Yang, and J. Fu: The effect of tellurium on the formation of MnTe-MnS composite inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel. Metals, 2018, vol. 8(8), p. 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080639.
P. Shen, L. Zhou, Q. Yang, Z. Zeng, K. Ai, and J. Fu: Modification of MnS inclusion by tellurium in 38MnVS6 micro-alloyed steel. Metall. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 117(6), p. 615. https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2020066.
P. Shen, H. Zhang, X. Xu, Q. Yang, and J. Fu: Study on the high-temperature evolution and formation mechanism of inclusions in Te-treated resulfurized special steel. Steel Res. Int., 2021, vol. 92(11), p. 2100235. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.202100235.
J.Y. Liu, C.S. Liu, R.J. Bai, W. Wang, Q.B. Wang, H. Zhang, and H.W. Ni: Morphological transformation of elongated MnS inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel during isothermal heating. J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00829-w.
J.L. Lu, G.G. Cheng, M. Wu, G. Yang, and J.L. Che: Detection and analysis of magnetic particle testing defects on heavy truck crankshaft manufactured by microalloyed medium-carbon forging steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2020, vol. 27, pp. 608–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00334-7.
X.Y. Xu, Z.Q. Zeng, Q.R. Tian, C.W. Cao, P. Shen, and J.X. Fu: Application of fractal theory to study morphology of manganese sulfide inclusion in resulfurized free-cutting steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2023, vol. 30, pp. 137–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00826-z.
Q.S. Zhang, Y. Min, J.J. Xu, and C.J. Liu: Formation and evolution behavior of inclusions in Al-killed resulfurized free-cutting steel with magnesium treatment. J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2020, vol. 27, pp. 631–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00401-4.
F. Wang, H. Guo, W. Liu, S. Yang, S. Zhang, and J. Li: Control of MnS inclusions in high- and low-sulfur steel by tellurium treatment. Materials, 2019, vol. 12(7), p. 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071034.
S. Zhang, F. Wang, S. Yang, J. Liu, and J. Li: Sulfide transformation with tellurium treatment for Y15 free-cutting steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50(5), pp. 2284–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01627-8.
X. Wu, L.P. Wu, J.B. Xie, P. Shen, and J.X. Fu: Modification of sulfide by Te in Y1Cr13 free-cutting stainless steel. Metall. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 117(1), p. 107. https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2019070.
J.B. Xie, T. Fan, H. Sun, Z.Q. Zeng, and J.X. Fu: Enhancement of impurity, machinability and mechanical properties in Te-treated 0Cr18Ni9 steel. Met. Mater. Int., 2021, vol. 27(6), pp. 1416–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00545-3.
A. Mahmutović, A. Nagode, M. Rimac, and D. Mujagić: Modification of the inclusions in austenitic stainless steel by adding tellurium and zirconium. Mater. Tehnol., 2017, vol. 51, pp. 523–28. https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2015.297.
P. Shen, Q.K. Yang, D. Zhang, Y.X. Wu, and J.X. Fu: Application of tellurium in free-cutting steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2018, vol. 25(8), pp. 787–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0123-2.
Y. Ito, N. Masumitsu, and K. Matsubara: Formation of manganese sulfide in steel. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1981, vol. 21(7), pp. 477–84. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational1966.21.477.
L. Zheng, A. Malfliet, P. Wollants, B. Blanpain, and M. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48(5), pp. 2447–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1050-5.
H. Yaguchi and N. Onodera: The effect of tellurium on the machinability of AISI 12L14+Te steel. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1988, vol. 28(12), pp. 1051–59. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational1966.28.1051.
T. Katoh, S. Abeyama, A. Kimura, and S. Nakamura: A study on resulfurized free-machining steel containing a small amount of tellurium. Denki Seiko, 1982, vol. 53(3), pp. 195–202. https://doi.org/10.4262/denkiseiko.53.195.
J.R. Rellick, C.J. McMahon, H.L. Marcus, and P.W. Palmberg: The effect of tellurium on intergranular cohesion in iron. Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2(5), pp. 1492–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913388.
M. Menyhard, B. Rothman, and C.J. McMahon: Observations of segregation and grain-boundary faceting by tellurium and oxygen in iron. Scripta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 29(8), pp. 1005–09. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-716X(93)90168-R.
C. Sudarshan, S. Jayakumar, K. Vaideki, and C. Sudakar: Te-rich Bi2Te3 thin films by electron−beam deposition: structural, electrical, optical and thermoelectric properties. Thin Solid Films, 2020, vol. 713, p. 138355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2020.138355.
