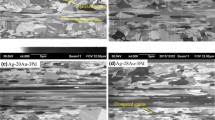
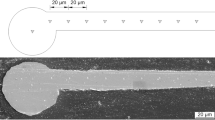
Ag-4Pd binary alloy wire has been produced as an alternative to a previously developed Ag-8Au-3Pd ternary alloy wire to meet requirements for high electrical conductivity and low cost. The electrical resistivity of this Ag-4Pd bonding wire, manufactured with a conventional method, is 3.7 μΩ cm, close to the values of traditional 3N Au wire (3.5 μΩ cm) and Pd-coated Cu wire (1.8 μΩ cm). To further improve the performance of this bonding wire, a large amount of annealing twins were introduced in this Ag-4Pd alloy wire through an innovative concept of sequential drawing and multiple annealing processes. The resulting electrical resistivity of this annealing-twinned Ag-4Pd wire is 3.5 μΩ cm. In contrast to the apparent increase in grain size in the conventional Ag-4Pd wire under electrical stressing with a current density of 1.23 × 105 A/cm2 for various times, the grains in this annealing-twinned wire grow much more slowly. The breaking load and elongation of this annealing-twinned Ag-4Pd wire are also higher than those of conventional wire. Furthermore, annealing twins increase the durability to electromigration of this Ag-4Pd wire under electrical stressing with various current densities.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.E. Schwartz, Elektrolytische Wanderung in flüssigen und festen Metallen, Leipzig:J A Barth, 1940.
Y.C. Chan and D.Yang, Progress in Mater. Sci., 2010, vol.55, pp. 428–75.
C.Y. Liu, C. Chen, K.N. Tu (2000) J. Appl. Phys. 88:5703–09.
H.J. Lin, C.Chen, and T.H. Chuang, J. Alloys and Compounds, 2009, vol. 487, pp. 458–65.
P.K. Tse and T.M. Lach: Proc. 45th IEEE ECTC, Las Vegas, Nevada, 1995, pp. 900–05.
L.De Schepper, W.De Ceuninck, G. Leken, L. Stals, B. Vanhecke, J. Roggen, and L. Tielemans, Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int.1994, Vol.10, pp. 15–26.
B. Krabbenborg, Micro-electronsReliability, Vol.39,1999, pp.77–88.
H.T. Orchard and A. L. Greer, J. Electron. Mater. 35,2006, pp.1961–68.
E. Zin, N. Michael, S.H. Kang, K.H. Oh, U. Chul, J.S. Cho, J.T. Moon, and C.U. Kim: Proc. 59th Electron. Comp. and Techno. Conf., 2009, pp. 943–47.
T.C. Wei and A.R. Daud, J. Electron. Packag., 2003, Vol. 125, pp. 617–20.
A. Kamijo and H. Igarashi: Proc. 35th IEEE Electron. Compon. Conf., Washington, DC, 1985, p. 91.
J.Lin and J. Chuang, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, Vol.144, pp.1652.
J.D. Lee: Taiwan Patent I 323199, 2010, and US Patent 8101123B2, 2012.
J.D. Lee, H.H. Tsai, and T.H. Chuang: Taiwan Patent I 384082 (2013) and Korea Patent 10-1328863 (2013).
R.W. Cahn: Physical Metallurgy, 2nd ed. North Holland, Amsterdam, 1970, pp. 1184.
S. Mandal, A.K. Bhaduri, V.S. Sarma, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, 515:134–40.
N.Souai, N.Bozzolo, L.Naze, Y.Chastel, R. Loge, Scripta Mater., 2010, Vol. 62, pp. 851–54.
S. Lee, Y.B. Chun, J.W. Hua, S.K. Hwang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 363:307–15.
L. Lu, Y. Shen, X.Chen, L.Qian, K.Lu, Science, 2004, Vol.304, pp.422–26.
L. Lu, X. Chen, X.Huang, K.Lu, Science, 2009, Vol.323, pp.607–10.
K.C. Chen, W.W. Wu, C.N. Liao, L.J. Chen, K.N. Tu, Science, 2008, Vol.321, pp.1066–69.
T.H. Chuang, H.C. Wang, C.H. Tsai, C.C. Chang, C.H. Chuang, J.D. Lee, and H. H. Tsai, Scripta Mater., 2012, vol. 67, pp. 605–08.
T.H. Chuang, C.H. Tsai, H.C. Wang, C.C. Chang, C.H. Chuang, J.D. Lee, and H.H. Tsai, J. Electron. Mater., 2012, vol. 41, pp. 3215–22.
T.H. Chuang, H.C. Wang, C.H. Chuang, J.D. Lee, and H.H. Tsai, J. Electron. Mater., 2013, vol.42, pp. 545–51.
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by a cooperative program of the National Science Council and Wire Technology, Taiwan, under Grant No. NSC-102-2622-E002-019-CC2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 14, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuang, TH., Lin, HJ., Chuang, CH. et al. Durability to Electromigration of an Annealing-Twinned Ag-4Pd Alloy Wire Under Current Stressing. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 5574–5583 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2538-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2538-0