Abstract
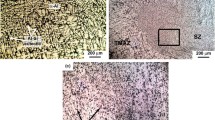
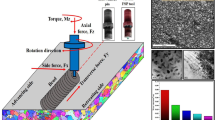
Annealed and wrought AA5052 aluminum alloy was subjected to friction stir processing (FSP) without and with 3 vol pct TiO2 nanoparticles. Microstructural studies by electron backscattered diffraction and transmission electron microscopy showed the formation of an ultra-fine-grained structure with fine distribution of TiO2 nanoparticles in the metal matrix. Nanometric Al3Ti and MgO particles were also observed, revealing in-situ solid-state reactions between Al and Mg with TiO2. Tensile testing at different strain rates determined that FSP decreased the strain rate sensitivity and work hardening of annealed Al-Mg alloy without and with TiO2 nanoparticles, while opposite results were obtained for the wrought alloy. Fractographic studies exhibited that the presence of hard reinforcement particles changed the fracture mode from ductile rupture to ductile-brittle fracture. Notably, the failure mechanism was also altered from shear to tensile rupture as the strain rate increased. Consequently, the fracture surface contained hemispherical equiaxed dimples instead of parabolic ones.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
INSTRON is a trademark of Illinois Tool Works Inc. (ITW), Glenview, IL.
References
T.W. Clyne and P.J. Withers: An Introduction to Metal Matrix Composites, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1993.
T.S. Srivatsan, T.S. Sudarshan, and E.J. Lavernia: Progr. Mater Sci., 1995, vol. 39, pp. 317–409.
C. Suryanarayana: J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, pp. 229–34.
C. Suryanarayana and N. Al-Aqeeli: Progr. Mater Sci., 2013, vol. 58, pp. 383–502.
H. Asgharzadeh, A. Simchi, and H.S. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 4897–4905.
M. Krasnowski and T. Kulik: Scripta Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 1489–94.
H.X. Peng, D.Z. Wang, L. Geng, C.K. Yao, and J.F. Mao: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 199–204.
H. Nasiri, J. Vahdati Khaki, and S.M. Zebarjad: J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, pp. 5305–08.
B. Adamczyk-Cieślak, J. Mizera, and K.J. Kurzydłowski: Mater. Characterization, 2011, vol. 62, pp. 327–32.
C.J. Hsu, C.Y. Chang, P.W. Kao, N.J. Ho, and C.P. Chang: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 5241–49.
C.J. Hsu, P.W. Kao, and N.J. Ho: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 341–45.
I.S. Lee, P.W. Kao, and N.J. Ho: Intermetallics, 2008, vol. 16, pp. 1104–08.
Q. Liu, L. Ke, F. Liu, C. Huang, and L. Xing: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 45, pp. 343–48.
M.A. Moghaddas and S.F. Kashani-Bozorg: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 559, pp. 187–93.
J. Qian, J. Li, J. Xiong, F. Zhang, and X. Lin: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, vol. 550, pp. 279–85.
M. Yang, C. Xu, C. Wu, K.C. Lin, Y.J. Chao, and L. An: J. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 45, pp. 4431–38.
Q. Zhang, B.L. Xiao, W.G. Wang, and Z.Y. Ma: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 7090–7103.
R.S. Mishra, Z.Y. Ma, and I. Charit: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, vol. 341, pp. 307–10.
Q. Zhang, B.L. Xiao, D. Wang, and Z.Y. Ma: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, vol. 130, pp. 1109–17.
Q. Zhang, B.L. Xiao, Q.Z. Wang, and Z.Y. Ma: Mater. Lett., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 2070–72.
L. Ke, C. Huang, L. Xing, and K. Huang: J. Alloys Compd., 2010, vol. 503, pp. 494–99.
X. Feng, H. Liu, and S. Suresh Babu: Scripta Mater., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 1057–60.
F. Iida, T. Suzuki, E. Kuramoto, and S. Takeuchi: Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 637–47.
R. Korla and A.H. Chokshi: Scripta Mater., 2010, vol. 63, pp. 913–16.
F. Li: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 32, pp. 463–68.
A.C. Magee and L. Ladani: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 582, pp. 276–83.
E. Romhanji, M. Dudukovska, and D. Glišić: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2002, vols. 125–126, pp. 193–98.
K.C. Chan and G.Q. Tong: Mater. Lett., 2001, vol. 51, pp. 389–95.
M.O. Lai, L. Lu, and B.Y. Chung: Compos. Struct., 2002, vol. 57, pp. 183-187.
ASTM Standard E8M: Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA, 1998.
M.M.Z. Ahmed, B.P. Wynne, W.M. Rainforth, and P.L. Threadgill: Scripta Mater., 2011, vol. 64, pp. 45–48.
M.M.Z. Ahmed, B.P. Wynne, W.M. Rainforth, and P.L. Threadgill: Mater. Characterization, 2012, vol. 64, pp. 107–17.
U.F.H.R. Suhuddin, S. Mironov, Y.S. Sato and H. Kokawa: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 1962–69.
S. Mironov, K. Masaki, Y.S. Sato, and H. Kokawa: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 1153–57.
W.F. Hosford: The Mechanics of Crystals and Textured Polycrystals, 3rd ed., Oxford University Press, New York, NY, 1993.
K.K. Chawla and M.A. Meyers: in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), Robert A. Meyers, ed., Academic Press, New York, NY, 2003, pp. 467–84.
T.R. McNelley, S. Swaminathan, and J.Q. Su: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 349–54.
L.P. Troeger and E.A. Starke, Jr.: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2000, vol. 293, pp. 19–29.
C.I. Chang, C.J. Lee, and J.C. Huang: Scripta Mater., 2004, vol. 51, pp. 509–14.
W. Woo, H. Choo, D.W. Brown, S.C. Vogel, P.K. Liaw, and Z. Feng: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 3871–82.
T. Shibayanagi, A.P. Gerlich, K. Kashihara, and T.H. North: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 920–31.
D.P. Field, T.W. Nelson, Y. Hovanski, and K.V. Jata: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2869–77.
E.O. Hall: Yield Point Phenomena in Metals and Alloys, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1970.
Y. Huang, W. Zheng, and J. Shen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43A, pp. 5202–08.
S. Ig Hong: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1986, vol. 82, pp. 175–85.
V.A. Romanova, R.R. Balokhonov, and S. Schmauder: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 97–107.
V.M. Segal: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, vol. 406, pp. 205–16.
K. Manigandan, T.S. Srivatsan, D. Tammana, B. Poorganji, and V.K. Vasudevan: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, vol. 601, pp. 29–39.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr. Frantisek Simančík, Institute of Materials and Machine Mechanics, Slovak Academy of Sciences, for useful discussions and help in performing the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodabakhshi, F., Simchi, A., Kokabi, A. et al. Strain Rate Sensitivity, Work Hardening, and Fracture Behavior of an Al-Mg TiO2 Nanocomposite Prepared by Friction Stir Processing. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 4073–4088 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2330-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2330-1