Y. Yin, Z. Zhang, H. Zhong, C. Shao, X. Wan, C. Zhang, J. Robertson, and Y. Guo: Tellurium nanowire gate-all-around MOSFETs for sub-5 nm applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, vol. 13(2), pp. 3387–396. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18767.
B.R. Aryal, D.R. Ranasinghe, T.R. Westover, D.G. Calvopiña, R.C. Davis, J.N. Harb, and A.T. Woolley: DNA origami mediated electrically connected metal—semiconductor junctions. Nano Res., 2020, vol. 13(5), pp. 1419–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2672-5.
M. Sakano, M. Hirayama, T. Takahashi, S. Akebi, M. Nakayama, K. Kuroda, K. Taguchi, T. Yoshikawa, K. Miyamoto, T. Okuda, K. Ono, H. Kumigashira, T. Ideue, Y. Iwasa, N. Mitsuishi, K. Ishizaka, S. Shin, T. Miyake, S. Murakami, T. Sasagawa, and T. Kondo: Radial spin texture in elemental tellurium with chiral crystal structure. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2020, vol. 124(13), p. 136404. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.136404.
G. Gatti, D. Gosálbez-Martínez, S.S. Tsirkin, M. Fanciulli, M. Puppin, S. Polishchuk, S. Moser, L. Testa, E. Martino, S. Roth, P. Bugnon, L. Moreschini, A. Bostwick, C. Jozwiak, E. Rotenberg, G. Di Santo, L. Petaccia, I. Vobornik, J. Fujii, J. Wong, D. Jariwala, H.A. Atwater, H.M. Rønnow, M. Chergui, O.V. Yazyev, M. Grioni, and A. Crepaldi: Radial spin texture of the Weyl fermions in chiral tellurium. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2020, vol. 125(21), p. 216402. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.216402.
G. Qiu, C. Niu, Y. Wang, M. Si, Z. Zhang, W. Wu, and P.D. Ye: Quantum hall effect of weyl fermions in n-type semiconducting tellurene. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2020, vol. 15(7), pp. 585–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0715-4.
N. Isik Goktas, A. Sokolovskii, V.G. Dubrovskii, and R.R. LaPierre: Formation mechanism of twinning superlattices in doped GaAs nanowires. Nano Lett., 2020, vol. 20(5), pp. 3344–351. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00240.
Y. Ma, B. Tang, W. Lian, C. Wu, X. Wang, H. Ju, C. Zhu, F. Fan, and T. Chen: Efficient defect passivation of Sb2Se3 film by tellurium doping for high performance solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, vol. 8(14), pp. 6510–16. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA00443J.
C. Ünlü: Controlling defect state emission in ultra-small sized tellurium doped CdSe nanocrystals via two-phase synthesis method. Opt. Mater., 2019, vol. 89, pp. 361–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.01.050.
D. Lee, G. Kang, K. Lee, S. Yoon, J. Kim, and S. Han: First-principles calculations on effects of Al and Ga dopants on atomic and electronic structures of amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5. J. Appl. Phys., 2019, vol. 125(3), p. 035701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5056185.
X.H. Li, H.L. Cui, and R.Z. Zhang: First-principles calculations of the effect of Ge content on the electronic, mechanical and acoustic properties of Li17Si4-xGex. Curr. Appl. Phys., 2019, vol. 19(6), pp. 663–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2019.03.014.
J. Kim, H. Kwon, and C.W. Kwon: Temperature dependent phase stability of Ti(C1−xNx) solid solutions using first-principles calculations. Ceram. Int., 2017, vol. 43(1, Part A), pp. 650–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.209.
X. Zhang, J. Tang, L. Deng, H. Deng, S. Xiao, and W. Hu: Effects of solute size on solid-solution hardening in vanadium alloys: a first-principles calculation. Scripta Mater., 2015, vol. 100, pp. 106–09. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.01.006.
S. Matsushima, Y. Tanaka, J. Ishii, and K. Obata: First-principles energy band calculation of a (Ca2+, V5+)-doped Y2Ti2O7 pigment. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2019, vol. 127(11), pp. 793–801. https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.19103.
W. Adli, A. Zaoui, and M. Ferhat: First-principles calculations of electronic and magnetic properties in ferromagnetic MnSeS, MnSeTe, and MnSePo ternary systems. J. Supercond. Novel Magn., 2016, vol. 29(3), pp. 839–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3335-8.
