Abstract
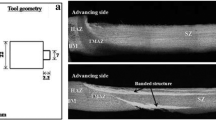
The effects of tool rotational speed (200 and 700 rpm) on evolving microstructure during friction stir welding (FSW) of a reduced activation ferritic-martensitic steel (RAFMS) in the stir zone (SZ), thermo-mechanically affected zone (TMAZ), and heat-affected zone (HAZ) have been explored in detail. The influence of post-weld direct tempering (PWDT: 1033 K (760 °C)/ 90 minutes + air cooling) and post-weld normalizing and tempering (PWNT: 1253 K (980 °C)/30 minutes + air cooling + tempering 1033 K (760 °C)/90 minutes + air cooling) treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties has also been assessed. The base metal (BM) microstructure was tempered martensite comprising Cr-rich M23C6 on prior austenite grain and lath boundaries with intra-lath precipitation of V- and Ta-rich MC precipitates. The tool rotational speed exerted profound influence on evolving microstructure in SZ, TMAZ, and HAZ in the as-welded and post-weld heat-treated states. Very high proportion of prior austenitic grains and martensite lath boundaries in SZ and TMAZ in the as-welded state showed lack of strengthening precipitates, though very high hardness was recorded in SZ irrespective of the tool speed. Very fine-needle-like Fe3C precipitates were found at both the rotational speeds in SZ. The Fe3C was dissolved and fresh precipitation of strengthening precipitates occurred on both prior austenite grain and sub-grain boundaries in SZ during PWNT and PWDT. The post-weld direct tempering caused coarsening and coalescence of strengthening precipitates, in both matrix and grain boundary regions of TMAZ and HAZ, which led to inhomogeneous distribution of hardness across the weld joint. The PWNT heat treatment has shown fresh precipitation of M23C6 on lath and grain boundaries and very fine V-rich MC precipitates in the intragranular regions, which is very much similar to that prevailed in BM prior to FSW. Both the PWDT and PWNT treatments caused considerable reduction in the hardness of SZ. In the as-welded state, the 200 rpm joints have shown room temperature impact toughness close to that of BM, whereas 700 rpm joints exhibited very poor impact toughness. The best combination of microstructure and mechanical properties could be obtained by employing low rotational speed of 200 rpm followed by PWNT cycle. The type and size of various precipitates, grain size, and evolving dislocation substructure have been presented and comprehensively discussed.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. L. Klueh and A.T. Nelson: J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, Vol.371, pp.37-52.
V.K. Sikka: Development of Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel for Elevated Temperature Service, in J.W. Davies and D.J. Michael, eds., Proceedings AIME Topical Conference Ferritic Alloys for Use in Nuclear Energy Technologies, Snowbird, Utah (1983) , pp. 317–27.
J.F. Salavy, I.V. Boccacini, P. Chaudhuri, S. Cho, M. Enoeda, L.M. Ginacarli, R.J. Kurtz, T.Y. Loo, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and C.P.C. Wong, Fus. Engr. Des., 2010, Vol.85, pp.1896-1902.
R.L. Klueh, D. S. Gelles, and T.A. Lechtenberg: J. Nucl. Mater, 1986, Vol.141-143, pp.1081-1087.
N. Baluc, D.S. Gelles, S. Jitsukawa, R.L. Klueh, G.R. Odette, B. Van der Schaaf, and J. Yu, J. Nucl. Mater, 2007, Vol 262-370, pp. 33-41.
H. Tanigawa, K. Shiba, A. Möslang, R. E. Stoller, R. Lindau, M. A. Sokolov, G. R. Odette,R. J. Kurtz, and S. Jitsukawa: J. Nucl. Mater, 2011, Vol.417, pp.9-15.
H. Tanigawa, K. Hirose, K. Shiba, R. Kasada, E. Wakai, H. Serizawa, Y. Kawahito, S. Jitsukawa, A. Kimura, Y. Kohno, A. Kohyama, S. Katayama, H. Mori, K. Noshimoto, R. L. Klueh, M. A. Sokolov, R.E. Stoller and S.J. Zinkle: Fus. Engr. Des, 2008, Vol.83, pp. 1471-1476.
J.Yu, Q. Haung and F.Wam, J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, Vol.367-370, pp.97-101.
Q. Haung, C. Li, Y. Li, M. Chen, M. Zhang, and L. Plug: J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, Vol.367-370, pp.142-146.
L. Haung, X.Hu, W. Van, W. Sha, F. Xiao, Y. Shan, and K. Yang, Mater. Des. 2014, Vol.63, pp.333-335.
B. Van der Schaaf, D. S. Gelles, S. Jitsukawa, A. Kimura, R. L. Klueh, A. Moeslang, G.R. Odette: J. Nucl. Mater. 2000, Vol.283-287, pp.52-59.
