Abstract
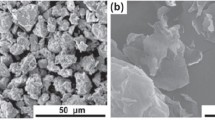
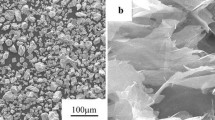
Ti-graphene composite films were prepared on polished Ti substrates by deposition of graphene platelets from suspension followed by deposition of Ti by magnetron sputtering. The films were annealed at different temperatures up to 1073 K (800 °C) and different time periods in argon atmosphere. The annealed films were characterized by X-ray diffraction for phase identification, scanning electron microscopy for microstructure, energy-dispersive spectrometry for chemical analysis, atomic force microscopy for surface roughness, and transient thermoreflectance for thermal conductivity and interface thermal conductance. The results showed that the interface between the composite film and Ti substrate remained continuous with the absence of voids. Oxygen concentration in the composite films has increased for higher temperature and time of annealing. TiO2 and TiC phases are formed only in the film annealed at 1073 K (800 °C). The thermal conductivity of the composite film decreased with increasing oxygen concentration. The effective thermal conductance of the film annealed at 1073 K (800 °C) was significantly lower. The interface thermal conductance between the composite film and the Ti substrate is also reduced for higher oxygen concentration. Formation of microscopic TiO2 phase bound by interface boundaries and oxygen incorporation is considered responsible for the lower thermal conductance of the Ti-graphene composite annealed at 1073 K (800 °C).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASM Metal Handbook, 9th ed., vol. 2, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Pure Metals, p. 615, ASM International, Metals Park, OH.
C.R.F. Azevedo, Engineering Failure Analysis, 2011, vol. 18, p. 1943–1962.
Titanium alloy property data, http://www.matweb.com/reference/titanium.aspx
C.R. Brooks: Heat treatment, structure and properties of nonferrous alloys, Ch. 9, p. 329, ASM, Metal Park, OH.
H. Zheng and K. Jaganandham, J. Heat Transfer, 2014, vol. 136, pp. 061301-1-9.
A. A. Balandin, S. Ghosh, W. Bao, I. Calizo, D. Teweldebrahn, F. Miao and C. N. Lau, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, vol. 92, pp. 151911-1-3.
A. A. Balandin, S. Ghosh, W. Bao, I. Calizo, D. Teweldebrahn, F. Miao and C. N. Lau, Nano Lett., 2008, vol. 8, pp. 902-907.
P. G. Klemens, Int. J. Thermophysics, 2001, vol. 22, pp. 265-275.
J. H. Seol, I. Jo, A. L. Moore, L. Lindsay, Z. H. Aitken, M. T. Pettes, X. Li, Z. Yao, R. Huang, D. Broido, N. Mingo, R. S. Ruoff and L. Shi, Science, 2010, vol. 328, pp. 213-216.
K. Jaganandham: J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 32A, pp. 051101-1–10.
K. Jagannadham: IEEE Trans. Elect. Dev., 2016, doi:10.1109/TED.2015.2501025.
K. Jagannadham: J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A, 2016 (in press).
S. T. Nguyen, R. S. Ruoff, S. Stankovich, D.A. Dikin, R.D. Piner, K.A. Kohlhaas, A. Kleinhammes, J. Yuanyuan and W. Yue, Carbon, 2007, vol. 45, pp. 1558–1565.
J. Kim, L. J. Cote, F. Kim, W. Yuan, K. R. Shull, and J. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, vol. 132, pp. 8180–8186
A. Bagri, C. Matte, M. Acik, Y.J.Chabal, M. Chhowalla and V. B. Shenoy, Nat. Chem. 2010, vol. 2, pp. 581–587.
S.H. Huh: Ch. 5 in Physics and Applications of Graphine-Experiments, Open Access Book, S. Mikhailov, ed., INTECH, 2011, pp. 73–90.
K. Jagannadham, J. Electron. Mater., 2011, vol. 40, pp. 25-34.
K. Jagannadham, Met. Mat. Trans. B, 2012,vol. 43, pp. 316-324.
H. Zheng and K. Jagannadham, Met. Mat. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 2480-2486.
M. A. Panzer, G. Zhang, D. Mann, X. Hu, E. Pop, H. Dai and K.E. Goodson, J. Heat Trans., 2008, vol.130, pp. 052401-1-9.
W. A. Harrison, Solid State Theory, page 263, Dover Publications Inc, New York, 1979.
JB Scarborough (1958) Numerical Mathematical Analysis. Oxford University Press: Oxford
Y. K. Koh, M. H. Bae, D. G. Cahill and E. Pop, Nano Lett., 2010, vol. 10, pp. 4363-4368.
P. E. Hopkins, M. Baraket, E. V. Barnat, T. E. Beechem, S. P. Kearney, J. C. Duda, J. T. Robinson and S. G. Walton, Nano Lett., 2012, vol. 12, pp. 590-595
M. Kazan, A. Bryant, P. Royer and P. Masri, Surf. Sci. Reports, 2010, vol. 65, pp. 111-127.
B. N. J. Persson, J. Phys. Conden. Matt., 2014, vol. 26, pp. 015009-1-3
W. S. Williams, JOM, 1998, vol. 50, pp. 62-66
D. T. Morelli, Phys. Rev. B, 1991, vol. 44, pp. 5453-5458.
J. Fang, C. Reitz, T. Brezesinski, E. J. Nemanick, C. B. Kang, S. H. Tolbert and L. Pilon, J. Phys. Chem., 2011, vol. 115, pp. 14606-14614
Z. Huang, T. Fisher and J. Murthy, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 109, pp. 074305-1-6.
D. G. Cahill and R. O. Pohl, Phys. rev. B, 1987, vol. 35, p. 4067-4073
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the use of the Analytical Instrumentation Facility (AIF) at North Carolina State University for SEM characterization, which is supported by the State of North Carolina and the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 27, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagannadham, K. Thermal Conductivity Changes in Titanium-Graphene Composite upon Annealing. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 907–915 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3259-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3259-8