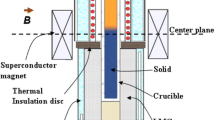
Abstract
The effects of an axial high magnetic field on the microstructure evolution, solute distribution, and preferred crystallography relationship in the directionally solidified Cu–15.6 wt pctGe peritectic alloy were investigated. According to the experimental results, the application of a high magnetic field resulted in the columnar-to-equiaxed transition (CET) of the primary dendrites, the change of peritectic phase fraction, and the modification of the crystallography relationship between peritectic two phases. Numerical simulations were performed that revealed that the thermoelectric (TE) magnetic force imposed on the dendrite could be responsible for the occurrence of the CET. It was also found that the TE magnetic convection formed in the liquid-α-ξ phase junction region and obviously influenced the solute distribution. Indeed, under lower magnetic fields (B < 0.5 T), the TE magnetic convection increased with the magnetic field and made the Ge solute float upwards. However, under higher magnetic fields (B > 0.5 T), the TE magnetic convection gradually decreased and was compressed to the peritectic reaction interface with the increase of the magnetic field. As a result, the lower magnetic field decreased the fraction of the peritectic ξ-phase because of the solute floating effect while the higher magnetic field increased the fraction of the peritectic ξ-phase by promoting the peritectic interface reaction. Moreover, due to the formation of the TE magnetic force and the magnetization force in the peritectic two phases, the crystallography orientation relationship between the peritectic two phases was modified.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.W. Kerr and W. Kurz: Int. Mater. Rev., 1996, vol. 41, pp. 129–64.
Y.Z. Chen, F. Liu, G.C. Yang, and Y.H. Zhou: J. Mater. Res., 2010, vol. 25, p. 1025.
Y.K. Xu, Z.H. Huang, Y.N. Chen, J.X. Xiao, J.M. Hao, X.H. Hou, and L. Liu: Materials, 2020, vol. 13, p. 911.
C. Brito, C.A. Siqueira, J.E. Spinelli, and A. Garcia: J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2012, vol. 73, pp. 1173–81.
X.F. Ding, J.P. Lin, L.Q. Zhang, Y.Q. Su, G.J. Hao, and G.L. Chen: Intermetallics, 2011, vol. 19, pp. 1115–19.
Y.H. Cai, F. Wang, Z.H. Zhang, and B. Nestler: Acta Mater., 2021, vol. 219, p. 117223.
L.S. Luo, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, X.Z. Li, S.M. Li, H. Zhong, L. Liu, and H.Z. Fu: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 461, pp. 121–27.
Q.L. Rao, X.L. Fan, D. Shu, and C.C. Wu: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 461, pp. L29-33.
B.A. Jensen, W. Tang, X.B. Liu, A.I. Nolte, G.Y. Ouyang, K.W. Dennis, and J. Cui: Acta Mater., 2019, vol. 181, pp. 595–602.
H. Zhong, S.M. Li, H.Y. Lü, L. Liu, G.R. Zou, and H.Z. Fu: J. Cryst. Growth, 2008, vol. 310, pp. 3366–71.
Y.Z. Chen, F. Liu, G.C. Yang, N. Liu, C.L. Yang, and Y.H. Zhou: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 779–82.
F. Kohler, L. Germond, J.D. Wagnière, and M. Rappaz: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 56–68.
Y.Z. Chen, K. Wang, X.H. Shi, X.Y. Ma, and F. Liu: J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 585, pp. 260–66.
S. Dobler, T.S. Lo, M. Plapp, A. Karma, and W. Kurz: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 2795–2808.
P. Peng, L. Lu, W.C. Zhang, J.T. Wang, and S.D. Zhou: J. Alloys Compd., 2021, vol. 872, p. 159558.
L.S. Wang, J. Shen, Y.L. Xiong, Y.J. Du, and H.Z. Fu: Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.), 2014, vol. 27, pp. 585–92.
S.J. Wang, L.S. Luo, Y.Q. Su, F.Y. Dong, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu: J. Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 28, pp. 1372–77.