B. Raj, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and A.K. Bhaduri, Fus Eng. Des., 2010, Vol. 85, pp.1460-1468.
K. Laha, S. Saroja, A. Moitra, R. Sandhya, M.D. Mathew, T. Jayakumar and E. Rajendrakumar: J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, Vol.439, pp.41-50.
S. Raju, B. Jeyaganesh, A.K. Rai, R. Mythili, S. Saroja, E. Mohandas, M. Vijayalakshmi, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and B. Raj: J Nucl Mater, 2009, Vol. 389, pp. 385-393.
K. Laha, K.S. Chandravathi, P. Parameswaran, and K. Bhanu: Metall Mater Trans A, 2009, Vol.40, pp. 386-397.
J.A. Francis, W. Mazur, and H.K.D. H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Tech., 2006, Vol.22, pp.1387-1395.
S. Shiju, C.R. Das, V. Ramasubbu, S. K. Albert and A. K. Bhaduri: J.Nucl.Mater.,2014, Vol.455, pp.343-348.
J. Wang, S. Lu, W. Dong, D. Li and L. Rong: Mater .Des. 2014, Vol.64, pp.550-558.
W.M. Thomas, E.D. Nicholas, J.C. Needham, M.G. Murch, P. Temple-Smith, G.J. Dawes and P. Dawes: Friction stir butt welding (1991), GB Patent No.9125978.8, International Patent No. PCT/GB92/02203.
R.S. Mishra and Z.Y. Ma: Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Reports, 2005,Vol.50, pp.1-78.
P.L. Threadgill, A.J. Leonard, H.R. Schercliff, and P.J. Whithers: Int. Mater. Reviews, 2009, Vol.54, pp. 49-93.
S. Noh, H. Tanigawa, H. Fujii, A. Kimura, J. Shim, and T. K. Kim: Microstructural evolutions of friction stir welded F82H steel for fusion applications, Trans. Korean Nucl. Soc. Autumn Meeting, Gyeongju, Korea,October 25-26, 2012.
Z. Yu, Z. Feng, D. Hoelzer, L. Tan, and M.A. Sokolov: Metall. Mater. Trans E, 2015, Vol.2E, pp.164-172.
W. Tang, J. Chen, X. Yu, D Frederick, and Z. Feng: Heat input and post weld heat treatment effects on reduced activation ferritic martensitic steel friction stir welds, in: R. S. Mishra, M.W. Mahoney, Y. Sato, Y. Hovanski (Eds), Friction stir welding and processing VIII, Wiley, New Jersey 2015, pp 83–88.
V.L.Manugula, K.V. Rajulapati, G.M. Reddy, R. Mythili and K. Bhanu: Mater. Design, 2016, Vol. 92, pp.200-212.
S. Saroja, A.Dasgupta, R. Divakar, S. Raju, E. Mohandas, M. Vijayalakshmi and K. Bhanu Sankara Rao: J.Nucl.Mater., 2011, Vol.409, pp.131-139.
R. Ravikirana: Study of Transformation Characteristics and Microstructural Evolution in 9Cr Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steel Using Electron Microscopy, Calorimetry and Computational Methods, Ph.D. Thesis, Homi Bhabha National Institute, August 2014.
R. Ravikirana, R. Mythili, S. Raju, S. Saroja, G. Paneerselvam, T. Jayakumar and E. Rajendrakumar: Bull. Mater. Sci., 2014, Vol. 37, pp.1453–1460.
N. A. McPherson, A.M. Galloway, S.R. Cater, and S.J. Hambling: Sci.Technol. Weld. Join, 2013, Vol.18, pp.441-450.
A. Toumpis, A. Galloway, S. Cater,and N. A. McPherson: Mater. Des, 2014, Vol. 62, pp.64-75.
Z. Lu, R.G. Faulkner, N. Riddle, F.D. Martino, and K. Yang, J. Nucl. Mater., 2009, Vol.386-388, pp. 445-48.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Professor I. Samajdar (IIT, Bombay), Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi, and Dr. S. Saroja (IGCAR, Kalpakkam) for many useful discussions. Professor K. Bhanu Sankara Rao is particularly thankful to Ministry of Steel, Government of India for providing Ministry of Steel Chair Professorship. This research is supported by the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences, Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 24, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manugula, V.L., Rajulapati, K.V., Reddy, G.M. et al. Influence of Tool Rotational Speed and Post-Weld Heat Treatments on Friction Stir Welded Reduced Activation Ferritic-Martensitic Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 3702–3720 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4143-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4143-5