Abstract
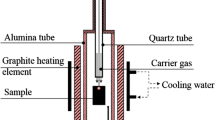
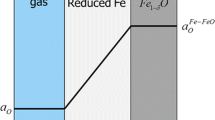
The isothermal reduction of oxide scale on hot-rolled, low-carbon steel strip in 10 pct H2-Ar mixtures in the temperature range of 673 K to 1073 K (400 °C to 800 °C) was investigated by using a thermo-gravimetric analyzer (TGA). During heating under an argon atmosphere, magnetite/iron eutectoid and proeutectoid magnetite in the oxide scale successively transformed into wüstite at a temperature above 843 K (570 °C). The kinetic plot of the isothermal reduction assumes a sigmoid shape, including induction, acceleration, and finally the decaying stage. Fitting the kinetic curve to mathematical models, the reaction at 1073 K (800 °C) and 773 K (500 °C) were determined to be controlled by phase-boundary-controlled reaction and three-dimensional growth of nuclei, respectively. The reduction product varies with temperature and itself affects the kinetics. Porous and dense iron were, respectively, obtained below and above 873 K (600 °C). A “rate-minimum” was observed at 973 K (700 °C) due to the formation of dense iron that blocks the gas diffusion. Due to the structural transformation of oxide scale during heating, the reactant depends on the heating process. However, compared with the oxide scale structure, the temperature is more important in determining the reduction kinetics at temperatures above 973 K (700 °C).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. K. Voges, A. Mueth, and B. Lehane: Iron Steel Technol., 2008, vol. 5, pp. 81-96.
2. L.V. Blgdandy and H.J. Engell: The Reduction of Iron Ores: Scientific Basis and Technology, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 1971, pp. 47-100.
3. M.F. Rau, D. Rieck, and J.W. Evans: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1987, vol. 18B, pp. 257-78.
4. P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41B, pp. 19-34.
5. P.C. Hayes: Steel Res. Int., 2011, vol. 82, pp. 480-93.
6. Y.K. Rao: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 243-55.
7. D.H. St. John and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1982, vol. 13B, pp. 117-24.
8. S.P. Matthew and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1990, vol. 21B, pp. 153-72.
9. S.P. Matthew, T.R. Cho, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1990, vol. 21B, pp. 733-41.
10. D.H. St. John, S.P. Matthew, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 709-17.
11. R. Nicolle and A. Rist: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 429-38.
12. H. Wang and H.Y. Sohn: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 906-12.
13. M.C. Bagatini, V. Zymla, E. Osorio, and A.C.F. Vilela: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1072-9.
14. M. Moukassi, P. Steinmetz, B. Dupre, and C. Gleitzer: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1983, vol. 14B, pp. 125-32.
15. A. Primavera, S. Cattarino, and M. Pavlicevic: Ironmaker Steelmaker, 2007, vol. 34, pp. 290-4.
16. M. Bahgat, Y. Sasaki, S. Hijino, M. Iguchi, and K. Ishii: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 2023-8.
17. M. Bahgat, Y. Sasaki, S. Hijino, M. Iguchi, and K. Ishii: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 657-61.
18. Y. Sasaki, M. Bahgat, M. Iguchi, and K. Ishii: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 1077-83.
19. I. Saeki, T. Ikeda, K. Ohno, T. Sato, and S. Kurosawa: Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2011, vol. 97, pp. 12-8.
20. R. Hudson: Met. Finish., 1985, vol. 83, pp. 59-61.
21. R. Hudson: Met. Finish., 1985, vol. 83, pp. 73-80.
22. J. Shi, D.R. Wang, Y.D. He, H.B. Qi, and G. Wei: Mater. Lett., 2008, vol. 62, pp. 3500-2.
23. C. Guan, J. Li, N. Tan, Y.Q. He, and S.G. Zhang: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, vol. 39, pp. 15116-24.
24. R.Y. Chen and W.Y.D. Yuen: Oxid. Met., 2000, vol. 53, pp. 539-60.
25. R.Y. Chen and W.Y.D. Yuen: Oxid. Met., 2001, vol. 56, pp. 89-118.
26. W.H. Kim, S. Lee, S.M. Kim, and D.J. Min: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, vol. 38, pp. 4194-200.
27J. D. Hancock and J.H. Sharp: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1972, vol. 55, pp. 74-7.
28. A. Ortega: Thermochim. Acta., 1996 vol. 284, pp. 379-87.
29. K. Piotrowski, K. Mondal, H. Lorethova, L. Stonawski, T. Szymanski, and T. Wiltowoski: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2005, vol. 30, pp. 1543-54.
30. A. Pineau, N. Kanari, and I. Gaballah: Thermochim. Acta., 2006, vol. 447, pp. 89-100.
31. A. Pineau, N. Kanari, and I. Gaballah: Thermochim. Acta., 2007 vol. 456, pp. 75-88.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the financial support of the National Science & Technology Pillar program of China (Grant No. 2011BAE13B04) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51204047 and 51204048) for this work. We also thank Dr. Guan Chuang from Shanghai Jiaotong University for the valuable discussions. In addition, the sponsorship of Baosteel is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 7, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Jia, T., Li, Z. et al. Isothermal Reduction of Oxide Scale on Hot-Rolled, Low-Carbon Steel in 10 pct H2-Ar. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 4845–4852 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3647-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3647-8