Abstract
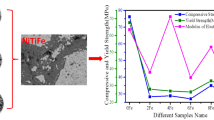
This paper investigates the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti50Ni(50−X)FeX alloys fabricated by powder metallurgy technique. Here, sintering temperatures varied from 1100 °C to 1200 °C for the compacted milled powder mixture. Microstructure, chemical composition, phase formation, porosity, density, hardness, wear, shape memory effect, and compressive strength of the sintered sample were carried out using SEM, EDS, XRD, and mechanical tests, respectively. The SEM and XRD analysis results show that the microstructure of alloys consists of (Ni, Fe)-rich, Ti-rich phases with less retained pore. The densification and hardness increase with increasing the sintering temperature. The 4 at. pct Fe sample sintered at 1200 °C shows higher densification, a lower friction coefficient, and a higher hardness value. The 4 at. pct Fe sample sintered at 1150 °C shows higher compressive, and yield strengths of 132.57 and 116.86 MPa, respectively, and the 6 at. pct Fe sample sintered at 1200 °C shows a higher shape memory effect of 3.37 pct, which are higher in comparison to other compositions and other sintering temperature samples. Abrasive wear of the sample has been carried out, and it found that there is a decrease in friction coefficient value with an increase in sintering temperature from 1150 °C to 1200 °C of the sample.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.P. Cheng, Z.L. Xie, and Y. Liu: J. Alloys Compd., 2006, vol. 415, pp. 182–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.08.014.
G.S. Firstov, J. Van Humbeeck, and Y.N. Koval: J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., 2006, vol. 17, pp. 1041–047. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X06063922.
J. Parida and S.C. Mishra: NiTi-Based Ternary Alloys, Elsevier, New York, 2022, pp. 191–213.
K. Otsuka and X. Ren: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2005, vol. 50, pp. 511–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2004.10.001.
T. H. M. Matsumoto: 1st JIM Int. In Symp. on Martensite, Kobe, Japan, 1976, vol. 199.
M.-S. Choi, T. Fukuda, and T. Kakeshita: Scr. Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 869–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.05.040.
Shape Memory Alloy Research Team (Smart), http://smart.tamu.edu, no. http://smart.tamu.edu, p., 2001.
H. Nakajima and M. Koiwa: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31, pp. 757–66. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.31.757.
T. Hara, T. Ohba, E. Okunishi, and K. Otsuka: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1997, vol. 38, pp. 11–7. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.38.11.
I. Yoshida, D. Monma, and T. Ono: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 448, pp. 349–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.04.217.
S. Xue, W. Wang, D. Wu, Q. Zhai, and H. Zheng: Mater. Lett., 2012, vol. 72, pp. 119–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.12.095.
J.L. Lemanski: AIP Conf. Proc., 2006, vol. 824, pp. 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2192327.
T. Ogawa, K. Yokoyama, K. Asaoka, and J. Sakai: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 393, pp. 239–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.10.020.
S. Aksöz: Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2017, vol. 42, pp. 2573–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2567-2.
S. Aksöz and B. Bostan: Springer Proc. Phy., 2014, vol. 154, pp. 129–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04639-6_18
L. Krone, E. Schüller, M. Bram, O. Hamed, H.-P. Buchkremer, and D Stöver.: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 378, pp. 185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.345.
C. Shearwood, Y. Q. Fu, L. Yu, and. K. A Khor: Scr. Mater., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.11.010.
S.L. Zhu, X.J. Yang, F. Hu, S.H. Deng, and Z.D. Cui: Mater. Lett., 2004, vol. 58, pp. 2369–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.02.017.
B. Liu, Z. Liu, X. Liu, W. Wang, and L. Wang: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 578, pp. 373–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.05.164.
A.A. Atiyah, A.-R.K.A. Ali, and N.M. Dawood: Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2015, vol. 40, pp. 901–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1538-0.
H. Jiang, C. Ke, S. Cao, X. Ma, and X. Zhang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2013, vol. 23, pp. 2029–036. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62692-8.
B.-Y. Li, L.-J. Rong, and Y.-Y. Li: Intermetallics, 2000, vol. 8, pp. 643–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-9795(99)00140-5.
S. Aksöz, A.T. Özdemir, and B. Bostan: J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ., 2012, vol. 27, pp. 109–15.
S. Aksöz and B. Bostan: J. Polytech., 2018, https://doi.org/10.2339/politeknik.389617.
B.B.S. Aksöz, Ü. Demir, H. Ada, and H. Gökmeşe: GU J. Sci. Part C, 2017, vol. 5, pp. 99–106.
T. Mousavi, F. Karimzadeh, and M.H. Abbasi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 487, pp. 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.09.051.
M. Karolus and J. Panek: J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 658, pp. 709–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.286.
R. Liu and D.Y. Li: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 328–32. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708300101507730.
D.Y. Li and X. Ma: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 45–6.
R. Neupane and Z. Farhat: Wear, 2013, vol. 301, pp. 682–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.11.017.
X.W. Huang, G.N. Dong, and Z.R. Zhou: J. Mater. Eng, 2004, vol. 6, pp. 41–3.
