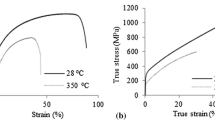
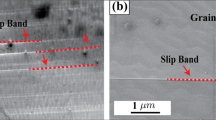
Abstract
Measurement of geometrically necessary dislocation (GND) density using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) has become rather common place in modern metallurgical research. The utility of this measure as an indicator of the expected flow behavior of the material is not obvious. Incorporation of total dislocation density into the Taylor equation relating flow stress to dislocation density is generally accepted, but this does not automatically extend to a similar relationship for the GND density. This is discussed in the present work using classical equations for isotropic metal plasticity in a rather straight-forward theoretical framework. This investigation examines the development of GND structure in a commercially produced interstitial free steel subject to tensile deformation. Quantification of GND density was carried out using conventional EBSD at various strain levels on the surface of a standard dog-bone-shaped tensile specimen. There is linear increase of the average GND density with imposed macroscopic strain. This is in agreement with the established framework.







Similar content being viewed by others
References:
J.F. Nye: Acta Metall., 1953, vol.1, pp.153–162.
B.A. Bilby, R. Bullough, E. Smith: Proc. R. Soc. Lond., 1955, vol. 231 (1185), pp. 263–273.
M.F. Ashby: Philos. Mag., 1970, vol. 21, pp. 399–424.
E.Kröner: Continuum Theory of Defects, in: R.Balian, M. Kléman, and J.-P. Poirier, eds., Physics of Defects, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1981, pp. 217–315.
S. Sun, B. Adams, and W. King: Philosophical Magazine A., 2000, vol. 80, pp. 9–25.
D.P. Field, P.B. Trivedi, S.I. Wright and M. Kumar: Ultramicroscopy, 2005, vol. 103, pp. 33-39.
W. Pantleon: Scr. Mater., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 994-997.
T.B. Britton, A.J. Wilkinson: Ultramicroscopy,2011, vol. 111, pp. 1395–1404.
D.P. Field, C.C. Merriman, N. Allain-Bonasso and F. Wagner: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2012, vol.20, pp. 1-12.
T.J. Ruggles, D.T. Fullwood: Ultramicroscopy, 2013, vol. 133, pp. 8–15.
P.J.Konijnenberg, S. Zaefferer, and D. Raabe: ActaMater.,2015, vol. 99, pp. 402-414.
B.C. Larson, J.Z.Tischler, A. El-Azab, and W.J. Liu: J. Eng. Mats. Tech., 2008, vol. 130, pp. 1 - 10.
B. S. El-Dasher, B. L. Adams and A. D. Rollett: Scr. Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 141-145.
A. J. Wilkinson, G. Meaden, D. J. Dingley: Ultramicroscopy, 2006, vol. 106, pp. 307-313.
J. Kacher, C. Landon, B.L. Adams, D. Fullwood: Ultramicroscopy,2009, vol. 109, pp. 1148-1156.
S. Villert, C. Maurice, C. Wyon, R. Fortunier: J. Microsc., 2009, vol. 233, pp. 290-301.
T. B. Britton, C. Maurice, R. Fortunier, J. H. Driver, A. P. Day, G. Meaden, D. J. Dingley, K. Mingard, A. J. Wilkinson:Ultramicroscopy,2010, vol. 110, pp. 1443-1453.
J. Jiang, T.B. Britton, A.J. Wilkinson: ActaMater.,2013, vol. 61, pp.7227–7239.
T. J. Hardin, B. L. Adams, D. T. Fullwood, R. H. Wagoner, E. R. Homer: International Journal of Plasticity,2013, vol. 50, pp. 146-157.
W. Pantleon: ActaMater.,1998, vol. 46, pp.451–456.
G. Nolze, R. Hielscher, A. Winkelmann: Cryst. Res. Technol., 2017, vol. 52, pp. 1-22.
S. S. Hazra, A. A. Gazder, E. V. Pereloma:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol.524, pp. 158-167.
J. H. Hollomon: Trans. AIME, 1945, vol. 162, pp. 268–290.
Q.Z. Chen, B.J. Duggan: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 3423–3430.
Y. Tomota, P. Lukas, S. Harjo, J H. Park, N. Tsuchida, D. Neov:Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 819–830.
N. Allain-Bonasso, F. Wagner, S. Berbenni, D. P. Field:Mater SciEngg A.,2012, vol. 548, pp. 56-63.
A. Kundu and D. P. Field: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, vol. 667, pp.435–443.
L.S. Toth, C.F. Gu, B. Beausir, J.-J. Fundenberger, M. Hoffman: Acta Materialia, 2016, vol. 117, pp. 35-42.
N. Zhang, W. Tong: Int. J. of Plasticity,2004, vol. 20, pp. 523–542.
P.Littlewood,A.J.Wilkinson: ActaMater.,2012, vol. 60, pp. 5516–5525.
J. Kadkhodapour, S. Schmauder, D. Raabe, S. ZiaeiRad, U. Weber, M. Calcagnotto: ActaMater.,2011, vol. 59, pp. 4387–4394.
M. Calcagnotto, D. Ponge, E. Demir, D. Raabe: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 2738–2746.
D. J. Prior: Journal of Microscopy,1999, vol. 195, pp. 217-225.
C. C. Merriman, D. P. Field and P. B. Trivedi:Mater. Sci. Eng. A,2008, vol.494, pp. 28-35.
M. Kamaya, A. J. Wilkinson, and J. M.Titchmarsh: Acta Mater.,2006, vol. 54, pp. 539-548.
M.B. Saada, N. Gey, B. Beausir, X. Iltis, H. Mansour and N. Maloufi: Materials Characterization, 2017, vol. 133, pp. 112-121.
M. Kamaya, K.Kubushiro, Y.Sakakibara, S. Suzuki, H. Morita, R. Yoda, D. Kobayashi, K. Yamagiwa, T. Nishioka, Y. Yamazaki, Y. Kamada, T. Hanada and T. Ohtani: Bulletin of the JSME,2016, vol. 3, pp. 1-15.
D. N. Githinji, S.Northover, P. J. Bouchard, and M. A. Rist: Metall. Mater. Trans A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 4150-4167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 7, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, A., Field, D.P. Geometrically Necessary Dislocation Density Evolution in Interstitial Free Steel at Small Plastic Strains. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 3274–3282 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4693-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4693-1