Abstract
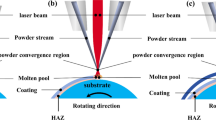
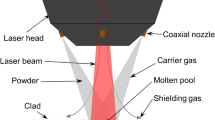
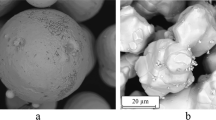
In this paper, crack-free Ni60 coatings were deposited by extreme-high-speed (EH-LIHC) and conventional (LIHC) laser-induction hybrid cladding technologies, respectively, and the forming features, microstructure and wear behaviors of them were studied comparatively. The surface roughness of EH-LIHCed coatings was decreased from ~ 24 to ~ 4 μm compared with that deposited by LIHC, while the deposition rates were improved by about 2 times. All Ni60 coatings were composed of the γ-Ni, Ni3B, CrB and Cr7C3 phases. However, the last three phases were significantly restricted in the 1st layer of LIHCed coatings due to the serious dilution of Fe element, making the microhardness therein about 40 pct lower than that of the EH-LIHCed coatings, which also showed obvious effects on the microstructure and hardness of the subsequent deposited layers until the distance between coating and coatings/substrate interface was larger than 1400 μm. Comparatively, the microstructure and hardness of EH-LIHCed Ni60 coating were uniform along the depth direction, as well as the grain sizes of γ-Ni, CrB and Cr7C3 phases therein were all lower, and the decreased ratio of γ-Ni grains was about 23 pct. Under the 200 N loads, the volume wear rates of Ni60 coatings deposited by both technologies were comparable, whereas much severer spalling were detected in the LIHCed coatings. This may be due to that the precipitates with larger size could protect the matrix from groove wear better, but usually associated with the faster cracks’ extension, in turn increasing the damage of coatings.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Holmberg and A. Erdemir: Friction, 2017, vol. 5, pp. 263–84.
M. Ali, A. Ul-Hamid, T. Khan, A. Bake, H. Butt, O.E. Bamidele, and A. Saeed: Corros. Rev., 2021, vol. 39, pp. 519–46.
J.A. Ajao: J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng., 2010, vol. 9, pp. 133–45.
C. Sun, L. Guo, G.X. Lu, Y.B. Lv, and F.X. Ye: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, vol. 317, pp. 908–13.
N. Tan, Z.G. Xing, X.L. Wang, H.D. Wang, G. Jin, S.Y. Chen, and B.S. Xu: Mater. Des., 2017, vol. 133, pp. 19–29.
P. Fauchais, A. Vardelle, M. Vardelle, and M. Fukumoto: J. Therm. Spray. Techn., 2004, vol. 13, pp. 337–60.
P. Fauchais: J. Phys. D, 2004, vol. 37, pp. 86–108.
J.L. Liu, H.J. Yu, C.Z. Chen, F. Weng, and J.J. Dai: Opt. Laser Eng., 2017, vol. 93, pp. 195–210.
F. Weng, C.Z. Chen, and H.J. Yu: Mater. Des., 2014, vol. 58, pp. 412–25.
J.H. Yao, Y.P. Ding, R. Liu, Q.L. Zhang, and L. Wang: Opt. Laser Technol., 2018, vol. 107, pp. 32–45.
A. Kelbassa, W. Gasser, G. Meiners, G. Backes, and B. Müller: Int. Matador Conf., 2013, vol. 37, pp. 385–90.
T. Schopphoven, A. Gasser, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe: J. Laser Appl., 2016, vol. 28, 022501.
L. Li-Yan, Z. Yu, J. Yun-Jie, L. Yan, T. Hong-Fang, C. Yu-Jun, and L. Cheng-Xin: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2020, vol. 392, p. 125697.
W.Y. Yuan, R.F. Li, Z.H. Chen, J.Y. Gu, and Y.T. Tian: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, vol. 405, 126582.