S. Asai: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2000, vol. 1, pp. 191–200.
Y.H. Liu, B.M. Zheng, T. Zhang, Y.G. Chen, J.H. Liu, Z. Wang, and X.Z. Gong: Electrochim. Acta, 2022, vol. 432, p. 141201.
I. Kaldre, Y. Fautrelle, J. Etay, A. Bojarevics, and L. Buligins: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 571, pp. 50–55.
Z. Shen, M.H. Peng, D.S. Zhu, T.X. Zheng, Y.B. Zhong, W.L. Ren, C.J. Li, W.D. Xuan, and Z.M. Ren: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 568–77.
P. Mazumder, R. Trivedi, and A. Karma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31, pp. 1233–46.
S.N. Tewari, R. Shah, and H. Song: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 1535–44.
T. Alboussiere, A.C. Neubrand, J.P. Garandet, and R. Moreau: Magnetohydrodynamics, 1995, vol. 31, pp. 228–35.
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, and R. Bolcato: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4067–79.
R. Moreau, O. Laskar, M. Tanaka, and D. Camel: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, vol. 173, pp. 93–100.
J. Wang, Y. Fautrelle, H. Nguyen-Thi, G. Reinhart, H.L. Liao, X. Li, Y.B. Zhong, and Z.M. Ren: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47A, pp. 1169–79.
X. Li, Z.Y. Lu, Y. Fautrelle, A. Gagnoud, R. Moreau, and Z.M. Ren: Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6, p. 37872.
Z.Y. Lu, Z.M. Ren, Y. Fautrelle, and X. Li: ISIJ Int., 2018, vol. 58, pp. 505–14.
Y.Q. Su, S.J. Wang, L.S. Luo, J.C. Jie, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu: J. Alloys Compd., 2012, vol. 539, pp. 44–49.
Y. Hou, Z.Q. Zhang, W.D. Xuan, J. Wang, J.B. Yu, and Z.M. Ren: Acta Metall. Sin. (English Lett.), 2018, vol. 31, pp. 681–91.
F. Baltaretu, J. Wang, S. Letout, Z.M. Ren, X.J. Li, O. Budenkova, and Y. Fautrelle: Magnetohydrodynamics, 2015, vol. 51, pp. 45–55.
F.J. Blatt, M. Garber, and B.W. Scott: Phys. Rev., 1964, vol. 136, pp. A729-737.
A.V. Gold, D.K.C. Macdonald, W.B. Pearson, and I.M. Templeton: Philos. Mag., 1960, vol. 5, pp. 765–86.
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, and Z.M. Ren: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 3803–13.
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, Y. Fautrelle, Z.M. Ren, R. Moreau, Y.D. Zhang, and C. Esling: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 3321–32.
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, J. Wang, X.L. Li, Y. Fautrelle, Z.M. Ren, X.G. Lu, G. Reinhart, and H. Nguyen-Thi: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 73, pp. 83–96.
D.F. Du, L. Hou, A. Gagnoud, Z.M. Ren, Y. Fautrelle, G.H. Cao, and X. Li: J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 588, pp. 190–98.
H. Liu, W.D. Xuan, X.L. Xie, C.J. Li, J. Wang, J.B. Yu, X. Li, Y.B. Zhong, and Z.M. Ren: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 4193–4203.
S. Liu and R. Trivedi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 3293–3304.
S.N. Geng, P. Jiang, X.Y. Shao, L.Y. Guo, and X.S. Gao: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, vol. 46, pp. 50–63.
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51904183 and 52130204), and the Independent Research and Development Project of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Special Steel, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced Ferrometallurgy, Shanghai University (No. SKLASS 2021-Z07), and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Nos. 19DZ2270200 and, 20511107700).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Z., Hu, S., Wang, T. et al. Effect of High Magnetic Field on Microstructure Evolution, Solute Distribution, and Crystallography in Directionally Solidified Cu–Ge Peritectic Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 3186–3198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07087-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07087-9