Abstract
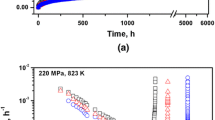
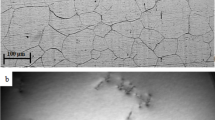
Tertiary creep deformation behavior of reduced activation ferritic–martensitic (RAFM) steels having different tungsten contents has been assessed. Creep tests were carried out at 823 K (550 °C) over a stress range of 180 to 260 MPa on three heats of the RAFM steel (9Cr-W-0.06Ta-0.22V) with tungsten content of 1, 1.4, and 2.0 wt pct. With creep exposure, the steels exhibited minimum in creep rate followed by progressive increase in creep rate until fracture. The minimum creep rate decreased, rupture life increased, and the onset of tertiary stage of creep deformation delayed with the increase in tungsten content. The tertiary creep behavior has been assessed based on the relationship, \( \varepsilon = \varepsilon_{\text{o}} + \dot{\varepsilon }_{\text{m}} t + \varepsilon_3{\exp }\left[ {p\left( {t - t_{\text{t}} } \right)} \right] \), considering minimum creep rate (\( \dot{\varepsilon }_{\text{m}} \)) instead of steady-state creep rate. The increase in tungsten content was found to decrease the rate of acceleration of tertiary parameter ‘p.’ The relationships between (1) tertiary parameter ‘p’ with minimum creep rate and time spent in tertiary creep deformation and (2) the final creep rate \( \dot{\varepsilon }_{\text{f}} \) with minimum creep rate revealed that the same first-order reaction rate theory prevailed in the minimum creep rate as well as throughout the tertiary creep deformation behavior of the steel. A master tertiary creep curve of the steels has been developed. Scanning electron microscopic investigation revealed enhanced coarsening resistance of carbides in the steel on creep exposure with increase in tungsten content. The decrease in tertiary parameter ‘p’ with tungsten content with the consequent decrease in minimum creep rate and increase in rupture life has been attributed to the enhanced microstructural stability of the steel.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. L. Klueh, D. S. Gelles and T.A. Lechtenberg, Journal of Nuclear Materials, 141-143 (1986) 1081-1087.
M. Victoria, N. Baluc and P. Spätig: Nuclear Fusion, 41 (2001) 1047-1053.
F. Abe, T. Noda, H. Araki and M. Okada: J. Nucl. Sci. Tech., 31 (1994) 279-292.
G. Yu, N. Nita, N. Baluc; Fusion Engineering and Design 75–79 (2005) 1037–1041.
Y. Li, Q. Huang, Y. Wu, T. Nagasaka, T. Muroga, Journal of Nuclear Materials 367–370 (2007) 117–121.
A.-A.F. Tavassoli, J.-W. Rensman, M. Schirra, K. Shiba; Fusion Engineering and Design 61-62 (2002) 617-628.
T. Hasegawa, Y. Abe, Y. Tomita. N. Maruyama and M. Sugiyama; ISIJ International, Vol. 41 (2001), No. 8, pp. 922–929.
J. Vanaja, K. Laha, R. Mythili, K.S. Chandravathi, S. Saroja and M.D. Mathew; Materials Science and Engineering A, 533 (2012) 17– 25.
F. Abe, H. Araki, and T. Noda; Met. Trans A, Vol. 22A (1991) 2225-2235.
A. Czyrska-Filemonowicz, A. Zielińska-Lipiec, P.J. Ennis; Journal of Achievements in materials and manufacturing Engineering, Vol. 19, (2006) 43-48.
P. Fernández, A.M. Lancha, J. Lapeña, R. Lindau, M. Rieth, M. Schirra, Fusion Eng. Des. 75–79 (2005) 1003–1008.
E. Isaac Samuel, B.K. Choudhary, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and B. Raj: Pressure Vessels, and Piping: Materials and Properties, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, India, 2008, pp. 83–100.
P. G. McVetty, Mech. Engng 56, 149 (1934).
F. Garofalo: Fundamentals of Creep and Creep Rupture in Metals. Macmillan, New York, 1965.
G.A. Webster, A.P.D. Cox, and J.E. Dorn: Metal. Sci. J., 1969, vol. 3, pp. 221–25.
P.W. Davies, W.J. Evans, K.R. Williams, and B. Wilshire: Scripta Metall., 1969, vol. 3, pp. 671–674.
Dobeš F., Čadek J.: Kovové Mater.19 (1981) 31.
F. Abe and S. Nakazawa: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 3025–3034.
S.G. Hong, W.B. Lee, and C.G. Park: J. Nucl. Mater., 2001, vol. 288, pp. 202–207.
J. Cermak, J. Kucera, B. Million, and J. Krumpos: Kov. Mater., 1980, vol. 18, pp. 537–547.
NIMS creep data sheet, Atlas of creep deformation property No. D-1, 2007.
K. Kimura, K. Sawada, and H. Kushima: Proc. 3rd Symp. Heat Res. Steels Alloys High Effic, USC Power Plants, Japan, 2009.
B. Wilshire, P.J. Scharning, Int. Mater. Rev. 53 (2008) 91–104.
F.C. Monkman, N.J. Grant; Proc. Am. Soc. Test. Mater. 56 (1956) 593.
N.J. Grant and A.W. Mullendore: Deformation Fracture at Elevated Temperatures, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass, 1965.
P. W. Davies and K. R. Williams; Acta Metall., Vol. 17, (1969) 897-903.
J. Vanaja, K Laha, and M.D. Mathew; Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, Vol. 45A (2014) 5076-5084.
W.J. Evans and B. Wilshire: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2133–2139.
C. Phaniraj, M. Nandagopal, S.L. Mannan, and P. Rodriguez and B. P. Kashyap: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44 (10), pp. 4059-4069.
B.K. Choudhary, C. Phaniraj, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and S.L. Mannan: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. S73–S80.
M. Maldini and V. Lupinc; Scripta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 32, No. 3, pp. 337-342.
F.A. Leckie, D.R. Hayhurst, Acta Metall. 25 (1977) 1059–1070.
M.F. Ashby, B.F. Dyson: Advances in Fracture Research, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1984, vol. 1, pp. 3–30.
B.F. Dyson, T.B. Gibbons, Acta Metall. 35 (1987) 2355–2369.
S. Goyal, K. Laha, S. Panneer Selvi and M. D. Mathew; Materials at High Temperatures, 2014, vol. 31, no.3, pp. 211-220.
L. Tan, Y. Yang, J.T. Busby; Journal of Nuclear Materials 442 (2013) S13–S17.
L. Tan, J.T. Busby, P.J. Maziasz, Y. Yamamoto; Journal of Nuclear Materials 441 (2013) 713–717.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. P. R. Vasudeva Rao, Director, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR), Dr. T. Jayakumar, Director, Metallurgy and Materials Group, and Dr. A. K. Bhaduri, Associate Director, Materials Development & Technology Group, IGCAR, for their constant encouragement and support. The collaboration with M/s. Mishra Dhatu Nigam, Hyderabad, and Institute for Plasma Research, Gujarat, India, is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 25, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanaja, J., Laha, K. Assessment of Tungsten Content on Tertiary Creep Deformation Behavior of Reduced Activation Ferritic–Martensitic Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 4669–4679 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3075-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3075-1