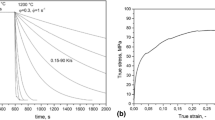
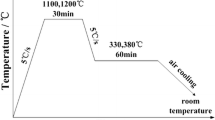
Abstract
Stress-affected bainite transformations were conducted on a Gleeble 3800 simulator, and the effects of different stress states (compressive, tensile, elastic, and plastic stresses) on the microstructural evolution and crystallography of a carbide-free bainite steel were investigated by optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and electron backscattering diffraction (EBSD). The results show that both compressive and tensile elastic stresses increase the thickness of bainite plates due to the additional mechanical driving force induced by the applied stress, and there is no significant difference between the effects of the two types of stress. Although prior deformation was reported to refine the bainite plates, the plastic stress, which induced prior deformation, coarsens the bainite plates because the effect of mechanical driving is more significant. The size of blocky martensite is refined and the length of bainite sheaves increases under the effect of stress, while the size of blocky RA is almost unaffected. In addition, EBSD results show that the orientation relationship between austenite and bainite ferrite is closer to the Nishiyama–Wassermann (N–W) relationship than to the Kurdjumov–Sachs (K–S) relationship for the stress-affected specimens. Strong variant selection occurs when a stress is applied during bainite transformation. Moreover, the elastic stress slightly decreases the hardness, while the plastic stress increased the hardness.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.G. Caballero and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Curr. Opin. Solid. State Mater., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 251–57.
X.X. Zhang, G. Xu, X. Wang, D. Embury, O. Bouaziz, G.R. Purdy, and H.S. Zurob: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2014, vol. 45A, pp. 1352–61.
H.J. Hu, G. Xu, L. Wang, Z.L. Xue, Y.L. Zhang, and G.H. Liu: Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 84, pp. 95–99.
H.D. Wu, G. Miyamoto, Z.G. Yang, C. Zhang, H. Chen, and T. Furuhara: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 133, pp. 1–9.
P.H. Shipway and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1995, vol. 201, pp. 143–49.
K. Hase, C. Garcia-Mateo, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 20, pp. 1499–1505.
M.C. Uslu, D. Canadinc, H.-G. Lambers, S. Tschumak, and H.J. Maier: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2011, vol. 19, pp. 45007–23.
M.J. Holzweissig, D. Canadinc, and H.J. Maier: Mater. Charact., 2012, vol. 65, pp. 100–08.
C.C. Liu, K.F. Yao, and Z. Liu: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 643–47.
M.X. Zhou, G. Xu, H.J. Hu, Q. Yuan, and J.Y. Tian: Steel Res. Int., 2017, vol. 88, p. 1600377.
M.X. Zhou, G. Xu, H.J. Hu, Q. Yuan, and J.Y. Tian: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2017, vol. 704, pp. 427–33.
C.C. Liu, D.Y. Ju, K.F. Yao, Z. Liu, and X.J. Xu: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 1229–37.
M.X. Zhou, G. Xu, H.J. Hu, Q. Yuan, and J.Y. Tian: Met. Mater. Int., 2018, vol. 4, pp. 28–34.
T.J. Su, E. Aeby-Gautier, and S. Denis: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 2185–89.
S.B. Zhang and W.J. Li: Adv. Mater. Res., 2001, vol. 194–196, pp. 341–46.
H. Beladi, V. Tari, I.B. Timokhina, P. Cizek, G.S. Rohrer, A.D. Rollett, and P.D. Hodgson: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 127, pp. 426–37.
V. Tari, A.D. Rollett, and H. Beladi: J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2013, vol. 46, pp. 210–15.
T. Furuhara, H. Kawata, S. Morito, G. Miyamoto, and T. Maki: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 1003–13.
N. Takayama, G. Miyamoto, and T. Furuhara: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 2387–96.
V. Pancholi, M. Krishnan, I.S. Samajdar, V. Yadav, and N.B. Ballal: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 2037–50.
J.Y. Tian, G. Xu, Z.Y. Jiang, Q. Yuan, G.H. Chen, and H.J. Hu: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 1539–50.
Y.S. Wu, X.Z. Qin, C.S. Wang, and L.Z. Zhou: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2019, vol. 768, p. 138454.
Y.S. Wu, Z. Liu, X.Z. Qin, C.S. Wang, and L.Z. Zhou: J. Alloys Compd., 2019, vol. 795, pp. 370–84.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels, 3rd ed. Institute of Materials, Minerals & Mining, London, 2015, pp. 21–23.
M. Azuma, N. Fujita, M. Takahashi, T. Senuma, D. Quidort, and T. Lung: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 45, pp. 1405–12.
S.B. Singh and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1998, vol. 245, pp. 72–79.
J.R. Patel and M. Cohen: Acta Metall., 1953, vol. 1, pp. 531–38.
Materials Algorithms Project (MAP), University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2015. http://www.msm.cam.ac.uk/map/.
K. Maryam, A. Behzad, and Y. Sasan: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2016, vol. 184, pp. 306–17.
W. Gong, Y. Tomota, Y. Adachi, A.M. Paradowska, J.F. Kelleher, and S.Y. Zhang: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 4142–54.
H.J. Hu, H.S. Zurob, G. Xu, D. Embury, and G.R. Purdy: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2015, vol. 626, pp. 34–40.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1999, vol. 273–275, pp. 58–66.
H. Kitahara, R. Ueji, M. Ueda, N. Tsuji, and Y. Minamino: Mater. Charact., 2005, vol. 54, pp. 378–86.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, S.A. David, J.M. Vitek, and R.W. Reed: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1991, vol. 7, pp. 686–98.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. 52004192, 52104381), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2021M692488), the Key Research Projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (No. 20A430020), and the Key Project of Hebei Iron and Steel Group (HG2019313).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Liu, G., Tian, J. et al. Microstructure and Crystallography of a Carbide-Free Bainite Steel Under the Effect of Stress. Metall Mater Trans A 53, 2226–2238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-022-06664-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-022-06664-8