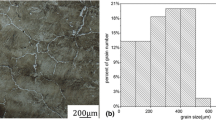
Abstract
Thermo-mechanical experiments on martensitic heat-resistant 40Cr10Si2Mo steel were conducted using a Gleeble simulator in temperature and strain rate ranges of 1073–1373 K and 0.1–20 s−1, respectively. Processing maps were developed and correlated with deformed microstructures based on the dynamic material model theory. The analysis of the maps revealed that both applied temperature and strain rate had significant effects on the power dissipation efficiency and flow instability of the steel alloy. Electron backscatter diffraction analysis was also implemented to study the effect of deformation conditions on martensitic morphology. The results showed that higher temperatures and strain rates led to a fine martensitic packet, and the martensite lath increased in width at high temperatures. Two deformation domains, which exhibit different recrystallization processes, were recognized. The discontinuous dynamic recrystallization (DRX) mechanism in the low strain rate domain was characterized by the migration and growth of high-angle grains during straining. In contrast, in the high strain rate domain, the development of new grain boundaries is primarily associated with the deformation microbands in the low-temperature deformation domain. As the temperature increased, the high dislocation density accelerated the migration of the grain boundaries. Furthermore, the DRX mechanism changed from continuous DRX to post-DRX. This change in the DRX mechanism type was attributed to the time during which the sample remained high temperature after deformation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study. The processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
P. Yan, Z.D. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 650 (2016) 290–294.
Z.M. Cai, H.C. Ji, W.C. Pei, X.F. Tang, X.M. Huang, J.P. Liu, Vacuum 165 (2019) 324–336.
D. Poddar, P. Cizek, H. Beladi, P.D. Hodgson, Acta Mater. 80 (2014) 1–15.
D. Poddar, P. Cizek, H. Beladi, P.D. Hodgson, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46 (2015) 5933–5951.
H. Beladi, P. Cizek, A.S. Taylor, D. Poddar, Mater. Sci. Forum 753 (2013) 76–79.
H. Beladi, P. Cizek, P.D. Hodgson, Scripta Mater. 62 (2010) 191–194.
H. Beladi, P. Cizek, P.D. Hodgson, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 1482–1492.
W.H. Huang, L.P. Lei, G. Fang, Mater. Charact. 163 (2020) 110307.
M. Chegini, M.R. Aboutalebi, S.H. Seyedein, G.R. Ebrahimi, M. Jahazi, J. Manuf. Process. 56 (2020) 916–927.
F. Ren, F. Chen, J. Chen, X.Y. Tang, J. Manuf. Process. 31 (2018) 640–649.
A. Momeni, K. Dehghani, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527 (2010) 5467–5473.
S. Saadatkia, H. Mirzadeh, J.M. Cabrera, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 636 (2015) 196–202.
W.F. Zhang, X.L. Li, W. Sha, W. Yan, W. Wang, Y.Y. Shan, K. Yang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 590 (2014) 199–208.
Q.C. Fan, X.Q. Jiang, Z.H. Zhou, W. Ji, H.Q. Cao, Mater. Des. 65 (2015) 193–203.
Y.B. Tan, L.H. Yang, C. Tian, W.C. Liu, R.P. Liu, X.Y. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 597 (2014) 171–177.
Y. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lark, D.R. Barker, Metall. Trans. A 15 (1984) 1883–1892.
D.G. He, Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, J. Chen, D.X. Wen, J. Alloy. Compd. 649 (2015) 1075–1084.
X. Ma, W.D. Zeng, B. Xu, Y. Sun, C. Xue, Y.F. Han, Intermetallics 20 (2012) 1–7.
D.G. He, Y.C. Lin, J. Chen, D.D. Chen, J. Huang, Y. Tang, M.S. Chen, Mater. Des. 154 (2018) 51–62.
L.Y. Ye, Y.W. Zhai, L.Y. Zhou, H.Z. Wang, P. Jiang, J. Manuf. Process. 59 (2020) 535–544.
J.L. Qu, X.F. Xie, Z.N. Bi, J.H. Du, M.C. Zhang, J. Alloy. Compd. 785 (2019) 918–924.
Z. Yanushkevich, A. Belyakov, R. Kaibyshev, Acta Mater. 82 (2015) 244–254.
J.J. Zhang, Y.P. Yi, S.Q. Huang, X.C. Mao, H.L. He, J.G. Tang, W.F. Guo, F. Dong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 804 (2021) 140650.
Q.J. Wang, B.T. Gao, K.S. Wang, W. Wang, L.B. Tong, X.J. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 820 (2021) 141578.
S.L. Long, Y.L. Liang, J. Yun, Y. Liang, M. Yang, Y.L. Yi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 676 (2016) 38–47.
C.M. Li, L. Huang, M.J. Zhao, X.T. Zhang, J.J. Li, P.C. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 797 (2020) 139925.
K. Huang, R.E. Logé, Mater. Des. 111 (2016) 548–574.
J.J. Jonas, I. Weiss, Met. Sci. 13 (1979) 238–245.
T. Sakai, A. Belyakov, R. Kaibyshev, H. Miura, J.J. Jonas, Prog. Mater. Sci. 60 (2014) 130–207.
Y.K. Xu, P. Birnbaumb, S. Pilz, X.C. Zhuang, Z. Zhao, V. Kräusel, Results Phys. 14 (2019) 102426.
Y. Wang, W.Z. Shao, L. Zhen, X.M. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 486 (2008) 321–332.
J.F. Xie, Y.L. Zhu, F.L. Bian, C. Liu, Mater. Charact. 132 (2017) 145–155.
Z.C. Hou, Z.H. Nie, Z.C. Liu, F. Hao, M.R. Li, G. Zhou, C.W. Tan, J. Alloy. Compd. 865 (2021) 158872.
Z.C. Sun, H.L. Wu, J. Cao, Z.K. Yin, Int. J. Plasticity 106 (2018) 73–87.
M. Hillert, Acta Metall. 13 (1965) 227–238.
Acknowledgements
Partial financial support was received from Science and Technology Program of Xi’an (2020KJRC0051). The research leading to these results received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Agreement No. 52174371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Qj., Wang, Qr., Du, Zz. et al. Deformation and phase transformation mechanisms of 40Cr10Si2Mo steel during hot compression. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 760–771 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00899-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00899-w