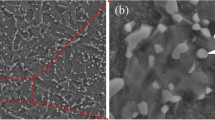
The dynamic recrystallization and hot-ductility behaviors in fine- and coarse-grained 18Mn18Cr0.5N steel were determined between 1273 K and 1473 K (1000 °C and 1200 °C) at a strain rate of 0.1 s−1 through compression and tensile tests. The microstructure was examined using optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction analysis, and transmission electron microscopy. The fracture morphology was observed using scanning electron microscopy. The coarse initial grain size delays the initiation and development of dynamic recrystallization and then results in a lower hot ductility. The nucleation of dynamic recrystallization grains at triple junctions and at grain boundaries is mainly accompanied by the evolution of twinning and low-angle grain boundaries, respectively. The nucleation mechanism of dynamic recrystallization grains affects the dynamic recrystallization grain size. Dynamic recrystallization grains evolved by the necklace mechanism are coarser than those evolved by the ordinary mechanism. The hot ductility of 18Mn18Cr0.5N steel is very sensitive to grain size, particularly at lower temperatures. The fine-grained material can tolerate higher damage before fracture. Finally, the optimized hot-working process was determined.













Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
J.W. Simmons: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, vol. 207, pp. 159-69.
Z.H. Wang, W.T. Fu, S.H. Sun, H. Li, Z.Q. Lv, and D.L. Zhao: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 1025-32.
Z.H. Wang, W.T. Fu, S.H. Sun, Z.Q. Lv, and W.H. Zhang: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 798-802.
R.D. Doherty, D.A. Hughes, F.J. Humphreys, J.J. Jonas, D. Juul Jensen, M.E. Kassner, W.E. King, T.R. McNelley, H.J. McQueen, and A.D. Rollett: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, vol. 238, pp. 219–74.
Y.P. Lang, Y. Zhou, F. Rong, H.T. Chen, Y.Q. Weng, and J. Su: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 45-49.
C.M. Hong, J. Shi, L.Y. Sheng, W.C. Cao, W.J. Hui, and H. Dong: Mater. Des., 2011, vol. 32, pp. 3711-17.
M. El Wahabi, L. Gavard, F. Montheillet, J.M. Cabrera, and J.M. Prado: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 4605-12.
A.D. Manshadi and P.D. Hodgson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39, pp. 2830-40.
A. Belyakov, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Scripta Mater., 2000, vol. 43, pp. 21-26.
A. Belyakov, K. Tsuzaki, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 847-61.
A.D. Manshadi, M.R. Barnett, and P.D. Hodgson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 485, pp. 664-72.
M.R. Barnett, A.G. Beer, D. Atwell, and A. Oudin: Scripta Mater., 2004, vol. 51, pp. 19-24.
C. Rehrl, S. Kleber, O. Renk, and R. Pippan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 6163-72.
M. Jafari and A. Najafizadeh: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 501, pp. 16-25.
C. Rehrl, S. Kleber, O. Renk, and R. Pippan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 540, pp. 55-62.
A.M.W. Sarnek, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 323, pp. 177-86.
A. Belyakov, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 255, pp. 139-47.
J. Deng, Y.C. Lin, S.S. Li, J. Chen, and Y. Ding: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 49, pp. 209-19.
N. Dudova, A. Belyakov, T. Sakai, and R. Kaibyshev: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 3624-32.
M. Faccoli and R. Roberti: J. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 48, pp. 5196-203.
Acknowledgments
The project is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province for Distinguished Young Scholars (E2011203131) and the Natural Science Foundation–Steel and Iron Foundation of Hebei Province (E2013203110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 4, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Sun, S., Wang, B. et al. Effect of Grain Size on Dynamic Recrystallization and Hot-Ductility Behaviors in High-Nitrogen CrMn Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 3631–3639 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2290-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2290-5