X. Xu, T.F. Chung, S. Hu, Q. Zhu, J. Fu, J.R. Yang, and Q. Tian: Effect of tin microalloying on the microstructure of low-carbon free-machining steels. J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, vol. 20, pp. 1172–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.153.
X. Xu, Z. Yan, Z. Niu, X. Shang, X. Wang, and C. Shang: Hot-deformation characteristics of Al-alloyed δ-ferritic and martensitic dual-phase steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, vol. 16, pp. 675–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.12.034.
X. Xu, X. Wang, J. Li, Z. Yan, D. Liu, Q. Liu, C. Shang, J. Fu, and P. Shen: Hot workability characteristics of low-density Fe–4Al–1Ni ferritic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, vol. 799, p. 140257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140257.
G. Kresse and J. Hafner: Norm-conserving and ultrasoft pseudopotentials for first-row and transition elements. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter., 1994, vol. 6, p. 8245. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/6/40/015.
G. Kresse and J. Furthmüller: Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B, 1996, vol. 54, p. 11169. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169.
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, vol. 77, p. 3865. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865.
P.E. Blöchl: Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B, 1994, vol. 50, p. 17953. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.50.17953.
F. Mehmed and H. Haraldsen: Magnetochemische Untersuchungen. XXVIII. Das magnetische Verhalten der allotropen Modifikationen des Mangan(II)-Sulfids. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1938, vol. 235(3), pp. 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19382350305.
G. Xiao, X. Yang, X. Zhang, K. Wang, X. Huang, Z. Ding, Y. Ma, G. Zou, and B. Zou: A protocol to fabricate nanostructured new phase: B31-type MnS synthesized under high pressure. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, vol. 137(32), pp. 10297–303. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b05629.
Y.B. Xue, Y.T. Zhou, D. Chen, and X.L. Ma: Structural stability and electronic structures of (111) twin boundaries in the rock-salt MnS. J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 582, pp. 181–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.073.
A.J. Panson and W.D. Johnston: The MnTe-MnSe system. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 1964, vol. 26(5), pp. 701–03. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1902(64)80312-2.
W.D. Johnston and D.E. Sestrich: The MnTe-GeTe phase diagram. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 1961, vol. 19(3), pp. 229–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1902(61)80111-5.
K. Momma and F. Izumi: VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2011, vol. 44(6), pp. 1272–276. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889811038970.
D. Zhang, P. Shen, J.B. Xie, J.M. An, Z.Z. Huang, and J.X. Fu: A method for observing tridimensional morphology of sulfide inclusions by non-aqueous solution electrolytic etching. J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2019, vol. 26(3), pp. 275–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0142-z.
W. Lv, L. Yan, X. Pang, H. Yang, L. Qiao, Y. Su, and K. Gao: Study of the stability of α-Fe/MnS interfaces from first principles and experiment. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, vol. 501, p. 144017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144017.
C.H. Leung and L.H. Van Vlack: Solubility limits in binary (Ca, Mn) chalcogenides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1979, vol. 62(11–12), pp. 613–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1979.tb12743.x.
C.H. Griffiths: Cubic manganous telluride. J. Mater. Sci., 1978, vol. 13(3), pp. 513–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00541800.
R. Shannon: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A, 1976, vol. 32(5), pp. 751–67. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551.
M.H.F. Sluiter and Y. Kawazoe: Site preference of ternary additions in Ni3Al. Phys. Rev. B, 1995, vol. 51, pp. 4062–73. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.51.4062.
D. SrivastavaAnurag: Dhar, Elastic and thermodynamic properties of divalent transition metal carbides MC (M = Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta). Can. J. Phys., 2012, vol. 90(4), pp. 331–38. https://doi.org/10.1139/p2012-021.
K. Jacob, S. Raj, and L. Rannesh: Vegard’s law: a fundamental relation or an approximation? Int. J. Mater. Res., 2007, https://doi.org/10.3139/146.101545.
Acknowledgments
Xiangyu Xu gratefully acknowledges support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Program No. 52104335) and Shanghai “Super Postdoctoral” Incentive Plan (Grant No. 2020194). Professor Jianxun Fu acknowledges support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program Nos. 52074179 and 51874195). We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XX: conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing, funding acquisition. YL: investigation, formal analysis. ZW: investigation, validation. XZ: investigation. QT: investigation. JF: resources, funding acquisition. XW: resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Li, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Tellurium Doping in MnS Inclusions and Corresponding Modification Effect: Experimental and First-Principles Study. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 4558–4571 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07189-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07189-4