X.X. Qiao, T.L. Xia, and P. Chen: Chin. Phys. B, 2021, vol. 30(1), p. 018104.
Y.J. Huang, X.Y. Zeng, Q.W. Hu, and S.F. Zhou: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, vol. 255, pp. 3940–945.
P. Farahmand, S. Liu, Z. Zhang, and R. Kovacevic: Ceram. Int., 2014, vol. 40, pp. 15421–5438.
S.F. Zhou, J.B. Lei, X.Q. Dai, J.B. Guo, Z.J. Gu, and H.B. Pan: Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2016, vol. 60, pp. 17–27.
D.Z. Wang, Q.W. Hu, and X.Y. Zeng: J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 588, pp. 502–508.
L. Meng, W.F. Zhao, K.L. Hou, D.H. Kou, Z.H. Yuan, X. Zhang, J.L. Xu, Q.W. Hu, D.Z. Wang, and X.Y. Zeng: Mat. Sci. Eng A-Struct., 2019, vol. 748, pp. 1–5.
G. Bidron, A. Doghri, T. Malot, F. Fournier-dit-Chabert, M. Thomas, and P. Peyre: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, vol. 277, 116461.
L. Meng, P.H. Sheng, and X.Y. Zeng: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, vol. 16, pp. 1732–746.
D. Wang, Y.Q. Yang, X.B. Su, and Y.H. Chen: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech., 2012, vol. 58(9–12), pp. 1189–199.
L.Y. Chen, Y. Zhao, F.W. Meng, T.B. Yu, Z.L. Ma, S. Qu, and Z.Y. Sun: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2022, vol. 25, 128678.
B. Song, T. Hussain, and K.T. Voisey: Phys. Procedis, 2016, vol. 83, pp. 706–15.
D.Z. Wang, Q.W. Hu, Y.L. Zheng, Y. Xie, and X.Y. Zeng: Opt. Laser Technol., 2016, vol. 77, pp. 16–22.
G. Chakraborty, S.K. Albert, and A.K. Bhaduri: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, vol. 4, pp. 454–59.
L.J. da Silva and A.S.C.M. D’Oliveira: Wear, 2016, vol. 350–351, pp. 130–40.
I. Hemmati, V. Ocelık, and J.T.M. De Hosson: Mater. Lett., 2012, vol. 84, pp. 69–72.
J. Gao, Y. Sun, K.N. Wang, Q. Song, and C.M. Wang: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2022, vol. 446, 128761.
S.M. Banait, C.P. Paul, A.N. Jinoop, H. Kumar, R.S. Pawade, and K.S. Bindra: Opt. Laser Technol., 2020, vol. 121, 105787.
J.S. Luo, W.T. Sun, R.X. Duan, W.Q. Yang, K.C. Chan, F.Z. Ren, and X.S. Yang: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, vol. 110, pp. 43–56.
C.G. He, Y.B. Huang, L. Ma, J. Guo, W.J. Wang, Q.Y. Liu, and M.H. Zhu: Tribol. Int., 2015, vol. 92, pp. 307–16.
L.J. da Silva, C.J. Scheuer, and A.S.C.M. D’Oliveira: Wear, 2019, vol. 429–429, pp. 387–94.
P.R. Reinaldo and A.S.C.M. Doliveira: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, vol. 22, pp. 590–97.
R. Dasgupta, R. Thakur, M.S. Yadav, and A.K. Jha: Wear, 1999, vol. 58, pp. 368–74.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52005197), the Postdoctoral Research Foundation of China (2020M682408) and the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX20200137). All the physical and chemistry testing were analyzed by Huazhong University of Science & Technology Analytical & Testing Center.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, L., Zhu, B., Liu, X. et al. Comparison on the Ni60 Coatings Deposited by Extreme-High-Speed and Conventional Laser-Induction Hybrid Cladding Technologies: Forming Features, Microstructure and Wear Behaviors. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 3118–3133 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07082-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07082-0