G. Tang, D. Zhang, J. Zhang, P. Lin, and G. Dong: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, vol. 321, pp. 371–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.151.
L. Yan and Y. Liu: J. Mater. Res., 2015, vol. 30, pp. 186–96. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.381.
H.W. Jin: Acta Metall. Sin., 1988, vol. 1, pp. 76–81.
Y.N. Liang, S.Z. Li, Y.B. Jin, W. Jin, and S. Li: Wear, 1996, vol. 198, pp. 236–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(96)06989-X.
D.Y. Li: Scr. Mater., 1996, vol. 34, p. 195.
W. Ni, Y.-T. Cheng, M.J. Lukitsch, A.M. Weiner, L.C. Lev, and D.S. Grummon: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, vol. 85, pp. 4028–030. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1811377.
E. Rabinowicz and R.I. Tanner: J. Appl. Mech., 1996, vol. 33, pp. 479–79. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3625110.
J. Singh and A.T. Alpas: Wear, 1995, vol. 181–183, pp. 302–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(95)90037-3.
L. Yan, Y. Liu, and E. Liu: Tribol. Int., 2013, vol. 66, pp. 219–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2013.05.012.
J. Parida, S.C. Mishra, and A. Behera: Met. Mater. Int., 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01277-7.
M. Farvizi, T. Ebadzadeh, M.R. Vaezi, E.Y. Yoon, Y.-J. Kim, J.Y. Kang, H.S. Kim, and A. Simchi: Wear, 2015, vol. 334–335, pp. 35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.04.011.
F. Alijani, R. Amini, M. Ghaffari, M. Alizadeh, and A.K. Okyay: Mater. Des., 2014, vol. 55, pp. 373–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.009.
J.L. Xu, X.F. Jin, J.M. Luo, and Z.C. Zhong: Mater. Lett., 2014, vol. 124, pp. 110–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.03.088.
F. Zhang, L. Zheng, Y. Wang, and H. Zhang: Intermetallics, 2019, vol. 112, p. 106548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2019.106548.
T.-S. Huang, S.-F. Ou, C.-H. Kuo, and C.-H. Yang: Metals (Basel), 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/met10040527.
J. De Keyzer: Thermodynamic Modeling of the Fe-Ni-Ti System: A Multiple Sublattice Approach. University of Leuven, 2008.
M. Matsumoto, and T. Honma: 1st JIM Int, In Symp. on Martensite, Kobe, Japan, 1976, pp. 199.
N. Zhang, K.P. Babayan, and J.H. Lindenhovius: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1992, vol. 150, pp. 263–70.
Archimedes’ Principle, in: n.d, pp. 37–38.
https://www.labdepotinc.com/articles/archimedes-principles.html, 2019.
https://www.andersonmaterials.com/density-and-porosity-measurements-of-solid-materials.html, 2020.
J.Y. Choi and S. Nemat-Nasser: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 432, pp. 100–07. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.155.
W. Bolton: Engineering Materials Technology, 2nd eds.Butter worth Heinemann Oxford, 2013.
ASTM Designation E 384-99, ASTM, Philadelphia PA, 1999.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical metallurgy. Mech Metall., 2011, https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.35895.
I. Manika and J. Maniks: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 2049–056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.12.031.
Y. G. G.M. Pharr and E.G. Herbert: Annu. Rev. Mater. Res, 2010, p. 271.
N. Zhou, C. Shen, M.F.-X. Wagner, G. Eggeler, M.J. Mills, and Y. Wang: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58(20), pp. 6685–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.08.033.
L. Zhang, Y.Q. Zhang, Y.H. Jiang, and R. Zhou: J. Alloys Compd., 2015, vol. 644, pp. 513–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.05.063.
S.L. Zhu, X.J. Yang, D.H. Fu, L.Y. Zhang, C. Li, and Z.D. Cui: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 408, pp. 264–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2005.08.012.
S. Waqar, A. Wadood, A. Mateen, and M.A.U. Rehman: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, vol. 108, pp. 625–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05380-0.
R. Shashanka, D. Chaira, and D. Chakravarty: J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2016. https://doi.org/10.17265/2161-6221/2016.5-6.001.
E. Rabinowicz, Friction and Wear of Materials, John Wiley & Sons. Inc., New York, 1995, pp. 65–123.
Y. Wen, Y.-F. Wang, H. Ran, W. Wei, J.-M. Zhang, and C.-X. Huang: Acta Metall. Sin., 2022, vol. 35(2), pp. 317–25.
M. Whitney, S.F. Corbin, and R.B. Gorbet: Acta Mater., 2008, pp.559–570.
Acknowledgments
This is a part of academic research work and is under the support of the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors are agreed to the publication of the above manuscript. The contribution of all the authors is given below: JP: writing-original draft preparation, data accumulation, analysis, SCM: supervision, execution, and AB: conceptualist, analysis, supervision, review, modification.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This manuscript is original, unpublished, and not submitted to another journal. There is no conflict of interest in this journal. There is no source of funding associated with this paper. All authors agreed to submit this research paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Parida, J., Mishra, S.C. & Behera, A. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti50Ni(50-X)FeX Alloys Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy Process. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 2585–2604 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07037-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07037-5